- How to Compare Two Lists in Python using set(), cmp() and difference() Functions
- Comparing lists in Python
- What is set() Function in Python?
- Example of set() Function
- 1) Initializing List and Convert into Set Object
- 2) Checking if List Are Equal Using set() Function
- Example Using Set() & Difference() Functions
- Example Using Sort() and == Operator
- Comparing two lists in Python using a Custom Function
- What is cmp() Function in Python?
- Compared Two Lists Using Cmp() Function
- Python Compare Two Lists
- Compare if 2 lists are equal with same order
- Method 1: == Operator
- Method 2: Using loop
- Compare if 2 lists are equal regardless of order
- Method 1: Sort both the lists
- Method 2: Compare Individual Element
- Get intersection of 2 lists
- Method 1: Find intersection using set
- Method 2: Find intersection using list comprehension
- Get the difference of 2 lists
- Compare if 2 lists are equal ignoring case
- Conclusion
How to Compare Two Lists in Python using set(), cmp() and difference() Functions
While working with lists in Python, you might have encountered two lists which seem similar. To figure out the difference, you have to compare the data items of both lists. You can do this by using the set() , difference() and sort() methods.
In this article, we will understand how to compare two lists in Python.
Comparing lists in Python
There are different ways to compare lists in Python. But it depends on the outcome required. Two of the most popular methods are set() and cmp() .
The set() function creates an object that is a set object. The cmp() function is used to compare two elements or lists and return a value based on the arguments passed.
In the following sections, we will see the application of set() , cmp() , and difference() functions.
What is set() Function in Python?
The set() function in Python uses to take an argument and convert it into a set object. It can take arguments like lists, tuples and dictionaries. The argument is called iterable. The output of elements might not be in the same order because items passed as list were not in order.
Example of set() Function
1) Initializing List and Convert into Set Object
# initializing list and convert into set object n = set(['n1','n4','n3','n2']) #Add new Element in set n n.add('n5'); print("Output with set Function : ") print(n)2) Checking if List Are Equal Using set() Function
At first, we convert a list into the set by using a set() function, now we need to check if both the lists are equal or not by using if operator.
# Python 3 code # check if list are equal # using set() # initializing list and convert into set object x = set(['x1','rr','x3','e4']) y = set(['x1','rr','e4','x3']) print ("List first: " + str(x)) print ("List second: " + str(y)) # check if list x equals to y if x == y: print("First and Second list are Equal") else: print("First and Second list are Not Equal")List first: List second: First and Second list is EqualExample Using Set() & Difference() Functions
In the following example, we first convert a list into the set by using set() function then we need to differentiate between these two sets by using difference() function and use the if() condition to check the return value.
# Python 3 code # check if list are equal # using set() & difference() # initializing list and convert into set object x = set(['x1','rr','x3','y4']) y = set(['x1','rr','rr','y4']) print ("List first: " + str(x)) print ("List second: " + str(y)) # take difference of two lists z = x.difference(y) print("Difference of first and second String: " + str(z)) # if lists are equal if not z: print("First and Second list are Equal") # if lists are not equal else: print("First and Second list are Not Equal")List first: List second: Difference of first and second String: First and Second list are Not EqualExample Using Sort() and == Operator
In this example, we first sort the list, so that element of the list is in the same order and then compare both the list with == operator
# Python 3 code # check if list are equal # using sort() & == operator # initializing list and convert into set object x = ['x1','rr','x3','y4'] y = ['x1','rr','rr','y4'] print ("List first: " + str(x)) print ("List second: " + str(y)) # sort list x and y x.sort() y.sort() # if lists are equal if x == y: print("First and Second list are Equal") # if lists are not equal else: print("First and Second list are Not Equal")List first: ['x1', 'rr', 'x3', 'y4'] List second: ['x1', 'rr', 'rr', 'y4'] First and Second list are Not EqualComparing two lists in Python using a Custom Function
In this example, we need to check the elements one by one whether it’s available in List 1 or List2.
# Custom python code to check if list one is equal to list two by taking difference # Define function name difference def difference (list1, list2): list_dif = [i for i in list1 + list2 if i not in list1 or i not in list2] return list_dif # Initializing list 1 and list 2 x = [10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40] y = [25, 40, 35] print ("List first: " + str(x)) print ("List second: " + str(y)) # Take difference of list 1 and list 2 z = difference (x, y) print("Difference of first and second String: " + str(z)) # if lists are equal if not z: print("First and Second list are Equal") # if lsts are not equal else: print("First and Second list are Not Equal")List first: [10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40] List second: [25, 40, 35] Difference of first and second String: [10, 15, 20, 30] First and Second list are Not EqualWhat is cmp() Function in Python?
The cmp() function is a built-in method in Python used to compare the elements of two lists. The function is also used to compare two elements and return a value based on the arguments passed. This value can be 1, 0 or -1.
Note: cmp() build to function for python version 2, In python version 3 it is not available.
For example, if a and b are two lists, then
If a>b, then value 1 is returned
If a If a=b, value 0 is returned
Compared Two Lists Using Cmp() Function
Below is an example of two lists being compared using the cmp() function.
#use of cmp() method #where a=b, ab these three comparison. #when ab a = 3 b = 2 print(cmp(a, b))Apart from the methods discussed above, you can use collection. Counter() , reduce() , map() and using sum() , zip() and len() methods together; to compare two lists in Python.
- Learn Python Programming
- Python Training Tutorials for Beginners
- Square Root in Python
- Python Min()
- Armstrong Number in Python
- Python lowercase
- Python Uppercase
- Python String find
- Top Online Python Compiler
- Polymorphism in Python
- Inheritance in Python
- Python String Concatenation
- Python Pass Statement
- Install Opencv Python PIP Windows
- Python String Title() Method
- Id() function in Python
- Python Split()
- Area of Circle in Python
- Python KeyError
- Pangram Program in Python
Python Compare Two Lists
In this article, we will learn how python compare two lists.
Comparing 2 lists may mean many different things. For example:
- Check if all elements of a list are present in same order in another list.
- Check if all elements of a list are present in another list in any order.
- Getting the intersection element of 2 lists.
- Getting the common elements of 2 lists.
- In case of string element compare ignoring case.
We will learn all possible cases of list comparison in Python. We will also learn different methods for the same purpose.
Compare if 2 lists are equal with same order
To compare something in Python, we use == operator or is operator.
- == (equal to) — It compares 2 values and returns True if both values are equal.
- is (identical to) — It compares 2 variables and returns True if both variables are pointing to the same object. This means the memory addresses of both variables are the same.
We are going to use == because when using is we are comparing the memory address of 2 variables which will be different in the case of 2 different lists.
Comparing 2 lists for same order of items
Method 1: == Operator
We can use the == operator to compare 2 lists. If both lists have the same element in the same order then it will return True .
# python compare two lists # Method 1: == Operator list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print(list1 == list2) # TrueMethod 2: Using loop
We can also use for loop to compare 2 lists.
Since we have to check only if the element at any position in list1 is equal to the element at the same position in list2, so we need not use any nested loop. We can compare it in a single iteration.
# Method 2: For loop list1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] for i in range(len(list1)): if list1[i] != list2[i]: print(False) break else: print(True)Compare if 2 lists are equal regardless of order
When you compare 2 lists regardless of the order of the elements in the list, it becomes a little complex task. Now you can’t just equate 2 lists and check if they are equal.
To compare the lists now you have 2 approaches:
- Sort both the lists and then compare them.
- Compare each element of the list1 with each element of the list2 and check if they exist in both lists.
Comparing 2 lists for a different order of items
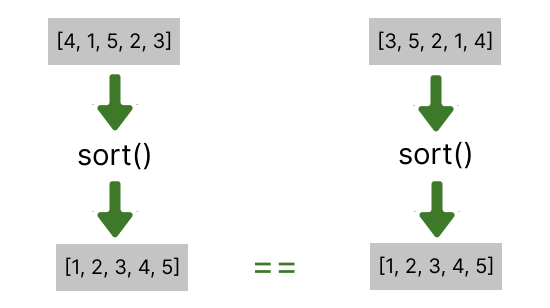
Method 1: Sort both the lists
Sort both the lists. This will make the list to be in the same order if they have the same elements.
Now simply compare both the lists using the == operator.
# Method 1 list1 = [4, 1, 5, 2, 3] list2 = [3, 5, 2, 1, 4] # Sort both the lists list1.sort() list2.sort() # Compare both the lists print(list1 == list2)Method 2: Compare Individual Element
Another approach is to compare each element of the list1 with each element of list2 and check if they exist in both lists.
Before comparing elements first check if both the lists have the same length. If they don’t have the same length then they are simply not equal.
We are going to create a function here that will take 2 lists as arguments and do the comparison.
# Python compare two lists individual element # Method 2 list1 = [4, 1, 5, 2, 3] list2 = [3, 5, 2, 1, 4] def compare(list1, list2): # Check if both the lists have the same length if len(list1) != len(list2): print(len(list1), len(list2)) return False # Check if all the elements of both the lists are same count = 0 for i in range(len(list1)): for j in range(len(list2)): if list1[i] == list2[j]: count += 1 break # check if count is equal to length of list if count == len(list1): return True else: return False # call the function print(compare(list1, list2))Get intersection of 2 lists
Finding the intersection of 2 lists means finding all the elements that are present in both lists.
There are many ways to find the intersection of 2 lists. The most common way to get intersections is using a set data structure.
Method 1: Find intersection using set
A set consists of unique elements. So if take a set of a list then it will return unique elements of the list.
To find the intersection of the lists you can take a set of both the lists and use & operator to find the intersection.
# set() + & operator a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find intersection result = set(a) & set(b) print(list(result)) result = set(b) & set(a) print(list(result))Both set(a) & set(b) or set(b) & set(a) will return same result.
You can also use the intersection() method of the set class to find intersections.
# set() + intersection() a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find intersection result = set(a).intersection(set(b)) print(list(result)) result = set(b).intersection(set(a)) print(list(result))Method 2: Find intersection using list comprehension
Another way to find the intersection of 2 lists is using list comprehension.
In list comprehension, we will use the if condition to check if an element exists in both lists.
# list comprehension a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find intersection result = [x for x in a if x in b] print(result)Alternatively, you can use for loop to find intersections.
The loop will also follow the same logic as a list comprehension.
# for loop a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find intersection result = [] for x in a: if x in b: result.append(x) print(result)Get the difference of 2 lists
Finding the difference of elements from the 1st list to the 2nd list means finding all the elements that are present in the 1st list but not in the 2nd list.
To get the difference between 2 lists you can use a set data structure and use the — operator to find the difference.
# set() + - operator a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find difference (a - b) result = set(a) - set(b) print(list(result)) # find difference (b - a) result = set(b) - set(a) print(list(result))The difference between list1 to list2 and list2 to list1 will be different.
You can also use the difference() method of the set class to find differences.
# set() + difference() a = [6, 2, 7, 1, 5] b = [9, 4, 6, 8, 2] # find difference (a - b) result = set(a).difference(set(b)) print(list(result)) # find difference (b - a) result = set(b).difference(set(a)) print(list(result))Compare if 2 lists are equal ignoring case
Suppose your list contans string values and you want to compare if 2 lists are equal ignoring case.
To do this you can use the lower() method of the str class to convert all the string values to lower case and then use the == operator to compare (If elements are not in the same order then you can use the methods discussed above).
# compare two lists ignoring the case a = ['a', 'B', 'c'] b = ['A', 'b', 'C'] # lower case both lists a = [x.lower() for x in a] b = [x.lower() for x in b] # compare both lists print(a == b)Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed multiple ways how Python compare two lists. We have seen cases like comparing 2 lists, finding intersections, finding differences, and comparing 2 lists ignoring the case.