- Comparing two CSV files in Python when rows have multiple values
- 2 Answers 2
- Compare Two CSV Files and Print Differences Using Python
- Method 1: Compare Two CSV Files Using the Most Pythonic Solution
- Method 2: Compare Two CSV Files Using csv-diff — An External Module
- Method 3: Compare Two CSV Files Using Pandas DataFrames
- Related Article — Python CSV
- Compare Two CSV Files for Differences in Python (Example)
- Example Data & Add-On Libraries
- Example: Compare Two CSV Files & Print Out Differences
- Video & Further Resources
Comparing two CSV files in Python when rows have multiple values
So «a» possesses the numbers 1,6,3,1,8 etc. The actual CSV file is 1,000s of lines long so you know for efficiency sake when writing the code. The second CSV file looks like this:
with open('winningnumbers.csv', 'rb') as wn: reader = csv.reader(wn) winningnumbers = list(reader) wn1 = winningnumbers[0] wn2 = winningnumbers[1] wn3 = winningnumbers[2] wn4 = winningnumbers[3] wn5 = winningnumbers[4] print(winningnumbers) with open('Entries#x.csv', 'rb') as en: readere = csv.reader(en) enl = list(readere) How would I now search cross reference number 4 so wn1 of CSV file 2 with the first csv file. So that it returns that «b» has wn1 in it. I imported them as a list to see if I could figure out how to do it but just ended up running in circles. I also tried using dict() but had no success.
wn1 (winning number 1) would be the first number in the second csv file so it would be the value 4. The first list value.
2 Answers 2
If I understood you correctly, you want to find the first index (or all indexes) of numbers in entries that are winning. If you want it, you can do that:
with open('winningnumbers.csv', 'rb') as wn: reader = csv.reader(wn) winningnumbers = list(reader) with open('Entries#x.csv', 'rb') as en: readere = csv.reader(en) winning_number_index = -1 # Default value which we will print if nothing is found current_index = 0 # Initial index for line in readere: # Iterate over entries file all_numbers_match = True # Default value that will be set to False if any of the elements doesn't match with winningnumbers for i in range(len(line)): if line[i] != winningnumbers[i]: # If values of current line and winningnumbers with matching indexes are not equal all_numbers_match = False # Our default value is set to False break # Exit "for" without finishing if all_numbers_match == True: # If our default value is still True (which indicates that all numbers match) winning_number_index = current_index # Current index is written to winning_number_index break # Exit "for" without finishing else: # Not all numbers match current_index += 1 print(winning_number_index) This will print the index of the first winning number in entries (if you want all the indexes, write about it in the comments).
Note: this is not the optimal code to solve your problem. It’s just easier to undestand and debug if you’re not familiar with Python’s more advanced features.
You should probably consider not abbreviating your variables. entries_reader takes just a second more to write and 5 seconds less to understand then readere .
This is the variant that is faster, shorter and more memory efficient, but may be harder to understand:
with open('winningnumbers.csv', 'rb') as wn: reader = csv.reader(wn) winningnumbers = list(reader) with open('Entries#x.csv', 'rb') as en: readere = csv.reader(en) for line_index, line in enumerate(readere): if all((line[i] == winningnumbers[i] for i in xrange(len(line)))): winning_number_index = line_index break else: winning_number_index = -1 print(winning_number_index) The features that might me unclear are probably enumerate() , any() and using else in for and not in if . Let’s go through all of them one by one.
To understand this usage of enumerate, you’ll need to understand that syntax:
Variables a and b will be assigned according values from the list. In this case a will be 1 and b will be 2. Using this syntax we can do that:
for a, b in [[1, 2], [2, 3], ['spam', 'eggs']]: # do something with a and b in each iteration, a and b will be 1 and 2, 2 and 3, ‘spam’ and ‘eggs’ accordingly.
Let’s assume we have a list a = [‘spam’, ‘eggs’, ‘potatoes’] . enumerate() just returns a «list» like that: [(1, ‘spam’), (2, ‘eggs’), (3, ‘potatoes’)]. So, when we use it like that,
for line_index, line in enumerate(readere): # Do something with line_index and line line_index will be 1, 2, 3, e.t.c.
any() function accepts a sequence (list, tuple, e.t.c.) and returns True if all the elements in it are equal to True .
Generator expression mylist = [line[i] == winningnumbers[i] for i in range(len(line))] returns a list and is similar to the following:
mylist = [] for i in range(len(line)): mylist.append(line[i] == winningnumbers[i]) # a == b will return True if a is equal to b So any will return True only in cases when all the numbers from entry match the winning numbers.
Code in else section of for is called only when for was not interrupted by break , so in our situation it’s good for setting a default index to return.
Compare Two CSV Files and Print Differences Using Python
- Method 1: Compare Two CSV Files Using the Most Pythonic Solution
- Method 2: Compare Two CSV Files Using csv-diff — An External Module
- Method 3: Compare Two CSV Files Using Pandas DataFrames
This article will discuss various methods of comparing two CSV files. We will include the most “Pythonic” way of performing this operation and an external Python module that can help simplify this task.
Lastly, we will include a method using Pandas DataFrames to identify differences in the CSV files.
We will assume that the two CSV files we need to compare are titled file1.csv and file2.csv . You can rename the files as you see fit.
Please also replace the file names appropriately in the code snippets given below.
For example purposes, we have our files setup as follows:
Method 1: Compare Two CSV Files Using the Most Pythonic Solution
In this method, we read the file’s contents into two lists, iterate over one of the lists and check whether or not each of the lines exists in the second list. Logically, this is a very simple solution.
Python’s underlying efficiencies make this comparison fairly efficient, despite what it looks like.
with open('file1.csv', 'r') as file1, open('file2.csv', 'r') as file2: f1_contents = file1.readlines() f2_contents = file2.readlines() for line in f1_contents: if line not in f2_contents: print(line) for line in f2_contents: if line not in f1_contents: print(line) The above code snippet will print the differing lines to your terminal.
In our test case, we get the following as output.
Method 2: Compare Two CSV Files Using csv-diff — An External Module
Firstly, install the module using the following command in your terminal.
python3 -m pip install csv-diff Once installed, you do not need to write a Python script. You can run this directly in the terminal with the following command.
csv-diff file1.csv file2.csv --key=id Running this command will display the differences on your terminal.
In our test case, we get the following as output.
1 row added, 1 row removed 1 row added 1: 2 2: 3 3: 1 4: 4 5: 1 6: 5 1 row removed 1: 1 2: 3 3: 4 4: 5 5: 6 6: 1 To use this module as part of a Python script, you can write a script similar to the following.
from csv_diff import load_csv, compare difference = compare( load_csv(open("file1.csv")), load_csv(open("file2.csv")) ) print(difference) The output for this will be the following.
], 'removed': [], 'changed': [], 'columns_added': [], 'columns_removed': []> Method 3: Compare Two CSV Files Using Pandas DataFrames
The following script can perform this task for you.
import pandas as pd import sys import csv def dataframe_difference(df1: pd.DataFrame, df2: pd.DataFrame, which=None): comparison_df = df1.merge( df2, indicator=True, how='outer' ) if which is None: diff_df = comparison_df[comparison_df['_merge'] != 'both'] else: diff_df = comparison_df[comparison_df['_merge'] == which] return diff_df if __name__ == "__main__": df1 = pd.read_csv("file1.csv", header=None) df2 = pd.read_csv("file2.csv", header=None) print(dataframe_difference(df1, df2)) Please note that in the read_csv method, the argument header=None is entered because our test file does not have any header. If your file has a header, you can read it using: pd.read_csv(«file1.csv») , where file1.csv will be replaced by your file instead.
In case your file is not present in the same directory as your script, please provide the full path to your CSV files.
The above Python scripts should generate an output like:
0 1 2 3 4 5 _merge 2 1 3 4 5 6 1 left_only 3 2 3 1 4 1 5 right_only The lines next to left_only and right_only contain all the differences. The line next to _merge only represents indices.
Related Article — Python CSV
Compare Two CSV Files for Differences in Python (Example)
This post explains how to compare two CSV files and print out differences in Python.
Example Data & Add-On Libraries
We first have to import the pandas library:
import pandas as pd # Load pandas
Furthermore, consider the example data below:
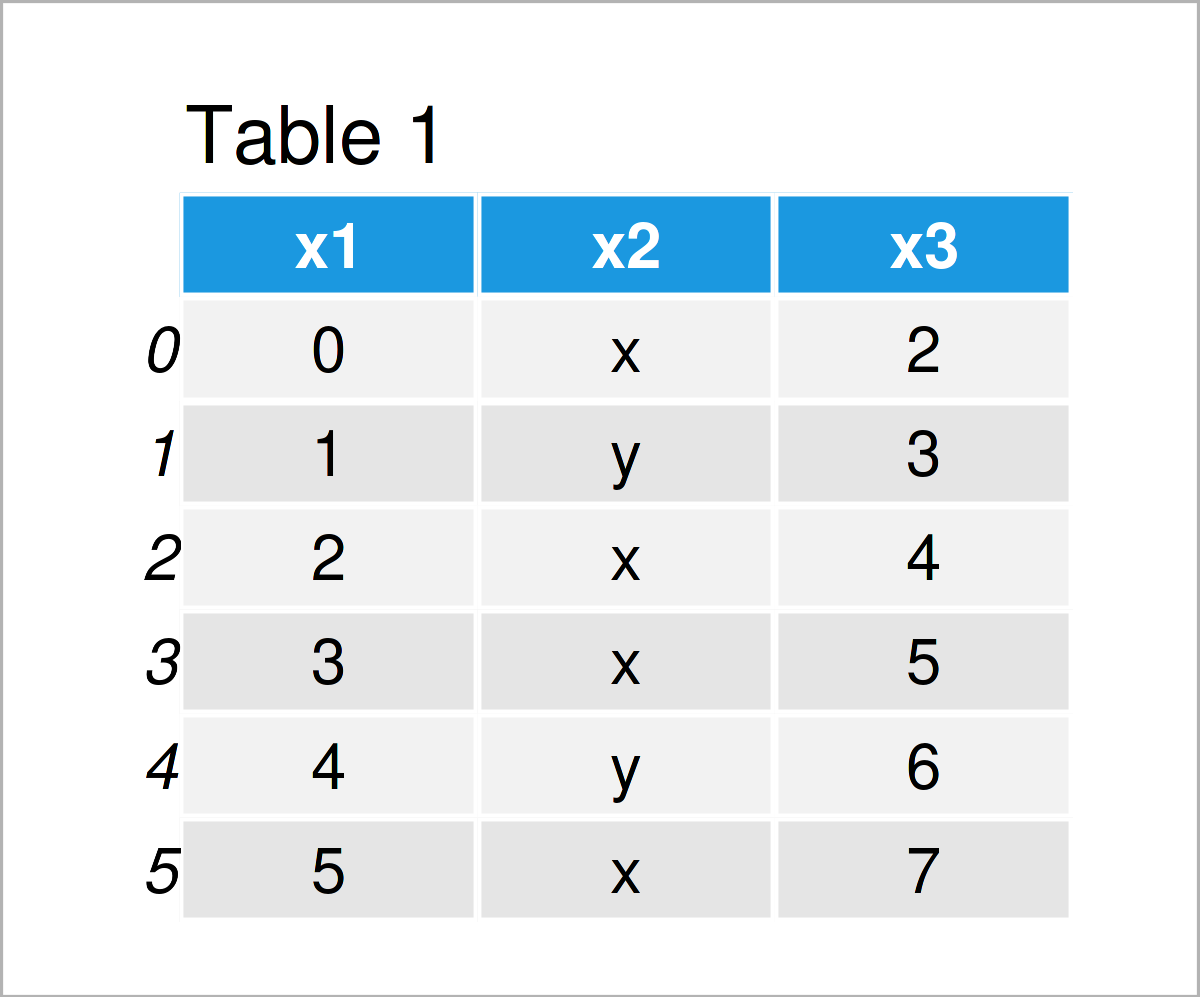
data1 = pd.DataFrame('x1':range(0, 6), # Create first pandas DataFrame 'x2':['x', 'y', 'x', 'x', 'y', 'x'], 'x3':range(2, 8)>) print(data1) # Print first pandas DataFrame
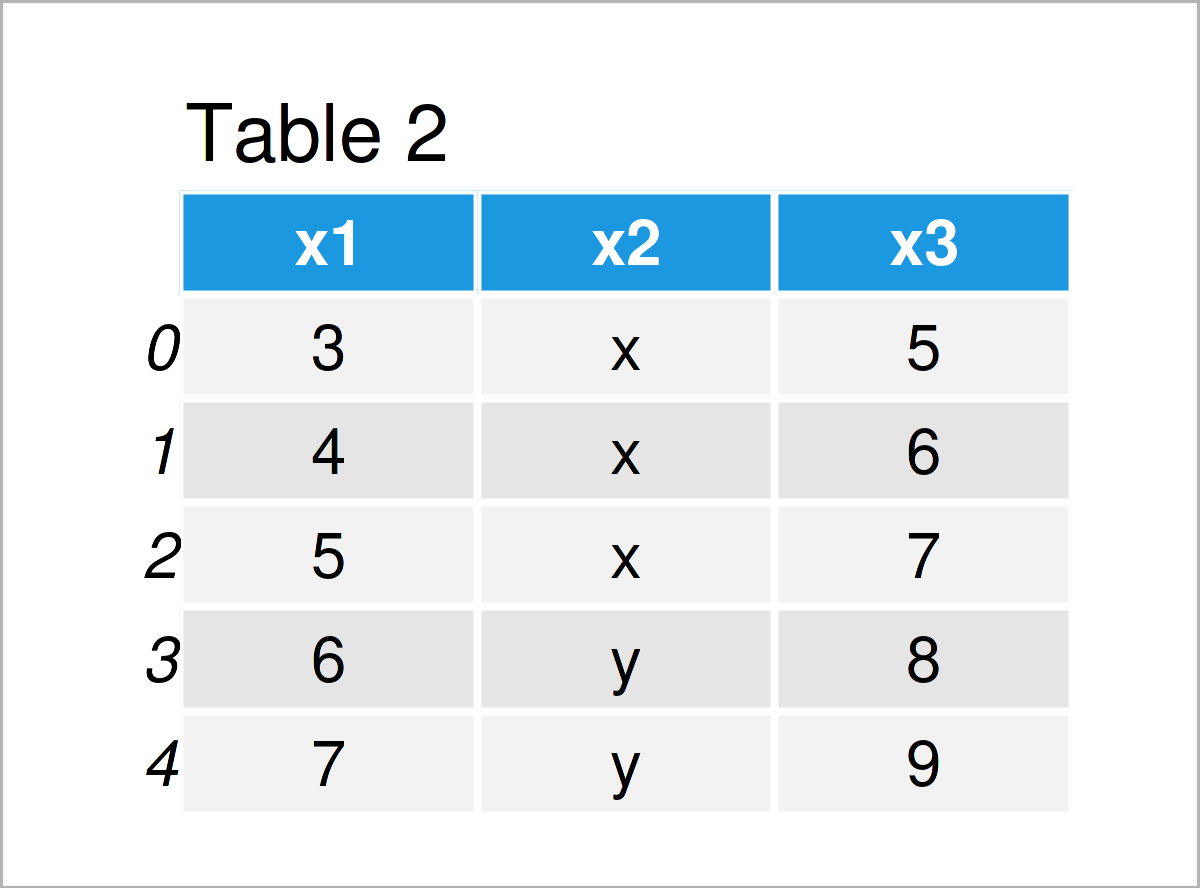
data2 = pd.DataFrame('x1':range(3, 8), # Create second pandas DataFrame 'x2':['x', 'x', 'x', 'y', 'y'], 'x3':range(5, 10)>) print(data2) # Print second pandas DataFrame
The output of the previous Python programming syntax is shown in Tables 1 and 2: We have created two pandas DataFrames with the same columns but different values.
data1.to_csv('data1.csv', index = False) # Export pandas DataFrames to CSV data2.to_csv('data2.csv', index = False)
After the previous Python syntax has been executed, you should find multiple CSV files in your current working directory. These two files will be used as a basis for the following example.
Example: Compare Two CSV Files & Print Out Differences
The following Python programming syntax shows how to compare and find differences between pandas DataFrames in two CSV files in Python.
More precisely, we are searching for rows that do exist in the second pandas DataFrame, but not in the first DataFrame.
In the first step of this example, we are importing the two pandas DataFrames:
with open('data1.csv', 'r') as csv1, open('data2.csv', 'r') as csv2: # Import CSV files import1 = csv1.readlines() import2 = csv2.readlines()
Next, we are using a loop to check for each line in the second CSV file if it exists in the first CSV file. Furthermore, we are creating a new CSV file that contains all rows that exist only in the second CSV file.
with open('data_diff.csv', 'w') as outFile: # Create CSV file with differences for row in import2: if row not in import1: outFile.write(row)
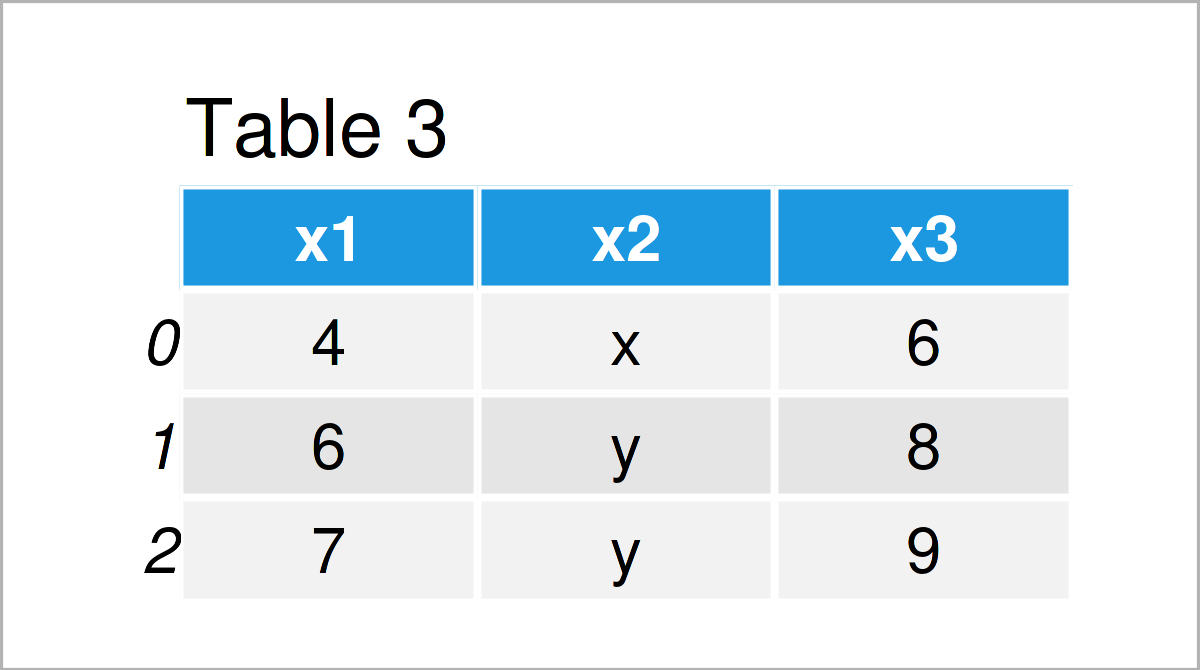
Table 3 shows the output of the previous Python syntax – A data set showing the differences between the first and the second pandas DataFrame.
Please note that the code of this tutorial is partly based on this Stack Overflow thread. You may have a look there for more details on how to compare different data sets stored in CSV files in Python.
Video & Further Resources
Have a look at the following video on the Statistics Globe YouTube channel. I illustrate the Python programming syntax of this article in the video.
The YouTube video will be added soon.
In addition, you may read some of the related tutorials on this website. A selection of articles is listed here.
This tutorial has demonstrated how to find differences between two CSV files in the Python programming language. If you have additional questions, please let me know in the comments below.