- Метод isalpha() в Python — как работает
- Что такое функция isalpha() в Python?
- Синтаксис
- Аргументы
- Возвращаемое значение
- Алгоритм
- Примеры программ с методом isalpha()
- isalpha() in Python
- Introduction to isalpha()
- Syntax of isalpha() in Python
- Parameters of isalpha() in Python
- Return Value of isalpha() in Python
- Errors and Exceptions
- Example 1: Working of isalpha()
- Example 2: Practical Application
- Example 3:
- Example 4: Identify non-alphabets in a string
- Conclusion
- See Also:
- How to Use the Python Isalpha Function
- Syntax
- Example 1: Simple Use of the isalpha() Function
- Example 2: Validate Data with the isalpha() Function
- Example 3: Count the Total Number of Alphabets in a Text
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
Метод isalpha() в Python — как работает
Чтобы проверить, содержит ли строка только алфавитные символы, используйте функцию Python isalpha().
Что такое функция isalpha() в Python?
Python String isalpha() — это встроенный метод проверки, состоит ли данная строка только из букв алфавита. Другими словами, мы можем сказать, что это метод обработки строк. Функция isalpha() возвращает True, если каждый символ строки является алфавитным, и возвращает False в противном случае.
Синтаксис
Аргументы
Метод isalpha() не принимает никаких параметров. Будет показана ошибка, если мы попытаемся передать какой-либо параметр методу.
Возвращаемое значение
Функция isalpha() возвращает значение true, если строка состоит только из букв алфавита (как в верхнем, так и в нижнем регистре).
Строковая функция Python isalpha() возвращает False, если строка не содержит букв и состоит из символов, отличных от алфавитных, таких как числа или специальные символы. Когда она идентифицирует пробел, он также возвращает False.
Алгоритм
1. Инициализируйте счетчик новой строки и переменной равным 0.
2. Перебрать заданную строку символ за символом до ее длины; проверьте, является ли символ алфавитным.
3. Если это буква, увеличьте счетчик на 1 и добавьте его к новой строке, иначе перейдите к следующему символу.
4. Выводимое значение счетчика и новая строка.
Примеры программ с методом isalpha()
isalpha() in Python
The isalpha() function is a built-in function used for string handling in python, which checks if the single input character is an alphabet or if all the characters in the input string are alphabets.
Introduction to isalpha()
While learning Python and working with strings, one might want to know or check if the string you are handling contains only alphabets and no special characters or numbers. Say you have a domain name validator, which has a strict rule of not allowing anything other than alphabets. That’s where the isalpha() in python function comes in handy. As the name of the method isalpha() in python suggests, we use this method to check if all the characters in a string are alphabets or not.
Syntax of isalpha() in Python
The syntax of the remove function in python is explained below:
The isalpha function is used with the string to checks if the single input character is an alphabet or if all the characters in the input string are alphabets. Read along to learn more about its parameter.
Parameters of isalpha() in Python
We can see that it doesn’t accept a parameter as we have understood the syntax of the isalpha function in python.
Return Value of isalpha() in Python
isalpha() in python is a boolean function and hence has return values as either True or False .
The return value is : True when all the characters in the input string to the method islapha() in python are alphabet. False if 1 or more non-alphabetic characters are in the string given as input to the isalpha() method.
Errors and Exceptions
When do errors or exceptions occur while using this particular method in python?
- You know that the method isalpha() in python does not take any parameters, so, if you happen to pass any parameters, an error occurs. More specifically, a TypeError.
- If the string consists of just uppercase, or just lowercase or even mixed case alphabets, the method isalpha() in python still returns True.
Here, we have initialized different strings with different cases in this code. One string with all uppercase alphabets, one with all lowercase alphabets, while one with mixed case alphabets to show that the method isalpha() in python will still return true for all the above strings.
- While using the method isalpha() in python, you must keep in mind that spaces are not considered as alphabets; hence, adding a space to the string will result in the isalpha() method returning False.
In this piece of code, we can see that our string consists of space right after the word «returns», and spaces are not considered alphabets; hence, the isalpha() method will return False.
Example 1: Working of isalpha()
Let’s look at some more examples of the isalpha() in python method to clarify our understanding.
As we can see in the first example, the string «word» also contains some numbers. The isalpha() method in python will return True only if all the characters in the string are alphabets. But since this string has numbers and alphabets, the method isalpha() in python returns False.
In the second example, the string only comprises numbers; hence the isalpha() method will return False.
Example 2: Practical Application
Counting alphabets in string using isalpha() in python
If you have a string that is a mix of alphabets, numerals, spaces, etc., and you need to know the total number of alphabetical characters in the string, then the method isalpha() in python can help with it.
How will we do it? Here’s the algorithm we follow, we initialize a counter variable that will hold the current value of the number of alphabets encountered. It is initialized to 0. We then iterate over the complete string, element by element, and whenever an alphabet is encountered, we increment the count variable by 1.
Let’s look at the code now.
What if you also wanted to extract the alphabet from the sentence? We create a new string, and every time we encounter an alphabet, we increase the counter by 1 and add the current character to the new string.
As discussed previously, spaces are not alphabets hence our new string does not contain the spaces.
Example 3:
The method isalpha() in python identifies unicode alphabets of other international languages.
For example, here we have a string in German:
The method isalpha() in python is not language-dependent, it works on languages other than English.
Example 4: Identify non-alphabets in a string
The method isalpha() in python can also be used to identify the non-alphabets in the string. How do we do that? If an element of the string is an alphabet, then we do not append it to the result string. However, if the isalpha() function returns False for a character, we can add it to our result string.
Conclusion
- The method — isalpha() in python checks if the string contains only alphabets
- It returns True if there are only alphabets, and False if not
- Some errors and exceptions are — passing parameters(TypeError raised), string with both lower and upper cases, and adding spaces. Spaces result in isalpha() returning False.
- Syntax = string.isalpha()
- The method — isalpha() in python can be used for counting the number of alphabets or non-alphabets in a string. It can even identify Unicode alphabets of languages other than English.
See Also:
How to Use the Python Isalpha Function
Sometimes, we need to check the content of data for programming purposes. There are many different types of built-in functions in Python for string data to check the content This content may include letters, numbers, or other special characters. The isalpha() function is one of the useful built-in functions of Python that can be used to find out whether or not the content of the data is alphabetic. This function searches the alphabet in the starting of the string value. If the starting value of the string is a letter, then this function returns true; otherwise, it returns false. This tutorial will show you how to can use the isalpha() function in Python.
Syntax
Here, the string will contain any string data. The isalpha() function has no argument and will check whether or not the data in the string includes letters.
Example 1: Simple Use of the isalpha() Function
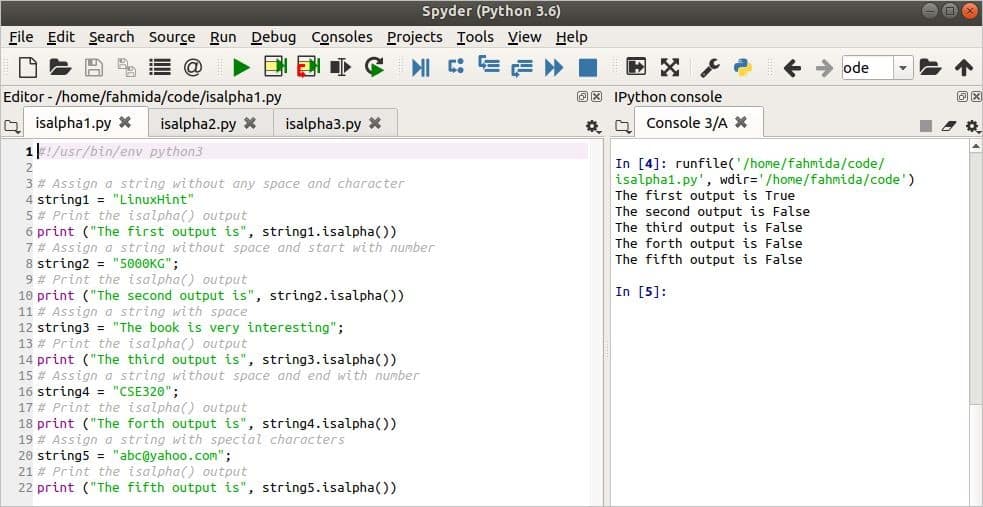
In the following example, the isalpha() function is applied to five different types of string data. The value of the string1 variable is a text of a single word that contains all alphabetic characters. The value of the string2 variable is a text of a single word that contains numbers at the beginning of the text. The value of the string3 variable is a text of multiple words. The value of the string4 variable is a text of a single word that contains the number at the end of the text. The value of the string5 variable is a text of a single word that contains special characters and alphabetic letters.
# Assign a string without any space and character
string1 = «LinuxHint»
# Print the isalpha() output
print ( «The first output is» , string1. isalpha ( ) )
# Assign a string without space and start with number
string2 = «5000KG» ;
# Print the isalpha() output
print ( «The second output is» , string2. isalpha ( ) )
# Assign a string with space
string3 = «The book is very interesting» ;
# Print the isalpha() output
print ( «The third output is» , string3. isalpha ( ) )
# Assign a string without space and end with number
string4 = «CSE320» ;
# Print the isalpha() output
print ( «The forth output is» , string4. isalpha ( ) )
# Assign a string with special characters
string5 = «abc@yahoo.com» ;
# Print the isalpha() output
print ( «The fifth output is» , string5. isalpha ( ) )
The following output will appear after running the script. The first output is true because all characters of the text are alphabetic letters. The second output is false because the text contains numeric characters at the beginning. The third output is false because the text contains multiple words with spaces. The fourth output is false because the text contains the number character at the end. The fifth output is false because the text contains special characters.
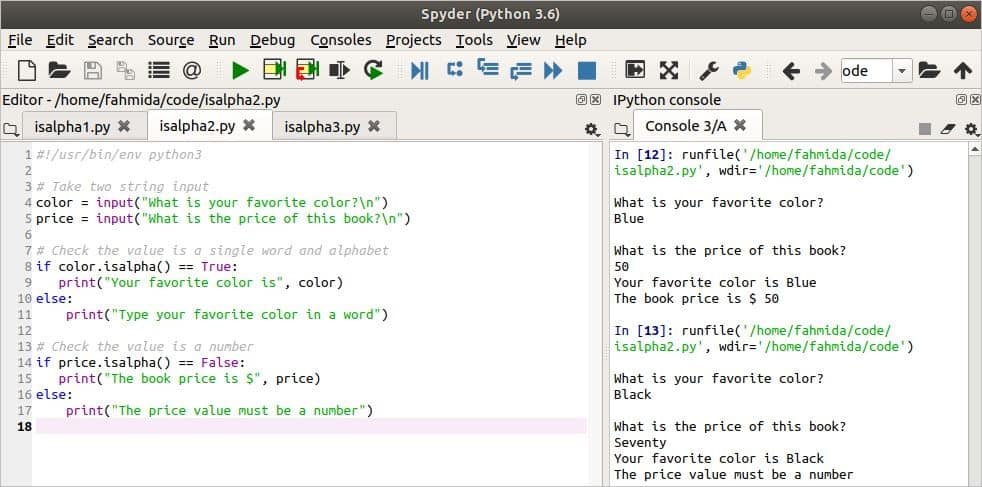
Example 2: Validate Data with the isalpha() Function
You can use the isalpha() function to validate any data you might need for programming purposes. This process is shown in the following script. Here, two string values will be taken from the users. The isalpha() function is used to validate that the first input value is a string of alphabets and the second input value is a number. The isalpha() function returns true for any text if the content of the text is all alphabetic characters. The isalpha() function returns false if any character of the text is not an alphabetic character.
# Take two string input
color = input ( «What is your favorite color? \n » )
price = input ( «What is the price of this book? \n » )
# Check the value is a single word and alphabet
if color. isalpha ( ) == True :
print ( «Your favorite color is» , color )
else :
print ( «Type your favorite color in a word» )
# Check the value is a number
if price. isalpha ( ) == False :
print ( «The book price is» , price )
else :
print ( «The price value must be a number» )
The above script is run two times with the valid data and the invalid data. The first time, the valid data are passed for both inputs and it shows the output properly. The second time, invalid data is passed for the second input and an error message is printed as this output.
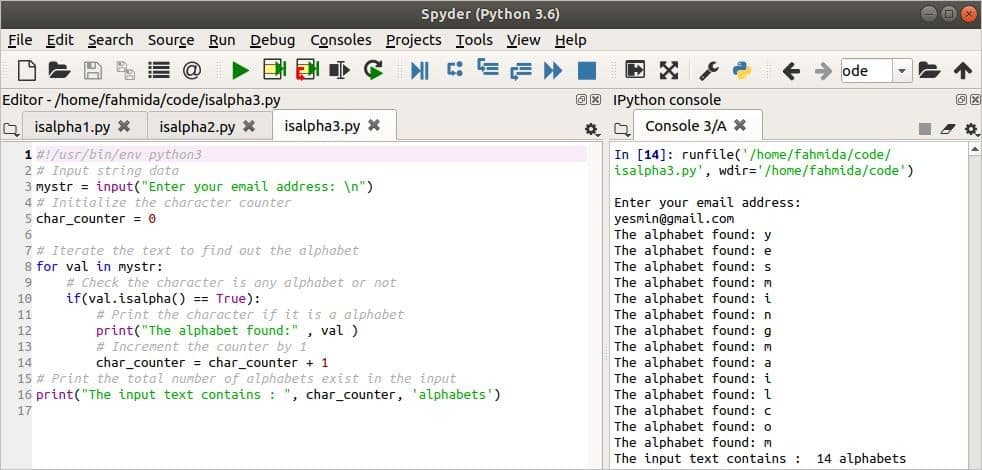
Example 3: Count the Total Number of Alphabets in a Text
The isalpha() function is used in the following script to count the total number of characters that are alphabetical in the given text. An email address will be taken as input and stored in the variable, mystr. In this example, the char_counter variable is used to count the total number of alphabetic characters in the mystr. This variable is initialized to 0 and each time that an alphabetic character is found in the mystr, the char_counter will be incremented by one. The for loop is used here to read each character of the mystr, while the isalpha() function is used to check whether or not the character is alphabetic.
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Input string data
mystr = input ( «Enter your email address: \n » )
# Initialize the character counter
char_counter = 0
# Iterate the text to find out the alphabet
for val in mystr:
# Check the character is any alphabet or not
if ( val. isalpha ( ) == True ) :
# Print the character if it is a alphabet
print ( «The alphabet found:» , val )
# Increment the counter by 1
char_counter = char_counter + 1
# Print the total number of alphabets exist in the input
print ( «The input text contains : » , char_counter , ‘alphabetal characters’ )
The output shows that yesmin@gmail.com is taken as the input value after running the script. The input value contains two special characters (‘@’ and ‘.’), and the remainder of the characters are alphabetic. So, the input text contains 14 alphabetic letters, after omitting the special characters.
Conclusion
It is essential to check the content of any text or variable before solving many programming problems. Python contains several built-in functions, such as isnumeric() , isdigit(), isalnum(), isdecimal(), isalpha(), and others, to check the content of the string data. The different uses of the isalpha() function are explained in this tutorial by using simple examples. This should help new Python users to understand the purposes of using the isalpha() function and others like it.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.