- Private Methods in Python
- What are Private Methods in Python?
- Differences Between Private and Public Methods
- Example 1: Creating Private Methods in Python
- Example 2: Accessing Private Methods in Python
- Example 3: Call Private Methods Outside the Class (Name mangling)
- Conclusion
- Python Private Method with Examples
- What is private method in Python?
- How do you call private methods?
- What is the difference between private and protected in Python?
- Are private methods inherited?
- Should I use private methods in Python?
- Python Private methods
- Name mangling
- Summary
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Private Methods in Python
Private methods are used to help users serve with “Encapsulation.” This means that methods are accessible only inside the same class and not from outside it. In Python, private methods cannot be accessed/called outside the class.
This post provides an in-depth guide on private methods using numerous examples and following the below contents:
What are Private Methods in Python?
In Python, private methods can only be called inside the same class where they are initialized. They cannot be called outside the class, even by subclasses. Private methods are denoted by double underscores (__), as shown below:
class class_name: def __private_method(self): # do something
Python’s private methods can be used for the following purposes:
- A class’s internal workings are hidden from the outside world by using private methods.
- They encapsulate the class’s behavior, preventing other classes from directly accessing or modifying the class’s state.
Differences Between Private and Public Methods
The difference between private and public methods are shown below:
| Private Methods | Public Methods |
|---|---|
| private methods can only be accessed/called inside the class. | Public methods can be called inside the class. |
| private methods are used to implement its internal behavior. | Public methods are used to define the external interface of a class. |
| private methods can only be called by other methods within the same class. | Public methods can be called by any object. |
Example 1: Creating Private Methods in Python
To create a private method, the member name must be prefixed with the double underscore “__.” Here is an example of how to create a private method in Python:
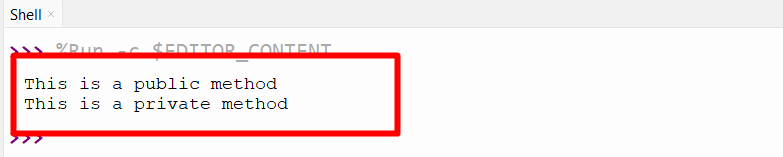
class school: def __private_method(self): print("This is a private method") def public_method(self): print("This is a public method") self.__private_method() obj = school() obj.public_method() - The class defined two methods named as “ __private_method” and “public_method”.
- The private method named “__private_method()” is defined using the double underscore at the start.
- The private is accessed inside the public method using the expression “self.__private_method()”.
- The class object named “obj” is used to call the public method.
The private and public methods are created and accessed using the class object.
Example 2: Accessing Private Methods in Python
Private methods cannot be accessed directly outside the class. However, they can be accessed indirectly using other methods within the class. For example, a public method within the same class can call a private method using the below code example:
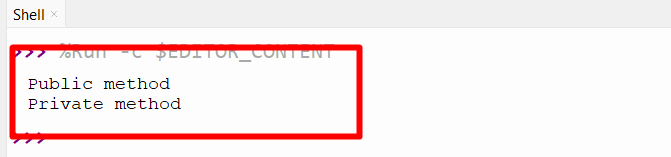
class Students: def free(self): print("Public method") def __free(self): print("Private method") def boys(self): self.free() self.__free() my_obj = Students() my_obj.boys() - The class “Students” is created using the keyword class.
- The public method, named “free,” and the private method, by prefixing with a double underscore, are defined.
- The third method, named “boys,” is defined.
- Inside the third method, the public and private method is accessed using the self parameter.
- The class object is used to access the third method, automatically accessing the private and public methods.
The private method has been successfully accessed.
Example 3: Call Private Methods Outside the Class (Name mangling)
The below example is used to call private methods using the Name mangling techniques. The private method is called from outside the class with the help of this technique.
The private method is created using the double underscore, just as shown below:
We need to replace the above with the given below syntax:
In the above case, the “_classname__method” replaces “__method,” where the class name is the current class name.
Now. let’s understand it via the following examples:
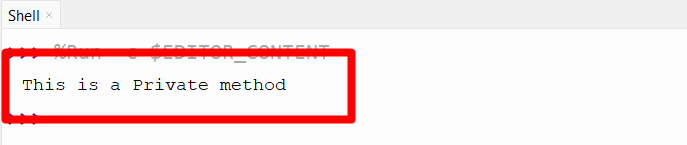
class School: def method(self): print("This is a Public method") def __method(self): print("This is a Private method") obj = School() obj._School__method() - The class name “School” is created at the start.
- The name mangling method, such as “obj._School__method(),” is used to access private methods outside the class.
The private method has been accessed successfully.
Conclusion
A private method in Python can only be accessed/called within the same class in which it is defined. Private methods are denoted by double underscores (__). Accessing private methods directly from outside of a class is impossible. Alternatively, they can be accessed indirectly through other class methods. The class’s private methods can also be accessed through other methods, such as name mangling. This tutorial provided an in-depth overview of Python’s private methods.
Python Private Method with Examples
This tutorial covers Python private method . We will be giving examples to show you how this method works.
In addition, we will explain how to call private methods, why private methods should be used, and the difference between the other modifiers.
Object-oriented programming languages such as C++, Java, and Python restrict access to class variables and methods by access changes. A class in the majority of computer languages has three access modifiers: Public, Protected, and Private.
Python determines the access control for a specific data member or member function of a class using the ‘_’ symbol. Access specifiers in Python play a crucial role in safeguarding data against unwanted access and preventing its exploitation.
A Class in Python has three types of access modifiers:
However, our focus in this article is private method. Moving on, let’s know what is Private method in Python!
What is private method in Python?
Private methods in Python are only accessible within the class in which they are declared. Basically, you cannot call a method outside the class.
To indicate private method you must prefix the member name with double underscore (__) .
Note that even the base class cannot access private class methods.
How do you call private methods?
- Step 1. To define a private attribute or function in Python, append an underscore(__).
Now, create the derived class or subclass grade that extends Name:
The call to the work() method is successfully executed, printing out the statements from the work() and the walk() method.
However, the call to takeCall() triggers an AttributeError because it does not recognize the __call() method from the Name class as a method of the Grade class. Extending a class to another class does not include its own private methods in the extension.
If you having a hard time to run your python program read this article how to run a python script
What is the difference between private and protected in Python?
The difference between private and protected method in python are the indicator of prefix name and accessibility. Basically, the private method indicates its prefix name with two underscore characters “__”. You can’t access or modify from outside the class.
The private method can only be called from within its own class.
However, the protected method is created by starting its name with single underscore”_”. Protected members can be accessible from outside the class like public members, but they are NOT intended to be so.
Are private methods inherited?
The private method in python can be inherited, as python doesn’t have mechanism that effectively restricts access to instance variables or methods.
The double underscore __ prefixed to a variable makes it private. It gives a strong suggestion not to touch it from outside the class. Any attempt to do so will result in an AttributeError:
Should I use private methods in Python?
We can use private method to hide the inner functionality of any class from the outside world. A Private methods are those that should neither be accessible externally nor by base classes.
Python Private methods
Private methods are those methods that should neither be accessed outside the class nor by any base class. In Python, there is no existence of Private methods that cannot be accessed except inside a class.
However, to define a python private method prefix the member name with double underscore “__”.
Example Program
class Base: def free(self): print("Public method") def __free(self): print("Private method") class Derived(Base): def __init__(self): Base.__init__(self) def call_public(self): print("\nInside derived class") self.free() def call_private(self): self.__free() obj1 = Base() obj1.free() obj2 = Derived() obj2.call_public()Program explanation:
The above example shows that private methods of the class can neither be accessed outside the class nor by any base class. However, private methods can be accessed by calling the private methods via public methods.
Public method Inside derived class Public method
Name mangling
Name mangling is a magic wand of python which allows private method called outside the class.
Further, name mangling is a method in which any given identifier with one trailing underscore and two leading underscores is explicitly replaced with the __ClassName__ Identifier. In __ClassName__ Identifier name, ClassName is the name of current class where the identifier is present.
Name mangling is about safety rather than security: it is intended to avoid unintentional access rather than intentional wrongdoing.”
Example program:
class X: def free(self): print("Public method") def __free(self): print("Private method") obj = X() obj._X__free() Summary
In summary, Python private methods are declared by appending two underscores, (__) to a method’s name. Declaring private methods allows a method to be reserved exclusively for the class that declares it. A class that extends a class containing private methods will not inherit them and will generate an error if it attempts to access them.
Private variables and methods play a significant role in Python, as we have seen. It provides encapsulation, giving you greater control over how to manage data in real-life problems. It makes data access more versatile by protecting certain data using modifiers such as private, protected, and public mode.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.