Excel VBA Tutorial in 20 Minutes: The Absolute Basics
Whether you’re new to Excel VBA or just want a refresher, this tutorial is for you. In 20 minutes (or less!), we’ll take you through the basics of working with VBA code. You’ll learn to write and run VBA code, use the macro recorder, and more! We also give you some common examples when working on VBA Excel. So, buckle up as we’re going to get started! 😉
What is VBA in Excel?
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications. It’s a programming language used to automate tasks in Microsoft Office products, including Excel, Word, and Outlook. With VBA Excel, you can write code to automate tasks, create custom functions, and even move data between Office programs.
This programming language was introduced with Excel 5.0 in 1993. It might be hard to believe that the Excel and VBA combo has been around for almost 30 years now. And as you can see, we’re still talking about it today! This means that this language is still popular among spreadsheet users—which makes sense considering what it offers and that few other spreadsheet apps can compete with this.
Why is VBA important?
VBA is important because of all the things it can do, but mainly its ability to automate mundane tasks that take a lot of time is particularly useful. As well as that, here are some common uses of VBA in Excel:
- Create custom functions. If you find yourself using the same complex formula over and over again, you can save yourself some time by creating a custom function using VBA.
- Create custom add-ins for Excel. Add-ins are small programs that extend the functionality of Excel. You can, for example, create an add-in that allows you to apply formatting to selected cells, generate random numbers, apply formulas, or anything else you may want to improve productivity.
- Simplify the data entry process. With Excel VBA, you can create custom forms that will simplify data entry and eliminate errors. You’ll be able to enter all information in one place with consistent formats. It’s easier for everyone involved.
- Automate tasks that you would otherwise have to do manually. Automating tedious, manual tasks with VBA Excel code is an easy way to save time and avoid mistakes. Here’s a common example. You might need to frequently update your spreadsheets by pulling data from various sources such as QuickBooks or Xero. However, doing this manually every day can prove costly in both efficiency and accuracy due to human error.
Are there no-code ways to automate workflows in Excel?
If you want to automate such processes without coding, Power Query is one of your best options. However, it’s not always ideal if any of your data sources isn’t supported by Power Query.
In this case, try using third-party integration tools like Coupler.io, which is a solution to import data from different sources into Excel automatically. You can even set up a schedule to refresh your data (hourly, daily, monthly, etc.) to keep it always up-to-date.
Coupler.io allows you to pull data from CRM applications like Pipedrive, time-tracking tools like Clockify and many other apps and sources including Microsoft Excel. Check out all the available Excel integrations to choose the ones you need. So, you basically can automate data flow between your workbooks or even merge Excel files using it.
Excel VBA programming: Before you get started
Before we get started with Excel VBA programming, let’s understand a few basic terminologies and how to open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
A few basic terminologies
Here are a few terminologies we’ll be looking at in this article:
- A macro is simply a procedure written in VBA Excel. You can write macros by using the macro recorder or write your own code.
- A module is where you will store your code. Think of it as a blank canvas where you can write whatever you want.
- A procedure is an instruction or a set of instructions. The two main types of procedures are Sub procedure and Function procedure.
- A Sub procedure (or Sub) is a procedure that only performs actions and does not return a value.
- A Function procedure (or Function) is a procedure that returns a value.
How to open VBA editor in Excel
To use VBA in Excel, you first need to open the Visual Basic Editor (VBE) by simply pressing Alt+F11 on your keyboard.
Alternatively, click on the Developer tab from the ribbon menu, then click on the Visual Basic button. If the Developer tab is not visible, see the section below on how to show the Developer tab in Excel.
After the Visual Basic Editor is open, you’ll be able to find multiple sections described below:
- Menu bar. This is the main menu of the VBE and contains various commands. Many of the commands have shortcut keys associated with them.
- Code pane. This area is where the macro/code can be found. Here are all declaration variables, procedures, functions, etc.
- Toolbar. It contains most of the useful commands that are used while codding. You can customize it by clicking View >Toolbars, then customize as you see fit. Most people just leave them as they are.
- Project Explorer. The Project Explorer Window can usually be found on the top left side of the VBA Excel editor, showing a hierarchical list of open projects. This list contains Microsoft Excel Objects (Sheets and ThisWorkbook section), Forms (all User Forms created in the project), Modules (all macro modules), and Class Modules.
- Properties Window. The Properties Window is where you can set all the properties for all objects from your application. The properties can be sorted alphabetically or by category.
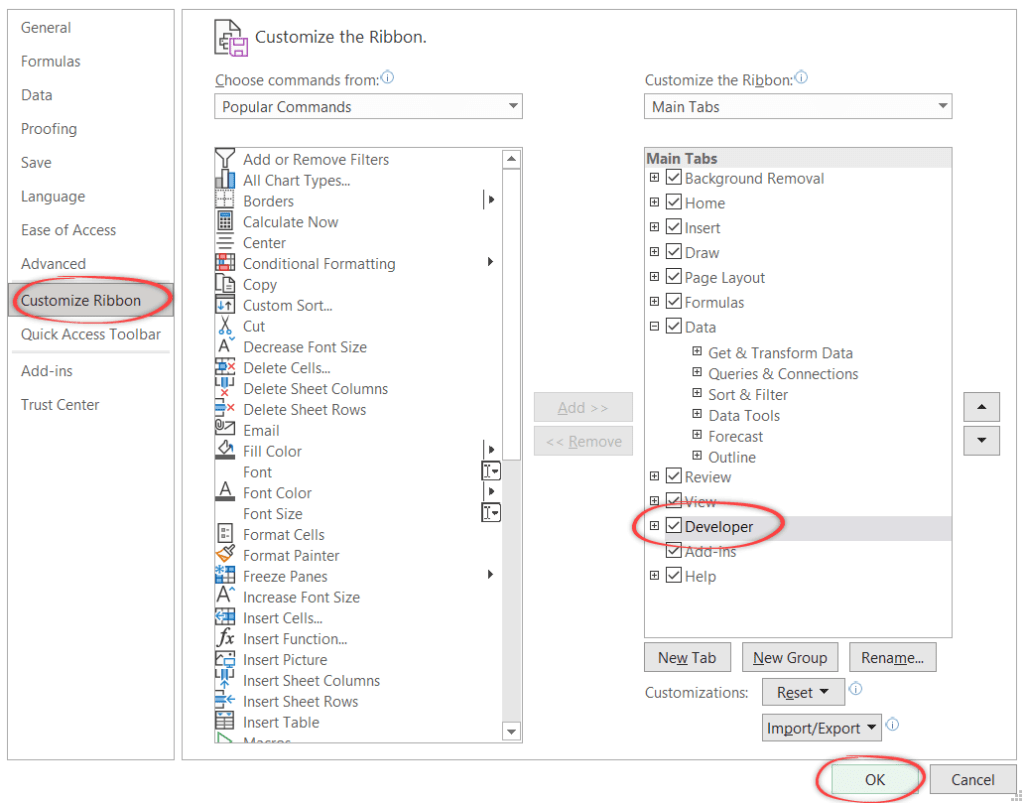
How to show the Developer tab in Excel
The Developer tab is hidden by default in Excel, but you can easily show it if you need to access the features it contains. To do so, here’s a quick guide:
- First, click on File >Options.
- In the Excel Options dialog box, click on Customize Ribbon.
- On the right pane, check the box next to Developer.
- Click OK to save your changes and close the dialog box.
Just that! Now when you open Excel, you will see the Developer tab listed among the other tabs at the top of the window.