- проверить, открыт ли файл в Python
- 4 ответа
- Ещё вопросы
- How to check a file is opened or closed in Python
- Create a file for checking:
- Example-1: Check the file is opened or not by using IOError
- Output:
- Example-2: Check the file is closed or not by using the closed property.
- Output:
- Example-3: Check the file is opened or not by using OSError
- Output:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Fahmida Yesmin
проверить, открыт ли файл в Python
В моем приложении я пишу файл excel. После записи пользователь может просмотреть файл, открыв его. Но если пользователь забывает закрыть файл перед любой последующей записью, должно появиться предупреждающее сообщение. Поэтому мне нужен способ проверить, что этот файл открыт перед записью процесса. Не могли бы вы предоставить мне код python для выполнения этой задачи? Спасибо заранее.
4 ответа
Я предполагаю, что вы пишете файл, затем закройте его (чтобы пользователь мог открыть его в Excel), а затем, прежде чем повторно открыть его для операций добавления/записи, вы хотите проверить, что файл isn ‘t все еще открыт в Excel? Вот как вы должны это делать:
try: myfile = open("myfile.csv", "r+") # or "a+", whatever you need except IOError: print "Could not open file! Please close Excel!" with myfile: do_stuff() Это специфично для Windows, вопрос, касающийся Excel, имеет смысл, но не в каждом сценарии это будет так. Например, если том подключен в сети, вы не можете знать, открыт ли файл, если вы попробуете это на другом компьютере в сети, в частности на серверах или клиентах UNIX или Linux.
Если все, о чем вы заботитесь, это текущий процесс, простой способ — использовать атрибут файлового объекта «закрытый»
f = open('file.py') if f.closed: print 'file is closed' Это не будет определять, открыт ли файл другими процессами!
.closed проверяет, закрыт ли файл текущим процессом Python. Он не проверяет, открыт ли файл или закрыт каким-либо другим процессом.
@Rmhero: рассмотрите возможность удаления своего ответа, потому что он неправильный, что может привести к тому, что люди будут писать код, который ведет себя не так, как предполагалось. Это работает так, как описывает @temoto Чтобы увидеть это, просто откройте две оболочки ipython , затем f = open(‘foo.txt’, ‘w’) в одной, а f = open(‘foo.txt’, ‘r’) в другой. Тогда f.closed is False , но f.close() во втором терминале достаточно, чтобы превратить это в f.closed is True .
@Ioannis Filippidis — Если бы он не дал свой ответ, вы бы не смогли доставить свое сообщение. Скорее, есть его сообщение и ваше, чем ни то, ни другое.
Это опубликовано как ответ, который это не так. Изменение в ответ, с комментарием о том, чего следует избегать, имело бы смысл.
Это именно то, что мне было нужно, и работает, как задумано, если вы выполняете файловую операцию, например, извлекаете данные из Интернета, затем записываете в файл и хотите знать, когда он будет завершен, чтобы продолжить выполнение операций или отобразить «выполнено» пользователю , Это ценный ответ.
Вы можете использовать с открытым ( «путь» ) в качестве файла: чтобы он автоматически закрывался, иначе, если он открывается в другом процессе, вы можете попробовать как в примере с Tims, вы должны использовать, кроме IOError, чтобы не игнорировать другие проблемы с вашим кодом:)
try: with open("path", "r") as file:#or just open #Code here except IOError: #raise error or print Никогда не делайте except не указав исключение, которое вы хотите поймать. Кроме того, область действия вашего блока try слишком широка — Shansal хочет проверить, можно ли вообще открыть файл. Обработка ошибок при записи в файл (или что-то еще происходит в блоке with ) должна быть отдельной.
Ни один из других приведенных примеров не будет работать для меня, когда вы сталкиваетесь с этой конкретной проблемой с excel на Windows 10. Единственный другой вариант, о котором я мог подумать, — это попробовать переименовать файл или каталог, содержащий файл, временно, а затем переименовать его назад.
import os try: os.rename('file.xls', 'tempfile.xls') os.rename('tempfile.xls', 'file.xls') except OSError: print('File is still open.') Это неплохое решение, если у вас мало пользователей для файла . это действительно своего рода механизм блокировки частного файла.
Имейте в виду, что это очень специфично для Windows, так как большинство других ОС с радостью переименуют файлы, если они уже открыты.
Ещё вопросы
- 1 Разбор больших файлов XML в Android
- 0 База данных для галереи изображений Node.js
- 0 Переменная как ключ массива — выбрано выпадающее меню Yii
- 0 Создание сохраненной страницы с помощью Javascript?
- 1 Как увеличить скорость использования нечеткого сопоставления в кадре данных?
- 1 Как ограничить перенаправления в Android App родной рекламы?
- 0 c ++ редактировать определенное слово из строки в текстовом файле
- 1 Что за выражение «throws» используется здесь, а что, если не используется?
- 0 выбор ячейки таблицы на основе ее идентификатора с помощью jquery
- 0 C ++ Передача указателей через функции класса из main ()
- 0 Получение подстроки между двумя разными разделителями
- 0 XChat 2 возвращает «No xchat_plugin_init symbol» для библиотеки DLL
- 0 Как мне найти префикс в таблице MySQL?
- 0 Как может angularjs контроллер доступа к функциям в non-angularjs iframe?
- 1 Python __ror__ без инициализации класса
- 1 Динамически загружать XML с помощью стилей CSS
- 0 Определение объекта подкласса
- 0 Rightsidebar начинается с нижней части содержимого в div содержимого
- 0 как получить разницу во времени между двумя в php
- 1 Java: байт [1] против байта [1024]
- 0 Наложение jQuery .fadeIn () (после просмотра другой вкладки браузера)
- 0 Как изменить функцию, чтобы она передавалась по ссылке для моей переменной y из данных, которые она получает из входного файла?
- 1 Геозона для кроссплатформенного ксамарина
- 0 Ошибка: недопустимое значение для атрибута x = «NaN» в angularJS nvd3-multi-bar-chart
- 1 Можно ли сериализовать и десериализовать объект, который содержит объект в качестве переменной в Firebase?
- 0 Появляется ошибка при попытке отобразить данные таблицы MySQL в таблице HTML [дубликаты]
- 1 Локализация MVC4 с DisplayName в базе данных
- 0 C ++ Утечка памяти при освобождении *?
- 0 Неопределенная ссылка на тип черты
- 1 Java ConcurrentSkipListSet несовместим с документацией
- 0 yii загружать элементы CRUD в другое место
- 0 используя неиндекс с составным индексом
- 0 как сделать меню полосы прокрутки из нескольких столбцов похожим на таблицу Excel
- 1 vert.x и BIO-потоки
- 0 Разбор строки Json через командную строку
- 0 Meteor.call не работает
- 1 изменить размер изображения по площади
- 1 Корреляция между уровнем и перекрытием в сообществе
- 0 обслуживать несколько каталогов в ngnix
- 1 Grails не кодирует в UTF-8 после публикации тела с помощью contentType application / json
- 1 Как установить высоту штрих-кода как 25 мм
- 0 AngularJS — не может изменить значение поля ввода
- 0 атрибут mailto не работает на мобильном телефоне
- 1 Подсчет символа «е»
- 1 D3 SVG с конечной высотой и шириной
- 0 PHP — извлекать числа и заключать их в
- 1 Recyclerview разделитель с пользовательским заполнением
- 1 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException при попытке суммировать двоичные числа
- 0 ajaForm возвращает неверный XML в responseXML
- 0 Методы событий плагина в Virtuemart для статуса заказа
How to check a file is opened or closed in Python
The file is used to store data permanently. Working with a file is a very common task of any programming language. Many built-in functions exist in Python to create, open, read, write and close the file. Two types of files can be created to store data. These are text files and binary files. Any file is required to open before reading or write. The open() function is used in Python to open a file. Using the open() function is one way to check a particular file is opened or closed. If the open() function opens a previously opened file, then an IOError will be generated. Another way to check a file is opened or closed is to check the values of the closed property of the file handler object. Using rename() function is another way to check the file is opened or closed. Different ways to check any file is opened or closed in Python have been shown in this tutorial.
Create a file for checking:
You can use any existing file or create a new file to test the example code shown in this tutorial. A new text file named clients.txt has been created with the following content to use later in the next part of the tutorial.
ID Name Email
01 Jony Liver jony@gmail.com
02 Manik Hossain manik@gmail.com
03 Neha Akter neha@gmail.com
04 Janatul Ferdous jannat@gmail.com
05 Helal Uddin helal@gmail.com
Example-1: Check the file is opened or not by using IOError
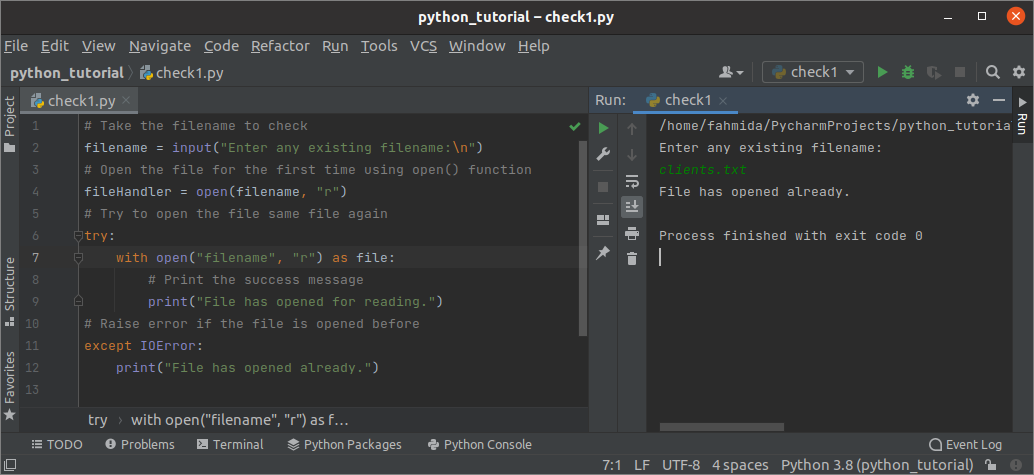
IOError generates when the open() function is called to open a file that has been opened before. Create a python file with the following script to check a file is opened or not by using try-except block. Here, any existing filename will be taken as input and opened for reading. Next, the open() function is called again to open the same file that will raise an IOError and print the error message.
# Take the filename to check
filename = input ( «Enter any existing filename: \n » )
# Open the file for the first time using open() function
fileHandler = open ( filename , «r» )
# Try to open the file same file again
try :
with open ( «filename» , «r» ) as file :
# Print the success message
print ( «File has opened for reading.» )
# Raise error if the file is opened before
except IOError :
print ( «File has opened already.» )
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. Here, clients.txt exists in the current location, and the error message, “File has opened already,” has printed for the IOError exception.
Example-2: Check the file is closed or not by using the closed property.
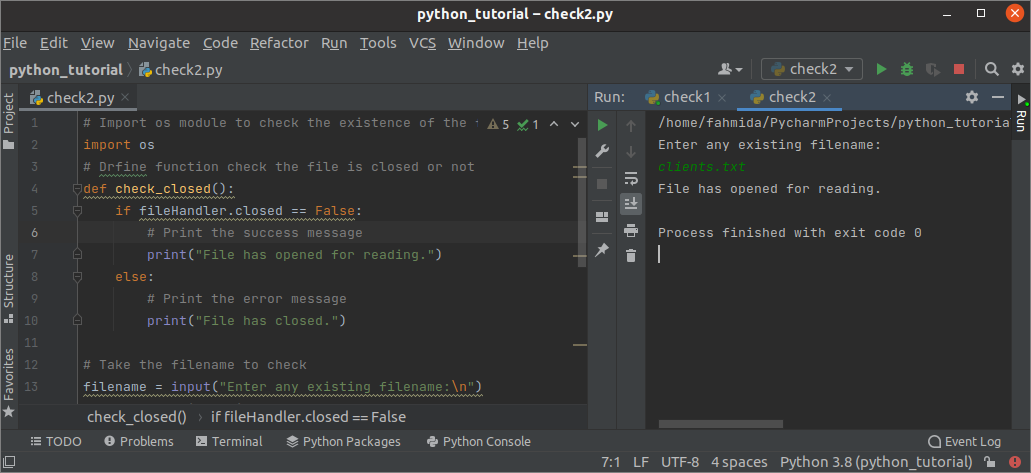
The value of the closed property will be true if any file is closed. Create a python file with the following script to check a file is closed or not that exists in the current location. The previous example script will generate an error if the filename taken from the user does not exist in the current location. This problem has solved in this example. The os module is used here to check the existence of the filename that will be taken from the user. The check_closed() function has defined to check the file is closed or not that will be called if the file exists.
# Import os module to check the existence of the file
import os
# Drfine function check the file is closed or not
def check_closed ( ) :
if fileHandler. closed == False :
# Print the success message
print ( «File has opened for reading.» )
else :
# Print the error message
print ( «File has closed.» )
# Take the filename to check
filename = input ( «Enter any existing filename: \n » )
# Check the file exist or not
if os . path . exists ( filename ) :
# Open the file for reading
fileHandler = open ( filename , «r» )
# Call the function
check_closed ( )
else :
# Print message if the file does not exist
print ( «File does not exist.» )
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. Here, clients.txt exists in the current location, and the success message, “File has opened for reading,” has printed because the value of the closed property returned False.
Example-3: Check the file is opened or not by using OSError
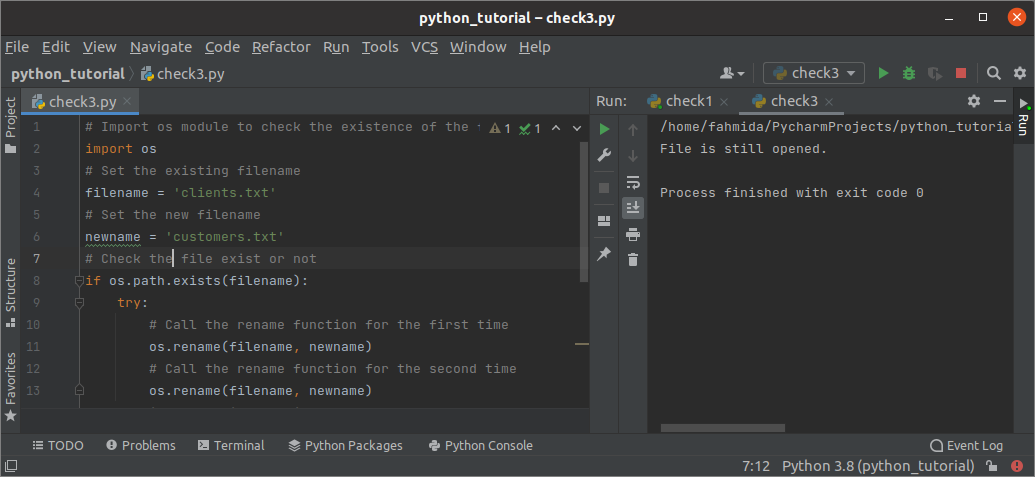
The OSError generates when the rename() function is called more than one time for a file that is opened already. Create a python file with the following script to check a file is opened or closed by using OSError. The os module has been used in the script to check the file’s existence and rename the file. When the rename() function is called for the second time, OSError will be generated, and the custom error message will be printed.
# Import os module to check the existence of the file
import os
# Set the existing filename
filename = ‘clients.txt’
# Set the new filename
newname = ‘customers.txt’
# Check the file exist or not
if os . path . exists ( filename ) :
try :
# Call the rename function for the first time
os . rename ( filename , newname )
# Call the rename function for the second time
os . rename ( filename , newname )
# Raise error if the file has opened
except OSError :
print ( «File is still opened.» )
else :
# Print message if the file does not exist
print ( «File does not exist.» )
Output:
The following output will appear after executing the above script. Here, clients.txt exists in the current location, and the error message, “File is still opened,” has printed because the OSError exception has generated when the second rename() function has been executed.
Conclusion:
When we need to work with the same file multiple times in a script, it is essential to know whether the file is opened or closed. It is better to call the close() function to close the file after completing the file operation. The error occurs when a file is opened for the second time in the same script without closing it. Different solutions to this problem have been shown in this tutorial by using simple examples to help the python users.
About the author
Fahmida Yesmin
I am a trainer of web programming courses. I like to write article or tutorial on various IT topics. I have a YouTube channel where many types of tutorials based on Ubuntu, Windows, Word, Excel, WordPress, Magento, Laravel etc. are published: Tutorials4u Help.