- Python Save Dictionary To File
- Table of contents
- How to save a dictionary to file in Python
- Example: save a dictionary to file
- Read Dictionary from a File
- Save a dictionary to a text file using the json module
- Save the dictionary to a CSV file
- About Vishal
- Related Tutorial Topics:
- Python Exercises and Quizzes
- save dictionary python
- save dictionary as csv file
- save dictionary to json file
- save dictionary to text file (raw, .txt)
- save dictionary to a pickle file (.pkl)
- Save Python Dictionary to a Pickle File
- How to write Python dictionary to a pickle file?
- Author
Python Save Dictionary To File
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to save a dictionary to a file in Python. Also, we’ll see how to read the same dictionary from a file.
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to:
- Use the pickle module to save the dictionary object to a file.
- Save the dictionary to a text file.
- Use the dump() method of a json module to write a dictionary in a json file.
- Write the dictionary to a CSV file.
Table of contents
How to save a dictionary to file in Python
Dictionaries are ordered collections of unique values stored in (Key-Value) pairs. The below steps show how to use the pickle module to save the dictionary to a file.
- Import pickle module The pickle module is used for serializing and de-serializing a Python object structure.
Pickling” is the process whereby a Python object is converted into a byte stream, and “unpickling” is the inverse operation whereby a byte stream (from a binary file) is converted back into an original object.
Example: save a dictionary to file
Let’s see the below example of how you can use the pickle module to save a dictionary to a person_data.pkl file.
import pickle # create a dictionary using <> person = print('Person dictionary') print(person) # save dictionary to person_data.pkl file with open('person_data.pkl', 'wb') as fp: pickle.dump(person, fp) print('dictionary saved successfully to file')Person dictionary dictionary saved successfully to file
Read Dictionary from a File
Now read the same dictionary from a file using a pickle module’s load() method.
import pickle # Read dictionary pkl file with open('person_data.pkl', 'rb') as fp: person = pickle.load(fp) print('Person dictionary') print(person)Save a dictionary to a text file using the json module
We can use the Python json module to write dictionary objects as text data into the file. This module provides methods to encode and decode data in JSON and text formats.
We will use the following two methods of a json module.
- The dump() method is used to write Python objects as JSON formatted data into a file.
- Using the load() method, we can read JSON data from text, JSON, or a binary file to a dictionary object.
Let’s see the below example of how you can use the json module to save a dictionary to a text file.
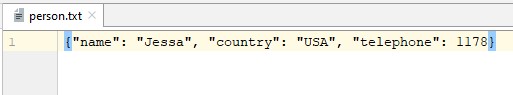
import json # assume you have the following dictionary person = print('Person dictionary') print(person) print("Started writing dictionary to a file") with open("person.txt", "w") as fp: json.dump(person, fp) # encode dict into JSON print("Done writing dict into .txt file")Person dictionary Started writing dictionary to a file Done writing dict into .txt file
Note: You can also use the dump() method to write a dictionary in a json file. Only you need to change the file extension to json while writing it.
Read a dictionary from a text file.
Now, let’s see how to read the same dictionary from the file using the load() function.
import json # Open the file for reading with open("person.txt", "r") as fp: # Load the dictionary from the file person_dict = json.load(fp) # Print the contents of the dictionary print(person_dict)Save the dictionary to a CSV file
The Python csv library provides functionality to read from and write to CSV files.
- Use the csv.DictReader() method to read CSV files into a dictionary.
- Use the csv.DictWriter() method to write a dictionary to a CSV file.
Example: Save the dictionary to a CSV file.
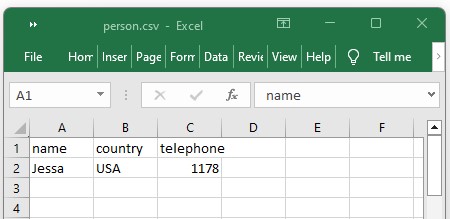
import csv # Dictionary to be saved person = print('Person dictionary') print(person) # Open a csv file for writing with open("person.csv", "w", newline="") as fp: # Create a writer object writer = csv.DictWriter(fp, fieldnames=person.keys()) # Write the header row writer.writeheader() # Write the data rows writer.writerow(person) print('Done writing dict to a csv file')Person dictionary Done writing dict to a csv file
Example: Read a dictionary from a csv file
import csv # Open the csv file for reading with open("person.csv", "r") as infile: # Create a reader object reader = csv.DictReader(infile) # Iterate through the rows for row in reader: print(row)OrderedDict([('name', 'Jessa'), ('country', 'USA'), ('telephone', '1178')]) Note: This will read the contents of the person.csv file and create a dictionary for each row in the file. You can then iterate through the rows and access the values in the dictionary using the column names as keys.
Did you find this page helpful? Let others know about it. Sharing helps me continue to create free Python resources.
About Vishal
I’m Vishal Hule, Founder of PYnative.com. I am a Python developer, and I love to write articles to help students, developers, and learners. Follow me on Twitter
Related Tutorial Topics:
Python Exercises and Quizzes
Free coding exercises and quizzes cover Python basics, data structure, data analytics, and more.
- 15+ Topic-specific Exercises and Quizzes
- Each Exercise contains 10 questions
- Each Quiz contains 12-15 MCQ
save dictionary python
How to make python save a dictionary to a file. These are small programs that allows you to create a dictionary and then, when running the program, it will create a file that contains the data in the original dictionary.
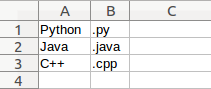
Given a dictionary such as:
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
- Comma seperated value file (.csv)
- Json file (.json)
- Text file (.txt)
- Pickle file (.pkl)
save dictionary as csv file
The csv module allows Python programs to write to and read from CSV (comma-separated value) files.
CSV is a common format used for exchanging data between applications. The module provides classes to represent CSV records and fields, and allows outputs to be formatted as CSV files.
In this format every value is separated between a comma, for instance like this:
Python,py,programming,
Bitmap,bmp,picture,
Sound,mp3,audio,
You can write it to a file with the csv module.
# load csv module
import csv
# define a dictionary with key value pairs
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# open file for writing, «w» is writing
w = csv.writer(open(«output.csv», «w»))
# loop over dictionary keys and values
for key, val in dict.items():
# write every key and value to file
w.writerow(Pickle python save dict)
The dictionary file (csv) can be opened in Google Docs or Excel
save dictionary to json file
Today, a JSON file has become more and more common to transfer data in the world. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format.
JSON is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate.
JSON is a text format that is completely language independent but uses conventions that are familiar to programmers of the C-family of languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python, and many others.
JSON was originally derived from the JavaScript scripting language, but it is not limited to any one programming language.
If you want to save a dictionary to a json file
# load json module
import json
# python dictionary with key value pairs
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# create json object from dictionary
json = json.dumps(dict)
# open file for writing, «w»
f = open(«dict.json»,«w»)
# write json object to file
f.write(json)
# close file
f.close()
save dictionary to text file (raw, .txt)
The program below writes a dictionary to an text string. It uses the str() call to convert the dictionary to a text string. While it is easy to write as a text string, this format makes it harder to read the file.
You can save your dictionary to a text file using the code below:
# define dict
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# open file for writing
f = open(«dict.txt»,«w»)
# write file
f.write( str(dict) )
# close file
f.close()
save dictionary to a pickle file (.pkl)
The pickle module may be used to save dictionaries (or other objects) to a file. The module can serialize and deserialize Python objects.
In Python, pickle is a built-in module that implements object serialization. It is both cross-platform and cross language, meaning that it can save and load objects between Python programs running on different operating systems, as well as between Python running on different platforms.
The pickle module is written entirely in Python, and is available in CPython implementations, such as Jython or IronPython. To enable the loading of pickles in other Python modules, pickle supports being executed from the command line.
The program below writes it to a pickle file.
# load pickle module
import pickle
# define dictionary
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# create a binary pickle file
f = open(«file.pkl»,«wb»)
# write the python object (dict) to pickle file
pickle.dump(dict,f)
# close file
f.close()
Save Python Dictionary to a Pickle File
Python objects can be saved (or serialized) as pickle files for later use. In this tutorial, we will look at how to save a Python dictionary as a pickle file with the help of some examples.
How to write Python dictionary to a pickle file?
You can use the Python pickle module’s dump() function to serialize a dictionary to a pickle file. The following is the syntax –
import pickle # save dictionary to pickle file with open('my_filename.pickle', 'wb') as file: pickle.dump(my_dict, file, protocol=pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL) It saves the object as a pickle file which you can later use.
Exercise caution when working with pickle files. The pickle module is not secure. Only unpickle data you trust. It is possible to construct malicious pickle data which will execute arbitrary code during unpickling. See here.
Let’s look at some examples of using the above syntax –
For example, you have a dictionary storing the names to department mappings of employees in an office. You want to save this information in a pickle file so that it can be used later.
import pickle # create a dictionary employees = < "Jim": "Sales", "Dwight": "Sales", "Angela": "Accounting" ># save dictionary to pickle file with open("employee_info.pickle", "wb") as file: pickle.dump(employees, file, pickle.HIGHEST_PROTOCOL) The above code saves the dictionary employees to the file employee_info.pickle in our current working directory.
You can also deserialize a pickle file to get back your object using the pickle module. Use the pickle.load() function.
Let’s read the same dictionary from its pickle file that we saved above.
# laod a pickle file with open("employee_info.pickle", "rb") as file: loaded_dict = pickle.load(file) # display the dictionary print(loaded_dict) We get our original dictionary with all its content loaded from its pickle file.
You might also be interested in –
Subscribe to our newsletter for more informative guides and tutorials.
We do not spam and you can opt out any time.
Author
Piyush is a data professional passionate about using data to understand things better and make informed decisions. He has experience working as a Data Scientist in the consulting domain and holds an engineering degree from IIT Roorkee. His hobbies include watching cricket, reading, and working on side projects. View all posts