- JSON PHP
- The PHP File
- PHP file
- The Client JavaScript
- Example
- PHP Array
- PHP file
- The Client JavaScript
- Example
- PHP Database
- Example
- Example explained:
- PHP file
- PHP File explained:
- Use the Data
- Example
- PHP Method = POST
- Example
- PHP file
- How to display data from JSON to HTML table using PHP?
- emp_records.json
- JSON-to-HTML.php
- tblClasses.css
- How to Parse JSON in PHP
- Reading JSON From a File or String in PHP
- doctor Brain
- json_decode
- Преобразование JSON в объект
- Преобразование JSON в ассоциативный массив
- Заключение
- Новые публикации
- JavaScript: сохраняем страницу в pdf
- HTML: Полезные примеры
- CSS: Ускоряем загрузку страницы
- JavaScript: 5 странностей
- JavaScript: конструктор сортировщиков
- Категории
- О нас
JSON PHP
A common use of JSON is to read data from a web server, and display the data in a web page.
This chapter will teach you how to exchange JSON data between the client and a PHP server.
The PHP File
PHP has some built-in functions to handle JSON.
Objects in PHP can be converted into JSON by using the PHP function json_encode() :
PHP file
The Client JavaScript
Here is a JavaScript on the client, using an AJAX call to request the PHP file from the example above:
Example
Use JSON.parse() to convert the result into a JavaScript object:
const xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() const myObj = JSON.parse(this.responseText);
document.getElementById(«demo»).innerHTML = myObj.name;
>
xmlhttp.open(«GET», «demo_file.php»);
xmlhttp.send();
PHP Array
Arrays in PHP will also be converted into JSON when using the PHP function json_encode() :
PHP file
The Client JavaScript
Here is a JavaScript on the client, using an AJAX call to request the PHP file from the array example above:
Example
Use JSON.parse() to convert the result into a JavaScript array:
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() const myObj = JSON.parse(this.responseText);
document.getElementById(«demo»).innerHTML = myObj[2];
>
xmlhttp.open(«GET», «demo_file_array.php», true);
xmlhttp.send();
PHP Database
PHP is a server side programming language, and can be used to access a database.
Imagine you have a database on your server, and you want to send a request to it from the client where you ask for the 10 first rows in a table called «customers».
On the client, make a JSON object that describes the numbers of rows you want to return.
Before you send the request to the server, convert the JSON object into a string and send it as a parameter to the url of the PHP page:
Example
Use JSON.stringify() to convert the JavaScript object into JSON:
const limit = <"limit":10>;
const dbParam = JSON.stringify(limit);
xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() document.getElementById(«demo»).innerHTML = this.responseText;
>
xmlhttp.open(«GET»,»json_demo_db.php?x=» + dbParam);
xmlhttp.send();
Example explained:
- Define an object containing a «limit» property and value.
- Convert the object into a JSON string.
- Send a request to the PHP file, with the JSON string as a parameter.
- Wait until the request returns with the result (as JSON)
- Display the result received from the PHP file.
Take a look at the PHP file:
PHP file
header(«Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8»);
$obj = json_decode($_GET[«x»], false);
$conn = new mysqli(«myServer», «myUser», «myPassword», «Northwind»);
$stmt = $conn->prepare(«SELECT name FROM customers LIMIT ?»);
$stmt->bind_param(«s», $obj->limit);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->get_result();
$outp = $result->fetch_all(MYSQLI_ASSOC);
PHP File explained:
- Convert the request into an object, using the PHP function json_decode() .
- Access the database, and fill an array with the requested data.
- Add the array to an object, and return the object as JSON using the json_encode() function.
Use the Data
Example
xmlhttp.onload = function() <
const myObj = JSON.parse(this.responseText);
let text = «»;
for (let x in myObj) <
text += myObj[x].name + «
«;
>
document.getElementById(«demo»).innerHTML = text;
>
PHP Method = POST
When sending data to the server, it is often best to use the HTTP POST method.
To send AJAX requests using the POST method, specify the method, and the correct header.
The data sent to the server must now be an argument to the send() method:
Example
const dbParam = JSON.stringify(<"limit":10>);
const xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onload = function() const myObj = JSON.parse(this.responseText);
let text =»»;
for (let x in myObj) text += myObj[x].name + «
«;
>
document.getElementById(«demo»).innerHTML = text;
>
xmlhttp.open(«POST», «json_demo_db_post.php»);
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader(«Content-type», «application/x-www-form-urlencoded»);
xmlhttp.send(«x=» + dbParam);
The only difference in the PHP file is the method for getting the transferred data.
PHP file
Use $_POST instead of $_GET:
header(«Content-Type: application/json; charset=UTF-8»);
$obj = json_decode($_POST[«x»], false);
$conn = new mysqli(«myServer», «myUser», «myPassword», «Northwind»);
$stmt = $conn->prepare(«SELECT name FROM customers LIMIT ?»);
$stmt->bind_param(«s», $obj->limit);
$stmt->execute();
$result = $stmt->get_result();
$outp = $result->fetch_all(MYSQLI_ASSOC);
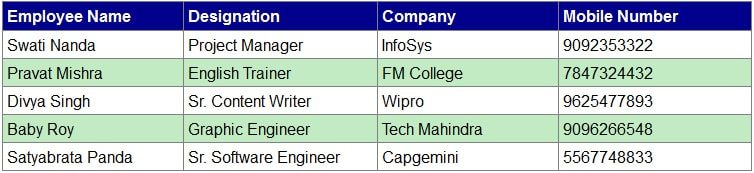
How to display data from JSON to HTML table using PHP?
JSON is a platform independent data inter-exchange technology. Like a database using JSON we can store and retrieve data. In this demo app let me show you how to fetch data from JSON to HTML table using PHP. To start with first let me create a valid JSON file as shown in below.
emp_records.json
, < "empName": "Pravat Mishra", "designation": "English Trainer", "company": "FM College", "mob": "7847324432" >, < "empName": "Divya Singh", "designation": "Sr. Content Writer", "company": "Wipro", "mob": "9625477893" >, < "empName": "Baby Roy", "designation": "Graphic Engineer", "company": "Tech Mahindra", "mob": "9096266548" >, < "empName": "Satyabrata Panda", "designation": "Sr. Software Engineer", "company": "Capgemini", "mob": "5567748833" >] >
Now create your PHP file with the below line of Codes.
JSON-to-HTML.php
/*Fetching JSON file content using php file_get_contents method*/ $str_data = file_get_contents("emp-records.json"); $data = json_decode($str_data, true); /*Initializing temp variable to design table dynamically*/ $temp = "| Employee Name | "; $temp .= "Designation | "; $temp .= "Company | "; $temp .= "Mobile Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| " . $data["employees"][$i]["empName"] . " | "; $temp .= "" . $data["employees"][$i]["designation"] . " | "; $temp .= "" . $data["employees"][$i]["company"] . " | "; $temp .= "" . $data["employees"][$i]["mob"] . " | "; $temp .= "
In the above codes first I am fetching the JSON file using file_get_contents() method. Then after I am decoding the JSON data and storing in a data variable. Temp is the variable which I used to generate dynamic html for table. Using string concatenation I am appending html and $data values to $temp. Finally using using echo I am printing the value of $temp.
Inside the table to Create dynamic rows I am using a for loop over total records count. To get total record count here I am using sizeof() method against $data[“employees”]. Then depending upon JSON record columns I am binding respective values to td’s.
tblClasses.css
/*Style for Table*/ table, th , td < border: 1px solid grey; border-collapse: collapse; padding: 4px; font-family: arial; >/*Style for Table Header*/ th < background: darkblue; color: white; text-align: left; >/*Style for Alternate Rows*/ table tr:nth-child(odd) < background-color: #C2EBC3; >table tr:nth-child(even)
Without the above CSS code this demo app will run. But to make your table beautiful this CSS classes can help. Just copy paste these classes under style tag. This will give you a table as shown in the above figure.
How to Parse JSON in PHP
Monty Shokeen Last updated May 31, 2021
JSON, short for JavaScript Object Notation, is a common lightweight format for storing and exchanging information. As the name suggests, it was initially derived from JavaScript, but it is a language-independent format for storing information. A lot of languages like PHP now implement functions to read and create JSON data.
This tutorial will teach you how to read a JSON file and convert it to an array in PHP. Learn how to parse JSON using the json_decode() and json_encode() functions.
Reading JSON From a File or String in PHP
Let’s say you have a file which contains information in JSON format. How do you access and store it in PHP?
First, you need to get the data from the file into a variable by using file_get_contents() . Once the data is in a string, you can call the json_decode() function to extract information from the string. Keep in mind that JSON simply provides a way to store information as a string using a set of predefined rules. It is our job to decode the strings properly and get the information we want.
The json_decode() function accepts four parameters, but you will only need the first two in most situations. The first parameter specifies the string that you want to decode. The second parameter determines how the decoded data is returned. Setting it to true will return an associative array, and false will return objects. Here is a basic example. We have a file called people.json with the following contents:
doctor Brain
Независимо от того, каким образом получены данные в формате JSON: в виде файла *.json переданного из стороннего API или входящей строки, нативный PHP, начиная с версии 5.2.0, предоставляет две замечательные функции json_encode и json_decode . Сегодня мы обратим внимание на функцию json_decode , которая позволяет преобразовать данные JSON в формат, пригодный для дальнейшей работы.
Итак, для начала нам нужны какие-то JSON-данные, и мы получим их, благодаря генератору случайных данных Mockaroo.
json_decode
Преобразование JSON в объект
Входящие JSON-данные всгеда являются строкой, как же их преобразовать? Посмотрим на код приведенный ниже:
$json = '[< "id": 1, "first_name": "Bertrando", "last_name": "Pedrollo", "email": "bpedrollo0@homestead.com", "gender": "Male", "ip_address": "62.137.20.86" >, < "id": 2, "first_name": "Pier", "last_name": "Winkworth", "email": "pwinkworth1@mit.edu", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "158.139.30.200" >, < "id": 3, "first_name": "Joyous", "last_name": "Glascott", "email": "jglascott2@smh.com.au", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "146.147.52.106" >, < "id": 4, "first_name": "Daniela", "last_name": "Hawes", "email": "dhawes3@timesonline.co.uk", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "148.153.203.134" >]'; $decodedJson = json_decode($json); var_dump($decodedJson); После преобразования JSON-данных с помощью функции json_decode , мы вывели их на странцу. Можно увидеть, что полученный результат — массив объектов (stdClass):
array(4) < [0]=>object(stdClass)#1 (6) < ["id"]=>int(1) ["first_name"]=> string(9) "Bertrando" ["last_name"]=> string(8) "Pedrollo" ["email"]=> string(24) "bpedrollo0@homestead.com" ["gender"]=> string(4) "Male" ["ip_address"]=> string(12) "62.137.20.86" > [1]=> object(stdClass)#2 (6) < ["id"]=>int(2) ["first_name"]=> string(4) "Pier" ["last_name"]=> string(9) "Winkworth" ["email"]=> string(19) "pwinkworth1@mit.edu" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(14) "158.139.30.200" > [2]=> object(stdClass)#3 (6) < ["id"]=>int(3) ["first_name"]=> string(6) "Joyous" ["last_name"]=> string(8) "Glascott" ["email"]=> string(21) "jglascott2@smh.com.au" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(14) "146.147.52.106" > [3]=> object(stdClass)#4 (6) < ["id"]=>int(4) ["first_name"]=> string(7) "Daniela" ["last_name"]=> string(5) "Hawes" ["email"]=> string(25) "dhawes3@timesonline.co.uk" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(15) "148.153.203.134" > > Теперь мы можем получить нужные данные из переменной decodedJson, использую синтаксис для работы с объектами:
echo $decodedJson[0]->first_name . " " . $decodedJson[0]->last_name; echo "
"; echo $decodedJson[1]->first_name . " " . $decodedJson[1]->last_name; // Результат: // Bertrando Pedrollo // Pier Winkworth Преобразование JSON в ассоциативный массив
Для того, чтобы результатом преобразования JSON-данных с помощью функции jsin_decode стал ассоциативный массив, а не объект (stdClass), нужно добавить второй параметр $assoc равный true (по умолчанию его значение — false).
$json = '[< "id": 1, "first_name": "Bertrando", "last_name": "Pedrollo", "email": "bpedrollo0@homestead.com", "gender": "Male", "ip_address": "62.137.20.86" >, < "id": 2, "first_name": "Pier", "last_name": "Winkworth", "email": "pwinkworth1@mit.edu", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "158.139.30.200" >, < "id": 3, "first_name": "Joyous", "last_name": "Glascott", "email": "jglascott2@smh.com.au", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "146.147.52.106" >, < "id": 4, "first_name": "Daniela", "last_name": "Hawes", "email": "dhawes3@timesonline.co.uk", "gender": "Female", "ip_address": "148.153.203.134" >]'; $decodedJson = json_decode($json, true); var_dump($decodedJson); array(4) < [0]=>array(6) < ["id"]=>int(1) ["first_name"]=> string(9) "Bertrando" ["last_name"]=> string(8) "Pedrollo" ["email"]=> string(24) "bpedrollo0@homestead.com" ["gender"]=> string(4) "Male" ["ip_address"]=> string(12) "62.137.20.86" > [1]=> array(6) < ["id"]=>int(2) ["first_name"]=> string(4) "Pier" ["last_name"]=> string(9) "Winkworth" ["email"]=> string(19) "pwinkworth1@mit.edu" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(14) "158.139.30.200" > [2]=> array(6) < ["id"]=>int(3) ["first_name"]=> string(6) "Joyous" ["last_name"]=> string(8) "Glascott" ["email"]=> string(21) "jglascott2@smh.com.au" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(14) "146.147.52.106" > [3]=> array(6) < ["id"]=>int(4) ["first_name"]=> string(7) "Daniela" ["last_name"]=> string(5) "Hawes" ["email"]=> string(25) "dhawes3@timesonline.co.uk" ["gender"]=> string(6) "Female" ["ip_address"]=> string(15) "148.153.203.134" > > Теперь, для того чтобы получить необходимые данные, нужно использовать синтаксис для работы с массивами:
echo $decodedJson[0]["first_name"] . " " . $decodedJson[0]["last_name"]; echo "
"; echo $decodedJson[1]["first_name"] . " " . $decodedJson[1]["last_name"]; // Результат: // Bertrando Pedrollo // Pier Winkworth Заключение
Примеры, разбираемые в данной статье, в очередной раз демонстрируют наличие в PHP великолепных нативных функций и замечательной документации. Не поленитесь изучить дополнительную информацию о json_decode на официальном сайте.
Новые публикации
JavaScript: сохраняем страницу в pdf
HTML: Полезные примеры
CSS: Ускоряем загрузку страницы
JavaScript: 5 странностей
JavaScript: конструктор сортировщиков
Категории
О нас
Frontend & Backend. Статьи, обзоры, заметки, код, уроки.
© 2021 dr.Brain .
мир глазами веб-разработчика