Environment Variables in PHP
The most effective practice for application setup is by using PHP environment variables, whether its database credentials, secret data parameters, API keys, or anything between deploys are now visible to code through the environment. The PHP environment variable allows developers to gather specific types of data from existing servers dynamically. In this tutorial, you will learn how to use PHP environment variables and what their features are.
PHP Environment Variables
Various PHP frameworks such as Laravel, Symfony, and others use the PHP environment variable itself to store different security-related credentials and other configurations. An ENV var or environment variable is nothing but a key-value pair used in the global scope. These variables are explicitly stored for each environment. In other words, an environment variable can be defined as a dynamic-named variable that is provided in a program for affecting the way successively running processes will work in a system.
These variables are brought into the global namespace of PHP from the environment under which the PHP runs its parser. Many of them are provided by the shell under which PHP runs with different systems that are likely to run different kinds of shells. Other environment variables include the CGI variables, irrespective of whether they are running as a server module or as a CGI processor in PHP.
More About PHP Environment Variables
As a process starts in a program, it uses its defined variables or inherits from the parent process. These variables are used for discovering facts about the environment on which it is running. These variables include details about the preferred location where the temporary files are being saved or the path where the home directory resides within the system.
If you use a Unix operating system such as Linux, you can see this by typing the value of the $HOME environment variable in the terminal:
Command:
Result:
In case, you use the Windows OS; you have to open PowerShell and use the command:
Command:
Result:
Example of Using Environment Variables in PHP
He output will look something like:
Why $_ENV Is Empty
I want to use $_ENV so that I can get the username of the logged-in user, but it is empty?
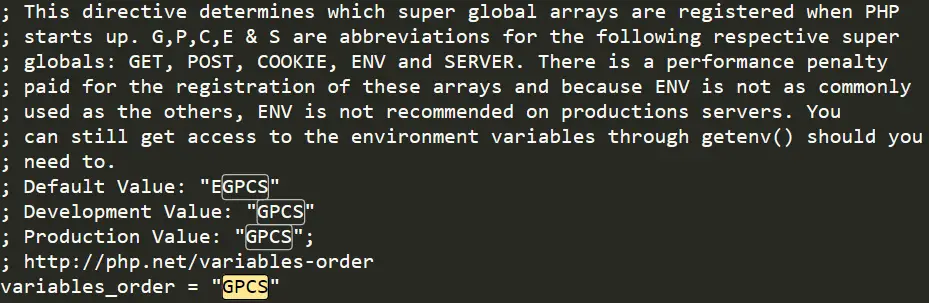
Everyone should use the getenv() function instead, but if you require $_ENV, you need to do so. To use $_ENV, you must activate it in your php.ini file. Find «variable_orders» and set it to:
Setting Environment Variables
Let us now discuss how to set an environment variable so that it can be made accessible from your PHP application.
Result:
But in case you want to include your variables in a PHP program, the simplest way to do this is to state the environment variable well before your run command, something like this:
» APP_ENV=local php -r 'var_dump(getenv("APP_ENV"));' Result:
Another well-known &convenient approach used in Unix systems is to make use of the «export» command. When the’export’ is used with an environment variable, it will be available in all successive commands until the shell exits.
» php -r ‘var_dump(getenv(«APP_ENV»));’
Result:
Related Functions of PHP Environment Variable
- getenv() is a PHP function used for returning the specific environment variable’s value
- putenv() is a PHP function that is used for setting the value of a particular environment variable
$_ENV
An associative array of variables passed to the current script via the environment method.
These variables are imported into PHP’s global namespace from the environment under which the PHP parser is running. Many are provided by the shell under which PHP is running and different systems are likely running different kinds of shells, a definitive list is impossible. Please see your shell’s documentation for a list of defined environment variables.
Other environment variables include the CGI variables, placed there regardless of whether PHP is running as a server module or CGI processor.
Examples
Example #1 $_ENV example
Assuming «bjori» executes this script
The above example will output something similar to:
Notes
Note:
This is a ‘superglobal’, or automatic global, variable. This simply means that it is available in all scopes throughout a script. There is no need to do global $variable; to access it within functions or methods.
See Also
User Contributed Notes 2 notes
If your $_ENV array is mysteriously empty, but you still see the variables when calling getenv() or in your phpinfo(), check your http://us.php.net/manual/en/ini.core.php#ini.variables-order ini setting to ensure it includes «E» in the string.
Please note that writing to $_ENV does not actually set an environment variable, i.e. the variable will not propagate to any child processes you launch (except forked script processes, in which case it’s just a variable in the script’s memory). To set real environment variables, you must use putenv().
Basically, setting a variable in $_ENV does not have any meaning besides setting or overriding a script-wide global variable. Thus, one should never modify $_ENV except for testing purposes (and then be careful to use putenv() too, if appropriate).
PHP will not trigger any kind of error or notice when writing to $_ENV.