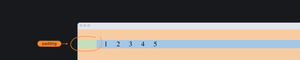
padding
Внутренний отступ, от края элемента до вложенного в него контента.
Время чтения: меньше 5 мин
Кратко
Скопировать ссылку «Кратко» Скопировано
Свойство padding — или внутренний отступ — позволяет оттолкнуть контент от границ родительского элемента.
Само свойство padding это шорткат, позволяющий задать отступы сразу со всех четырёх сторон.
Можно управлять отступами по отдельности при помощи свойств padding — top , padding — left , padding — right , padding — bottom .
Или при помощи логических свойств padding — block , padding — block — start , padding — block — end , padding — inline , padding — inline — start , padding — inline — end .
Пример
Скопировать ссылку «Пример» Скопировано
Сублимация, как бы это ни казалось парадоксальным, .
div class="parent"> p class="content">Сублимация, как бы это ни казалось парадоксальным, . p> div>
Для наглядности зададим фон родителю:
.parent background-color: #2E9AFF;>.parent background-color: #2E9AFF; >
🛠 Попробуй менять размеры окна браузера и понаблюдать за поведением обоих блоков. Первый будет всегда сохранять пропорции 16:9, а вот второй всегда будет высотой 200 пикселей.
Таблица значений padding-bottom для разных стандартных соотношений сторон:
padding
CSS свойство padding устанавливает расстояние (его также называют «внутренний отступ») между внутренним краем рамки элемента и его содержимым. Обратите внимание, что добавление внутренних полей будет влиять на общий размер элемента.
Свойство padding обеспечивает краткий метод установки значений сразу нескольких свойств внутреннего отступа в одном объявлении. Оно может содержать от одного до четырех значений, разделяемых между собой пробелами. Если указывается более одного значения, внутренний отступ устанавливается начиная с верхней позиции:
Визуальный эффект зависит от количества заданных значений:
| Количество значений | Результат |
|---|---|
| 4 значения | Значения устанавливаются сразу для четырех внутренних полей. В этом случае они будут идти в определенном порядке: первое значение относится к верхнему полю, второе к правому, третье к нижнему, четвертое к левому. |
| 3 значения | Первое значение устанавливает внутреннее поле сверху, второе — одновременно слева и справа, а третье — снизу. |
| 2 значения | Первое значение устанавливает внутренние поля сверху и снизу, второе — слева и справа от содержимого. |
| 1 значение | Поля будут установлены одновременно со всех сторон, при этом ширина всех полей будет одинаковая. |
Отрицательные значения внутренних полей не допускаются.
Имейте ввиду, когда вертикальный внутренний отступ используется для строчного элемента, это может вызвать перекрытие элементов, расположенных выше или ниже этого элемента, в тех случаях, когда внутренний отступ элемента превышает высоту строки.
Примечание: для установки внутренних полей отдельно для каждой стороны элемента, используйте следующие свойства: padding-top, padding-bottom, padding-left, padding-right.
| Значение по умолчанию: | 0 |
|---|---|
| Применяется: | ко всем элементам кроме тех, которые относятся к типу display: table-row-group, table-header-group, table-footer-group, table-row, table-column-group и table-column |
| Анимируется: | да |
| Наследуется: | нет |
| Версия: | CSS1 |
| Синтаксис JavaScript: | object.style.padding=»10px 5px» |
Синтаксис
padding: [размер | проценты] | inherit;
Значения свойства
| Значение | Описание |
|---|---|
| размер | Определяет размер внутреннего поля в единицах измерения, используемых в CSS. |
| % | Величина, указанная в процентах, вычисляется в зависимости от ширины области содержимого родительского элемента. |
| inherit | Указывает, что значение наследуется от родительского элемента. |
CSS Padding
Padding is used to create space around an element’s content, inside of any defined borders.
CSS Padding
The CSS padding properties are used to generate space around an element’s content, inside of any defined borders.
With CSS, you have full control over the padding. There are properties for setting the padding for each side of an element (top, right, bottom, and left).
Padding — Individual Sides
CSS has properties for specifying the padding for each side of an element:
All the padding properties can have the following values:
- length — specifies a padding in px, pt, cm, etc.
- % — specifies a padding in % of the width of the containing element
- inherit — specifies that the padding should be inherited from the parent element
Note: Negative values are not allowed.
Example
Set different padding for all four sides of a element:
Padding — Shorthand Property
To shorten the code, it is possible to specify all the padding properties in one property.
The padding property is a shorthand property for the following individual padding properties:
If the padding property has four values:
- padding: 25px 50px 75px 100px;
- top padding is 25px
- right padding is 50px
- bottom padding is 75px
- left padding is 100px
Example
Use the padding shorthand property with four values:
If the padding property has three values:
- padding: 25px 50px 75px;
- top padding is 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
- bottom padding is 75px
Example
Use the padding shorthand property with three values:
If the padding property has two values:
- padding: 25px 50px;
- top and bottom paddings are 25px
- right and left paddings are 50px
Example
Use the padding shorthand property with two values:
If the padding property has one value:
Example
Use the padding shorthand property with one value:
Padding and Element Width
The CSS width property specifies the width of the element’s content area. The content area is the portion inside the padding, border, and margin of an element (the box model).
So, if an element has a specified width, the padding added to that element will be added to the total width of the element. This is often an undesirable result.
Example
Here, the element is given a width of 300px. However, the actual width of the element will be 350px (300px + 25px of left padding + 25px of right padding):
To keep the width at 300px, no matter the amount of padding, you can use the box-sizing property. This causes the element to maintain its actual width; if you increase the padding, the available content space will decrease.
Example
Use the box-sizing property to keep the width at 300px, no matter the amount of padding:
More Examples
Set the left padding
This example demonstrates how to set the left padding of aelement.
Set the right padding
This example demonstrates how to set the right padding of aelement.
Set the top padding
This example demonstrates how to set the top padding of aelement.
Set the bottom padding
This example demonstrates how to set the bottom padding of aelement.
All CSS Padding Properties
Property Description padding A shorthand property for setting all the padding properties in one declaration padding-bottom Sets the bottom padding of an element padding-left Sets the left padding of an element padding-right Sets the right padding of an element padding-top Sets the top padding of an element