- Overloading in PHP
- PHP’s Overloading
- Dynamic Entities on PHP Overloading
- PHP’s Overloading Types
- Property Overloading
- Example: PHP Property Overloading
- Method Overloading
- PHP example for Method Overloading
- Method Overloading in PHP
- How does Method Overloading work in PHP?
- Examples of Method Overloading in PHP
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Example #5
- Example #6
- Example #7
- Example #8
- Example #9
- Recommended Articles
Overloading in PHP
We are going to see a surprise in this PHP tutorial. We all know about overloading and it is a basic concept in OOPS and we have beaten it enough in our colleges. We have operator overloading, function overloading etc.
When different operations are performed using the same operator, then it is called operator overloading. Similarly, if we define functions having an identical name but different set of arguments, then it is called function overloading.
In PHP we have to overload. A lot of people say different things like we do not have to overload in PHP or there is only partial support for overloading in PHP and what PHP does is not overloading.
So what is my take? I am going to go by PHP bible, the php.net manual. Following is what the PHP manual says about overloading,
PHP’s interpretation of “overloading” is different than most object oriented languages. Overloading traditionally provides the ability to have multiple methods with the same name but different quantities and types of arguments.
This is kind or tricky, it says PHP’s interpretation. There is for sure something muddy here. I would say, let us not worry about whether it is the traditional OOPS overloading or not and just skip to PHP’s overloading 😉
PHP’s Overloading
PHP’s overloading is to create dynamic entities. In this tutorial, we will understand about those dynamic entities, how they are created and how to access them.
Dynamic Entities on PHP Overloading
Properties and methods are those entities created dynamically by using PHP overloading. After creating an object for a class, we can access set of entities, that are, properties or methods not defined within the scope of the class.
Such entities are said to be overloaded properties or methods, and the process is called as overloading.
For working with these overloaded properties or functions, PHP magic methods are used. Most of the magic methods will be triggered in object context except __callStatic() method which is used in static context.
PHP’s Overloading Types
Overloading in PHP can be classified as,
Property Overloading
PHP property overloading allows us to create dynamic properties in the object context. For creating those properties no separate line of code is needed. A property associated with the class instance, and it is not declared within the scope of the class, is considered as overloaded property.
We can perform the following operations with overloaded properties in PHP.
- Setting and getting overloaded properties.
- Evaluating overloaded properties setting.
- Undo such properties setting.
Before performing the above three operations, we should define appropriate magic methods. Those methods are,
- __set() – triggered while initializing overloaded properties.
- __get() – triggered while using overloaded properties with PHP print statements.
- __isset() – This magic method is invoked when we check overloaded properties with isset() function
- __unset() – Similarly, this function will be invoked on using PHP unset() for overloaded properties.
Example: PHP Property Overloading
This PHP example is to create property array elements dynamically.
str[$name] = $value; > public function __get($name) < echo "Overloaded Property name = " . $this->str[$name] . "
"; > public function __isset($name) < if (isset($this->str[$name])) < echo "Property \$$name is set.
"; > else < echo "Property \$$name is not set.
"; > > public function __unset($name) < unset($this->str[$name]); echo "\$$name is unset
"; > > $objToys = new Toys(); /* setters and getters on dynamic properties */ $objToys->overloaded_property = "new"; echo $objToys->overloaded_property . "\n\n"; /* Operations with dynamic properties values */ isset($objToys->overloaded_property); unset($objToys->overloaded_property); isset($objToys->overloaded_property); ?> In the above example PHP program, the dynamic property is created. While initializing this dynamic property, __set() is invoked with name and value pair to be initialized as the name and value of class property array element $str.
Added to that, isset() and unset() with overloaded property will trigger __isset() and __unset() magic methods. After unset(), if we call isset(), then it will print “property not set” message to the browser.
Method Overloading
This type of overloading is for creating dynamic methods that are not declared within the class scope. PHP method overloading also triggers magic methods dedicated for the appropriate purpose.
Unlike property overloading, PHP method overloading allows function call in both object and static context. The related magic functions are,
- __call() – triggered while invoking overloaded methods in the object context.
- __callStatic() – triggered while invoking overloaded methods in static context.
PHP example for Method Overloading
Let us call the undefined class function with both object reference and with the class name itself. For accessing function from outside class with the name of the class itself, it should be a static member of that class.
So accessing some overloaded method with the name of the class will trigger static magic member defined within the class. For example,
"; > public static function __callStatic($name, $param) < echo "Magic method invoked while method overloading with static access
"; > > $objToys = new Toys(); $objToys->overloaded_method(); Toys::overloaded_property(); ?> Method Overloading in PHP
Method Overloading is one type of Overloading other than Property Overloading. It is to create one/many dynamic methods not created within that class scope/scope. PHP method overloading concept also helps trigger the magic methods dictated for the appropriate purpose. Apart from the property overloading concept, the PHP method’s overloading concept allows function call/calls on both the object and the static context. Basically is one of the methods of OOPs.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Public _call (string $name1 , array $arguments1 ) : mixed Public static _callStatic (string $name1 , array $arguments1 ) : mixedHow does Method Overloading work in PHP?
Method Overloading works with the declaration inside the class by creating dynamic methods. It also works by triggering some magic methods for an appropriate purpose and calls function/function calls on both the static context and the object. Method Overloading concept is also fine with most other programming languages like c, java, etc. We refer to Method Overloading as static polymorphism.
There are some of the magic functions, they are:
- _call(): An object’s context can trigger the execution of overloaded methods using the call() function.
- _callStatic(): The callstatic() magic function activates the overloaded concepts/methods in the static context.
Examples of Method Overloading in PHP
Here are the examples of Method Overloading in PHP mentioned below
Example #1
The $name1 argument, in the below PHP programming language, is the name of the method to be called, whereas $arguments are one of the enumerated arrays containing the parameters/arguments used to pass to the $name’ ed method.
_call() function used using 2 parameters $name1 and $arguments1. Implode() function returns a string from the array elements, i.e., from the string/sentence. In Implode(separator, array), the separator is the optional parameter, but it is just a recommendation to use both parameters for backward compatibility. The specific type of separator in the separator parameter will insert a separator to the words/strings present in the array parameter.
The Obj variable will create a new object called SPK. Obj-> will help to access the object’s methods and properties. Spk will execute from the static context, whereas the obj will run from the object context.
public static function __callStatic($name1, $arguments1) < echo "static method Calling '$name1' " . implode(', ', $arguments1). "\n"; >> // Create new object $obj = new SPK; $obj->runTest('in one of the object context'); SPK::runTest('in one of the static context'); ?>Example #2
The code example defines the foo1 class with a single _call() function that executes the die() function to display a message and terminate the current PHP script. Die() is the same as the exit() function, which accepts just one parameter inside its parenthesis.
Foo1-> will help to access the object’s methods and properties from the variable $foo1.
> $foo1 = new Foo1; print $foo1->(); // outputs ' wow !' ?>Example #3
This is an example of method overloading in the PHP programming language using the call() function and private/protected methods.
Here calling the private/protected methods is done by accessing by the typo or something etc.
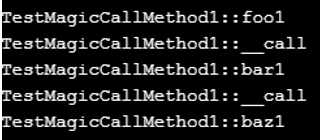
Echo _METHOD_PHP_EOL will return what type of method is used. It uses only the _call() function, which runs from the object context.
public function __call($method1, $args1) < echo __METHOD__.PHP_EOL; if(method_exists($this, $method1)) < $this->$method1(); > > protected function bar1() < echo __METHOD__.PHP_EOL; >private function baz1() < echo __METHOD__.PHP_EOL; >> $test = new TestMagicCallMethod1(); $test->foo1(); $test->bar1(); $test->baz1(); ?>Example #4
This is the program of call() and call static() functions concept, which is used for the method overloading concept. This PHP program below will first call the _call() function before the _callstatic() function in the instance.
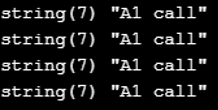
Var dump() will provide information about the variable in the parenthesis in PHP & some of the other object-oriented programming languages. Other than that, everything is the same, just like the above examples.
who(); > public static function __callStatic($a1, $b1) < var_dump('A1 static'); >public function __call($a1, $b1) < var_dump('A1 call'); >> $a1 = new A1; $a1->test1(); ?>Example #5
This is the example of the _call() function; if the object’s class is called with the method, which doesn’t even exist, then the _call() function’s concept is called instead of the method.
Execute the _call() function to support the concept of method overloading through the dynamic area() method included in the PHP program below. The object’s behavior will vary depending on the parameters that pass to it.
> > $circle1 = new Shape1(); echo $circle1->area1(3); $rect1 = new Shape1(); echo $rect1->area1(8,6); ?>Example #6
Here, the _call() and _callstatic() functions are used like in the 1 st example.
public static function __callStatic($name1,$pavan1) < echo "Magic method invoked while method overloading with static access"; >> $objToys1 = new Toys1; $objToys1->overloaded_method(); Toys1::overloaded_property(); ?>Example #7
The call () function of method Overloading triggered and invoked the inaccessible methods in the object context. Call() is mixed with the syntax _call(string $name1 , array $arguments1).
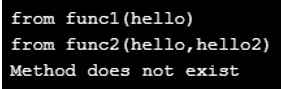
Then $name1 parameter is for the name of the method which is to be called, whereas the array $arguments1 is the parameter that is an enumerated array that contains/has the parameters which are to be passed to the $name variables method.
if (count($arguments1) === 2) < $this->displayMessage12($arguments1[0],$arguments1[1]); > elseif (count($arguments1) === 1) < $this->displayMessage11($arguments1[0]); > else < echo "\n unknown method"; return false; >> function displayMessage11($var11) < echo "\n from func1($var11)"; >function displayMessage12($var11,$var12) < echo "\n from func2($var11,$var12)"; >> $obj1 = new ABC1; $obj1->displayMessage11('hello'); $obj1->displayMessage12('hello','hello2'); $obj1->displayMessage13('Hello'); ?>Example #8
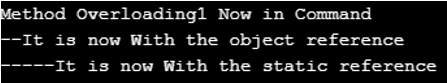
It is also just like the first example program. Check it once.
public static function __callStatic($name1,$pavan1) < echo "\n-----It is now With the static reference \n"; >> // Here now creating the object of the class " MethodOverloading " $obj1 = new MethodOverloading1; echo "Method Overloading1 Now in Command "; // Now using the object's reference $obj1->DemoTest1(); // Now using the static's reference MethodOverloading1::DemoTest1(); ?>Example #9
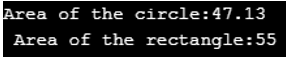
This program shows the area of the circle and rectangle using some parameters and the call() function of the method overloading concept. The program will only run with the object context due to the object assigning an object variable to the class, etc.
> > $circle1 = new TDshape1(); echo "Area of the circle:".$circle1->area1(15); // display output of the area of circle $rect1 = new TDshape1(); echo "\n Area of the rectangle:".$rect1->area1(5,11); // display output of the area of rectangle ?>Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Method Overloading in PHP” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,
25+ Hours of HD Videos
5 Courses
6 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
92+ Hours of HD Videos
22 Courses
2 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
83+ Hours of HD Videos
16 Courses
1 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
PHP Course Bundle — 8 Courses in 1 | 3 Mock Tests
43+ Hours of HD Videos
8 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5