- Python MySQL connection
- py mysql
- MySQLdb
- pyodbc
- Python code for Installing sample student table
- Installing MySQL connection from Anaconda
- Using SQLAlchemy
- SQLAlchemy
- MariaDB
- Google Cloud & MySQL
- Data Transfer from Google sheets to MySQL and vice versa
- 2. MySQL with Python¶
- 2.2. Connect and load data¶
- 2.3. Read data from table¶
- 2.4. Connection in try-except block¶
Python MySQL connection
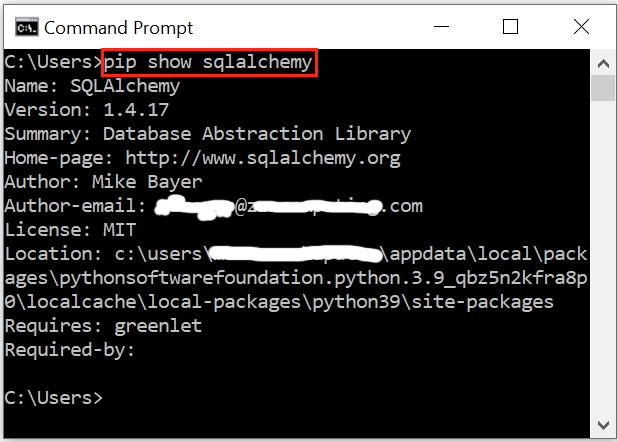
This is MySQL driver written in Python. Install ( pip ) install MySQL connector from your Command Prompt like this.
C:\Users\user>pip install mysql-connector-pythonimport mysql.connector my_conn=mysql.connector.connect( host='localhost', user='root', password = 'your_password', db='my_database', ) my_cursor = my_conn.cursor() my_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM student") my_result = my_cursor.fetchall() # we get a tuple print(my_result)py mysql
This driver is written in Python and contains a pure-Python MySQL client library. We can install (pip) from our command prompt.
C:\Users\user>pip install PyMySQLimport pymysql my_conn=pymysql.connect( host='localhost', user='root', password = 'password', db='my_tutorial', ) my_cursor = my_conn.cursor() my_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM student") my_result = my_cursor.fetchall() # we get a tuple print(my_result)Note : Don’t give the file name as pymysql.py and use the import. Give a different file name. You may get error like this.
AttributeError: partially initialized module ‘pymysql’ has no attribute ‘connect’ (most likely due to a circular import)
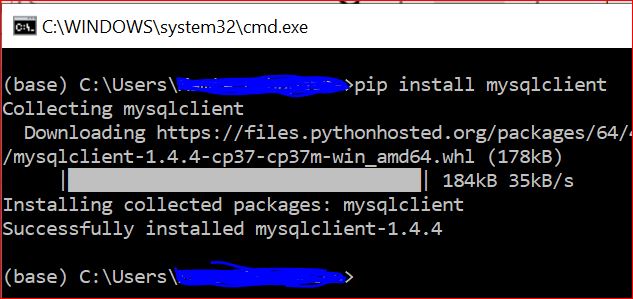
MySQLdb
MySQLdb, is a C extension module. After MySQLDB2 now it is evolved as mysqlclient. Here is how to install mysqlclient.
C:\Users\user>pip install mysqlclient import MySQLdb my_conn=MySQLdb.connect( host='localhost', user='root', password = "your_password", db='db_name', ) my_cursor = my_conn.cursor() my_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM student") my_result = my_cursor.fetchall() # we get a tuple print(my_result)pyodbc
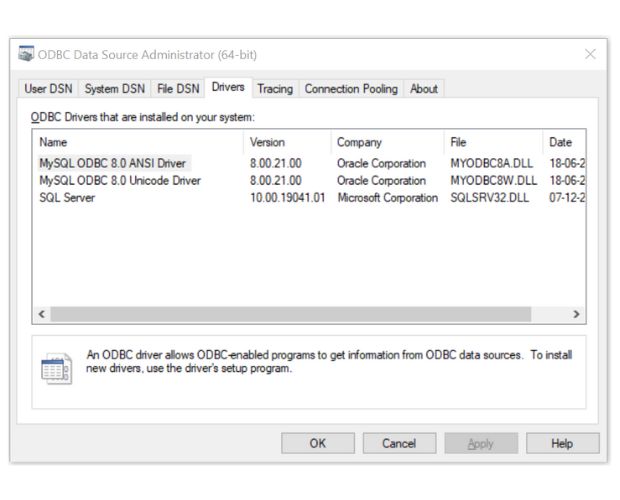
In your system check for the driver name
Administrative tools -> ODBC Data Sources -> Driver tab then copy the river name to the first parameter
import pyodbc my_conn = pyodbc.connect("DRIVER=; \ SERVER=localhost;DATABASE=my_tutorial; UID=root; PASSWORD=your_password;") my_cursor = my_conn.cursor() my_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM student LIMIT 0,10") my_result = my_cursor.fetchall() # we get a tuple print(my_result)Download & Install MySQL with Workbench and creating database with sample student table with records
Database Management using Python
| BLOB | Managing MySQL Blob Data type |
| connection | Python MySQL connection string |
| create | Create table by Query and showing structure |
| rowcount | Number of rows affected due to Query |
| error | Capturing Error in MySQL Query |
| Collect records | Select Query to get records from database table |
| Add record | Using sqlalchemy to Insert record to database table |
| Add record | Insert Query to add record to database table |
| Delete Table | Drop table Query to remove table from MySQL database |
| Update record | Update Query to update records of a database table |
| Delete record | Delete records of a database table |
| read_sql | Using MySql records to create Pandas DataFrame |
| mysqlclient | Using sqlalchemy and create_engine to manage MySQL |
| pickle | How to Pickle MySQL table and restore records. |
Python code for Installing sample student table
Installing MySQL connection from Anaconda
Download & install Anaconda with Python by using mysqlclient to connect to MySQL database server
Before this you must have MySQL database running and keep your connection userid and password with your database name ready.
We need to install MySQL connector to connect from Python to MySQL database.
Inside Anaconda goto Environment at your left side navigational menu

Middle you can see Base root
From Base root select Open Terminal
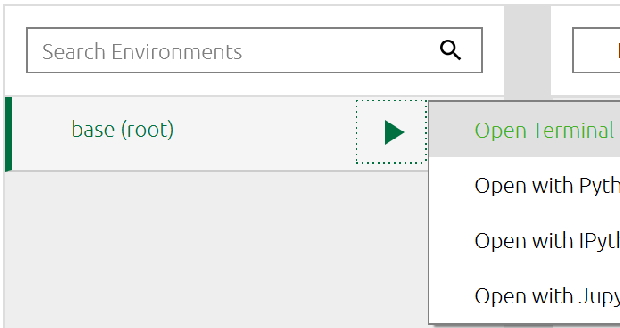
You will reach the Anaconda terminal where you can install any package . Just enter this line at the prompt to install MySQL connector.
conda install -c anaconda mysql-connector-pythonThis will install your MySQL connector by downloading packages from the internet. Now it is time to check the connection.
Using SQLAlchemy
For updating the database you need to use sqlalchemy and its create_engine
Here is the code to get the connection by using sqlalchemy
from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine = create_engine("mysql+mysqldb://userid_here:password_here@localhost/db_name") my_conect = engine.connect()If you are getting error message like this.
No module named ‘MySQLdb’
then you need to install mysqlclient.
Open your Anaconda terminal as explained above and then enter
To check the installation
SQLAlchemy
To check the installation
MariaDB
This is a open source community developed relational database. To connect to MariaDB from Python installa this .
my_conn = create_engine("mariadb+mariadbconnector://root:pw@localhost/db_name")Google Cloud & MySQL
Data Transfer from Google sheets to MySQL and vice versa
By using Pandas DataFrame we can transfer data from MySQL database table to Google sheets and from Google sheets to MySQL.
Data Transfer between Google sheet and MySQL »
Exercise
Here is a list of Queries you can execute using the above learning and display the outcome.
plus2net.com
Python programming Basics ⇩
2. MySQL with Python¶
The ‘mysql-connector’ is not supported by Django-framework. The good option is ‘mysqlclient’ which is supported by Django as well.
$ mysql -u root -p Enter password: mysql> CREATE DATABASE pythonSQL; 2.2. Connect and load data¶
Following code can be used to connect and load the data to database. Note that, the commands in the c.execute(…) statements are exactly same as the commands in the previous chapters.
# create_fill_database.py import mysql.connector as mc # connect to database conn= mc.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='d',db='pythonSQL') c = conn.cursor() # cursor to perform operations def create_table(): """ Create table in the database """ # optional: drop table if exists c.execute('DROP TABLE IF EXISTS writer') c.execute('CREATE TABLE writer \ ( \ id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, \ name VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL UNIQUE, \ age int \ )' ) def insert_data(): """ Insert data to the table """ c.execute("INSERT INTO writer (name) VALUES ('Pearl Buck')") c.execute(" INSERT INTO writer VALUES \ (NULL, 'Rabindranath Tagore', 80), \ (NULL, 'Leo Tolstoy', 82)" \ ) c.execute(" INSERT INTO writer (age, name) VALUES \ (30, 'Meher Krishna Patel')" \ ) def commit_close(): """ commit changes to database and close connection """ conn.commit() c.close() conn.close() def main(): """ execute create and insert commands """ create_table() insert_data() commit_close() # required for save the changes # standard boilerplate to call main function if __name__ == '__main__': main()
$ python create_fill_database.py
2.3. Read data from table¶
Following code can be used to read data from the table,
# read_database.py import mysql.connector as mc conn= mc.connect(host='localhost',user='root',password='d',db='pythonSQL') c = conn.cursor() def read_data(): c.execute('SELECT * FROM writer') writers = c.fetchall() # data is read in the form of list for writer in writers: # print individual item in the list print(writer) # data at each row is saved as tuple def main(): read_data() if __name__ == '__main__': main()
$ python read_database.py (1, 'Pearl Buck', None) (2, 'Rabindranath Tagore', 80) (3, 'Leo Tolstoy', 82) (4, 'Meher Krishna Patel', 30)
- In this way, we can get the data from the table and perform various operations on the data.
- Also, we can use all those queries with python, as queries in the execute statements are same as queries in previous chapter.
2.4. Connection in try-except block¶
We can use following code to put the connection string in the try except block, so that we can get proper message for not connecting with the database,
# connect_try.py import mysql.connector as mq from mysql.connector import errorcode try: conn = mq.connect(host='localhost', user='root', password='d', db='pythonSQL') print("Connected") except mq.Error as err: if err.errno == errorcode.ER_ACCESS_DENIED_ERROR: print("Something is wrong with your user name or password") elif err.errno == errorcode.ER_BAD_DB_ERROR: print("Database does not exist") else: print(err) else: print("Connection closed") conn.close()
$ python connect_try.py Connected Connection closed
$ python connect_try.py Something is wrong with your user name or password
$ python connect_try.py Database does not exist
© Copyright 2017, Meher Krishna Patel. Revision 31d452b4 .
Versions latest Downloads pdf html epub On Read the Docs Project Home Builds Free document hosting provided by Read the Docs.