- PHP mysqli code to update data
- Update data using PHP mysqli Object-Oriented Script
- Update data using PHP mysqli procedural script
- PHP mysqli Object-Oriented: Update Multiple Columns
- PHP mysqli Procedural: Update Multiple Columns
- PHP mysqli: Update All Rows at Once
- Php mysqli update row
- Объектно-ориентированный стиль
- Список пользователей
- Обновление пользователя
- Процедурный стиль
- Список пользователей
- Обновление пользователя
- PHP MySQL Update Data
- Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
- Example (MySQLi Procedural)
- Example (PDO)
PHP mysqli code to update data
This article is created to describe the way to update or modify specific data using PHP mysqli script. These are the two approaches, that can be used to update any specific or all data in the database:
Whatever the approach we choose to update the data, we need to follow these simple steps:
- Open a connection to the database.
- Write an SQL statement regarding the data modification.
- Initialize the written SQL statement to a variable.
- Use this variable to perform the query against the database to modify particular data.
- Close the database connection.
The SQL statement to update specific data is:
UPDATE tableName SET column1=value1, column2=value2, column3=value3, . columnN=valueN WHERE particularColumn=particularValue;
Be careful when updating the data. The WHERE clause is used when we need to update particular records.
Be careful when omitting the WHERE clause; update all records in the table.
Update data using PHP mysqli Object-Oriented Script
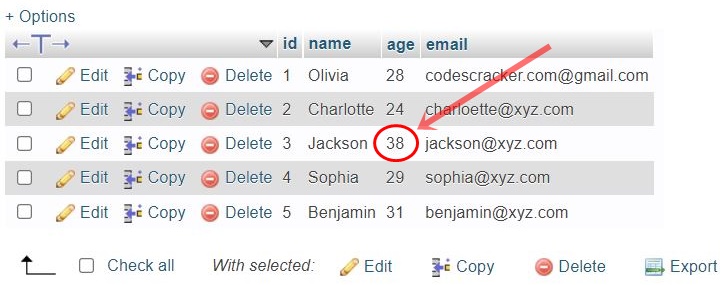
Follow the example given below to update particular data (a record or row) using a PHP mysqli object-oriented script. In this example, I am going to update the age of a record whose id is 3.
connect_errno) < echo "Connection to the database failed!"; echo "Reason: ", $conn->connect_error; exit(); > $sql = "UPDATE customer SET age='40' WHERE $result = $conn->query($sql); if($result) < echo "Data updated successfully."; // block of code to process further. > else < echo "Error occurred while updating the record!"; echo "Reason: ", $conn->error; > $conn->close(); ?> Before executing the above PHP script, here is a snapshot of the table customer:
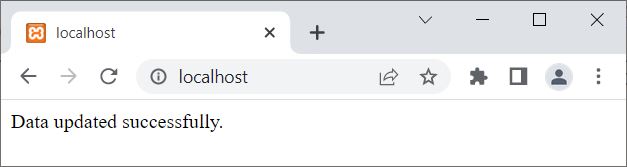
Here is the output produced by the above PHP example on updating the record using a PHP mysqli object-oriented script:
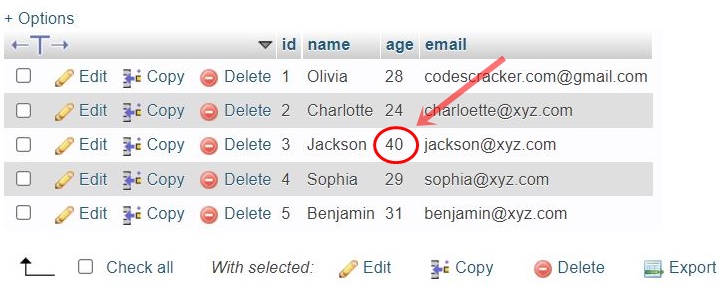
And following is the snapshot of the table named «student» after executing the above PHP script:
Note: The mysqli() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in object-oriented style.
Note: The new keyword is used to create a new object.
Note: The connect_errno is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in object-oriented style.
Note: The connect_error is used to get the error description (if any) from the last connection in object-oriented style.
Note: The exit() function is used to terminate the execution of the current PHP script.
Note: The query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
Note: The error is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The close() function is used to close an opened connection in object-oriented style.
Note: If you remove the WHERE clause from the above PHP script, then the age column of all rows will be set to 40.
The above example can also be written as:
connect_errno) < if($conn->query("UPDATE customer SET age='40' WHERE echo "Data updated successfully."; > $conn->close(); ?> Update data using PHP mysqli procedural script
To update data using a PHP mysqli procedural script, follow the example given below:
"; echo "Reason: ", mysqli_error($conn); > > mysqli_close($conn); ?>
Note: The mysqli_connect() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_errno() function is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_error() function is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_close() function is used to close an opened connection to the MySQL database in procedural style.
PHP mysqli Object-Oriented: Update Multiple Columns
To update multiple columns at once, everything will be the same as done in the section Update Data using PHP mysqli Object-Oriented Script, except the SQL statement. That is, to update two columns, say age and email, use the following SQL statement:
$sql = "UPDATE customer SET age='42', email='newmail@xyz.com' WHERE >And to update more columns, say three columns, use the following SQL statement:
$sql = "UPDATE customer SET name='Lucas', age='42', email='newmail@xyz.com' WHERE >Here is the complete PHP mysqli script to update multiple columns at once:
connect_errno) < $sql = "UPDATE customer SET name='Lucas', age='42', email='newmail@xyz.com' WHERE if($conn->query($sql)) echo "Data updated successfully."; else < echo "Error occurred while updating the record!"; echo "Reason: ", $conn->error; > > $conn->close(); ?>
PHP mysqli Procedural: Update Multiple Columns
"; echo "Reason: ", mysqli_error($conn); > > mysqli_close($conn); ?>
PHP mysqli: Update All Rows at Once
To update all rows using the PHP mysqli script, all the processes will be the same, except that you will remove or omit the WHERE clause. That is, to update all rows with particular columns, use this similar SQL statement:
$sql = "UPDATE customer SET email='newmail@xyz.com'";
And to update all rows with multiple columns, use this similar SQL statement:
$sql = "UPDATE customer SET name='Lucas', age='42', email='newmail@xyz.com'";
Liked this article? Share it!
Php mysqli update row
В MySQL для обновления применяется sql-команда UPDATE :
UPDATE Таблица SET столбец1 = значение1, столбец2 = значение2. WHERE столбец = значение
Для примера возьмем использованную в прошлых темах таблицу Users со следующим определением:
CREATE TABLE Users (id INTEGER AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(30), age INTEGER)
Объектно-ориентированный стиль
Сначала определим файл index.php , который будет выводить список пользователей с ссылками на их обновление:
Список пользователей
connect_error)< die("Ошибка: " . $conn->connect_error); > $sql = "SELECT * FROM Users"; if($result = $conn->query($sql))< echo "
| Имя | Возраст | |
|---|---|---|
| " . $row["name"] . " | "; echo "" . $row["age"] . " | "; echo "Изменить | "; echo "
Здесь используется команда SELECT, которая получает всех пользователей из таблицы Users. В таблице третий столбец хранит ссылку на скрипт update.php, который мы далее создадим и которому передается параметр id с идентификатором пользователя, которого надо изменить.
Для обновления данных определим скрипт update.php :
connect_error)< die("Ошибка: " . $conn->connect_error); > ?> real_escape_string($_GET["id"]); $sql = "SELECT * FROM Users WHERE "; if($result = $conn->query($sql))< if($result->num_rows > 0) < foreach($result as $row)< $username = $row["name"]; $userage = $row["age"]; >echo "Обновление пользователя
Имя:
Возраст:
"; > else< echo "Пользователь не найден"; > $result->free(); > else< echo "Ошибка: " . $conn->error; > > elseif (isset($_POST["id"]) && isset($_POST["name"]) && isset($_POST["age"])) < $userid = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["id"]); $username = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["name"]); $userage = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["age"]); $sql = "UPDATE Users SET name = '$username', age = '$userage' WHERE "; if($result = $conn->query($sql)) < header("Location: index.php"); >else< echo "Ошибка: " . $conn->error; > > else < echo "Некорректные данные"; >$conn->close(); ?> Весь код обновления структурно делится на две части. В первой части мы обрабатываем запрос GET. Когда пользователь нажимает на ссылку «Обновить» на странице index.php , то отправляется запрос GET, в котором передается id редактируемого пользователя.
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] === "GET" && isset($_GET["id"]))
И если это запрос GET, то нам надо вывести данные редактируемого пользователя в поля формы. Для этого получаем из базы данных объект по переданному id
$userid = $conn->real_escape_string($_GET["id"]); $sql = "SELECT * FROM Users WHERE "; if($result = $conn->query($sql))Далее получаем полученные данные и, если они имеются, выводим их в поля формы. Таким образом, пользователь увидит на форме данные обновляемого объекта.
Вторая часть скрипта представляет обработку POST-запроса - когда пользователь нажимает на кнопку на форме, то будет отправляться POST-запрос с отправленными данными. Мы получаем эти данные и отправляем базе данных команду UPDATE с этими данными, используя при этом параметризацию запроса:
$userid = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["id"]); $username = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["name"]); $userage = $conn->real_escape_string($_POST["age"]); $sql = "UPDATE Users SET name = '$username', age = '$userage' WHERE "; if($result = $conn->query($sql))После выполнения запроса к БД перенаправляем пользователя на скрипт index.php с помощью функции
Таким образом, пользователь обращается к скрипту index.php , видит таблицу с данными и нажимает на ссылку "Обновить" в одной из строк.
После нажатия его перебрасывает на скрипт update.php , который выводит данные редактируемого объекта. Пользователь изменяет данные и нажимает на кнопку.
Данные в запросе POST отправляются этому же скрипту update.php , который сохраняет данные и перенаправляет пользователя обратно на index.php .
Процедурный стиль
Список пользователей
$sql = "SELECT * FROM Users"; if($result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql))< echo "
| Имя | Возраст | |
|---|---|---|
| " . $row["name"] . " | "; echo "" . $row["age"] . " | "; echo "Изменить | "; echo "
?> 0) < foreach($result as $row)< $username = $row["name"]; $userage = $row["age"]; >echo "Обновление пользователя
Имя:
Возраст:
"; > else< echo "Пользователь не найден"; > mysqli_free_result($result); > else < echo "Ошибка: " . mysqli_error($conn); >> elseif (isset($_POST["id"]) && isset($_POST["name"]) && isset($_POST["age"])) < $userid = mysqli_real_escape_string($conn, $_POST["id"]); $username = mysqli_real_escape_string($conn, $_POST["name"]); $userage = mysqli_real_escape_string($conn, $_POST["age"]); $sql = "UPDATE Users SET name = '$username', age = '$userage' WHERE "; if($result = mysqli_query($conn, $sql))< header("Location: index.php"); >else < echo "Ошибка: " . mysqli_error($conn); >> else < echo "Некорректные данные"; >mysqli_close($conn); ?>
PHP MySQL Update Data
The UPDATE statement is used to update existing records in a table:
Notice the WHERE clause in the UPDATE syntax: The WHERE clause specifies which record or records that should be updated. If you omit the WHERE clause, all records will be updated!
To learn more about SQL, please visit our SQL tutorial.
Let's look at the "MyGuests" table:
| id | firstname | lastname | reg_date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Doe | john@example.com | 2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 | Mary | Moe | mary@example.com | 2014-10-23 10:22:30 |
The following examples update the record with in the "MyGuests" table:
Example (MySQLi Object-oriented)
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if ($conn->connect_error) die("Connection failed: " . $conn->connect_error);
>
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE ($conn->query($sql) === TRUE) echo "Record updated successfully";
> else echo "Error updating record: " . $conn->error;
>
Example (MySQLi Procedural)
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDB";
// Create connection
$conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $dbname);
// Check connection
if (!$conn) die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
>
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE (mysqli_query($conn, $sql)) echo "Record updated successfully";
> else echo "Error updating record: " . mysqli_error($conn);
>
Example (PDO)
$servername = "localhost";
$username = "username";
$password = "password";
$dbname = "myDBPDO";
try $conn = new PDO("mysql:host=$servername;dbname=$dbname", $username, $password);
// set the PDO error mode to exception
$conn->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
$sql = "UPDATE MyGuests SET lastname='Doe' WHERE // Prepare statement
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
// execute the query
$stmt->execute();
// echo a message to say the UPDATE succeeded
echo $stmt->rowCount() . " records UPDATED successfully";
> catch(PDOException $e) echo $sql . "
" . $e->getMessage();
>
After the record is updated, the table will look like this:
| id | firstname | lastname | reg_date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Doe | john@example.com | 2014-10-22 14:26:15 |
| 2 | Mary | Doe | mary@example.com | 2014-10-23 10:22:30 |