- Java Collections Looping Example
- while Loop
- Concept of the Iterator
- Java Collections Looping Approaches
- Iterate through List Collections
- Iterate through Queue Collections
- Iterate through Deque Collections
- Iterate through Set Collections
- Iterate through Map collections
- Other Java Collections Tutorials:
- About the Author:
- How to iterate through Java List? Seven (7) ways to Iterate Through Loop in Java
- There are 7 ways you can iterate through List.
- Java Example:
- Output:
- Suggested Articles.
- How to loop ArrayList in Java
- How to iterate arraylist elements using Enumeration interface
- Top Related Articles:
- About the Author
- Comments
- How to traverse iterate or loop ArrayList in Java
Java Collections Looping Example
Since Java 5, there are 2 forms of for loop: classic and enhanced. The classic for loop is in the form:
for (initialization; termination; increment/decrement)
The major difference between the 2 for loops is that the classic for loop allows us to keep track of the index or position of the collection.
while Loop
Concept of the Iterator
An iterator is an object that enables us to traverse a collection. There is an iterator ( java.util.Iterator ) in all the top level interfaces of the Java Collections Framework that inherits java.util.Collection interface. These interfaces are java.util.List , java.util.Queue , java.util.Deque , and java.util.Set . Furthermore, there is the java.util.Map interface that does not inherit java.util.Collection .
List s also have a special iterator called a list iterator ( java.util.ListIterator ). What’s the difference? The java.util.Iterator is forward looking only while the java.util.ListIterator is bidirectional (forward and backward). Furthermore, the java.util.ListIterator inherits java.util.Iterator . The result of using either iterator to loop through a list will be the same as we will see later.
Java Collections Looping Approaches
Can you guess how many ways we can loop through a collection given there are 2 forms of loop constructs and all interfaces have an iterator.
Iterate through List Collections
List strList = new ArrayList(); strList.add("list item 1"); strList.add("list item 2"); strList.add("list item 3"); strList.add("list item 4"); strList.add("list item 5"); for (Iterator it = strList.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
We mentioned earlier that List s have a special iterator called ListIterator . We can easily replace for loop’s initialization to either of the following and it would work as well.
ListIterator it = strList.listIterator(); Iterator it = strList.listIterator();
Iterator itA = strList.iterator(); while (itA.hasNext())
Similarly the iterator declaration (variable itA ) can be replaced to either of the following and it would work as well.
ListIterator itA = strList.listIterator(); Iterator itA = strList.listIterator();
Finally the last approach is the do-while loop. We can easily refactor the while loop to become a do-while loop as shown below.
Iterator itB = strList.iterator(); do < System.out.println(itB.next()); >while (itB.hasNext());
ListIterator itB = strList.listIterator(); Iterator itB = strList.listIterator();
Iterate through Queue Collections
Queue strQueue = new PriorityQueue(); strQueue.add("queue item 1"); strQueue.add("queue item 2"); strQueue.add("queue item 3"); strQueue.add("queue item 4"); strQueue.add("queue item 5"); for (Iterator it = strQueue.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
Iterator itA = strQueue.iterator(); while (itA.hasNext())
Iterator itB = strQueue.iterator(); do < System.out.println(itB.next()); >while (itB.hasNext());
Iterate through Deque Collections
Deque strDeque = new ArrayDeque(); strDeque.add("deque item 1"); strDeque.add("deque item 2"); strDeque.add("deque item 3"); strDeque.add("deque item 4"); strDeque.add("deque item 5"); Here we are using this deque as a queue. If we were to use it as a stack, then we would have used the push() method to populate the deque.
for (Iterator it = strDeque.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
Iterator itA = strDeque.iterator(); while (itA.hasNext())
Iterator itB = strDeque.iterator(); do < System.out.println(itB.next()); >while (itB.hasNext());
Iterate through Set Collections
Set strSet = new HashSet(); strSet.add("set item 1"); strSet.add("set item 2"); strSet.add("set item 3"); strSet.add("set item 4"); strSet.add("set item 5"); for (Iterator it = strSet.iterator(); it.hasNext(); )
Iterator itA = strSet.iterator(); while (itA.hasNext())
Iterator itB = strSet.iterator(); do < System.out.println(itB.next()); >while (itB.hasNext());
Iterate through Map collections
Map strMap = new HashMap(); strMap.put("key 1", "value 1"); strMap.put("key 2", "value 2"); strMap.put("key 3", "value 3"); strMap.put("key 4", "value 4"); strMap.put("key 5", "value 5"); Other Java Collections Tutorials:
About the Author:
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos you YouTube.
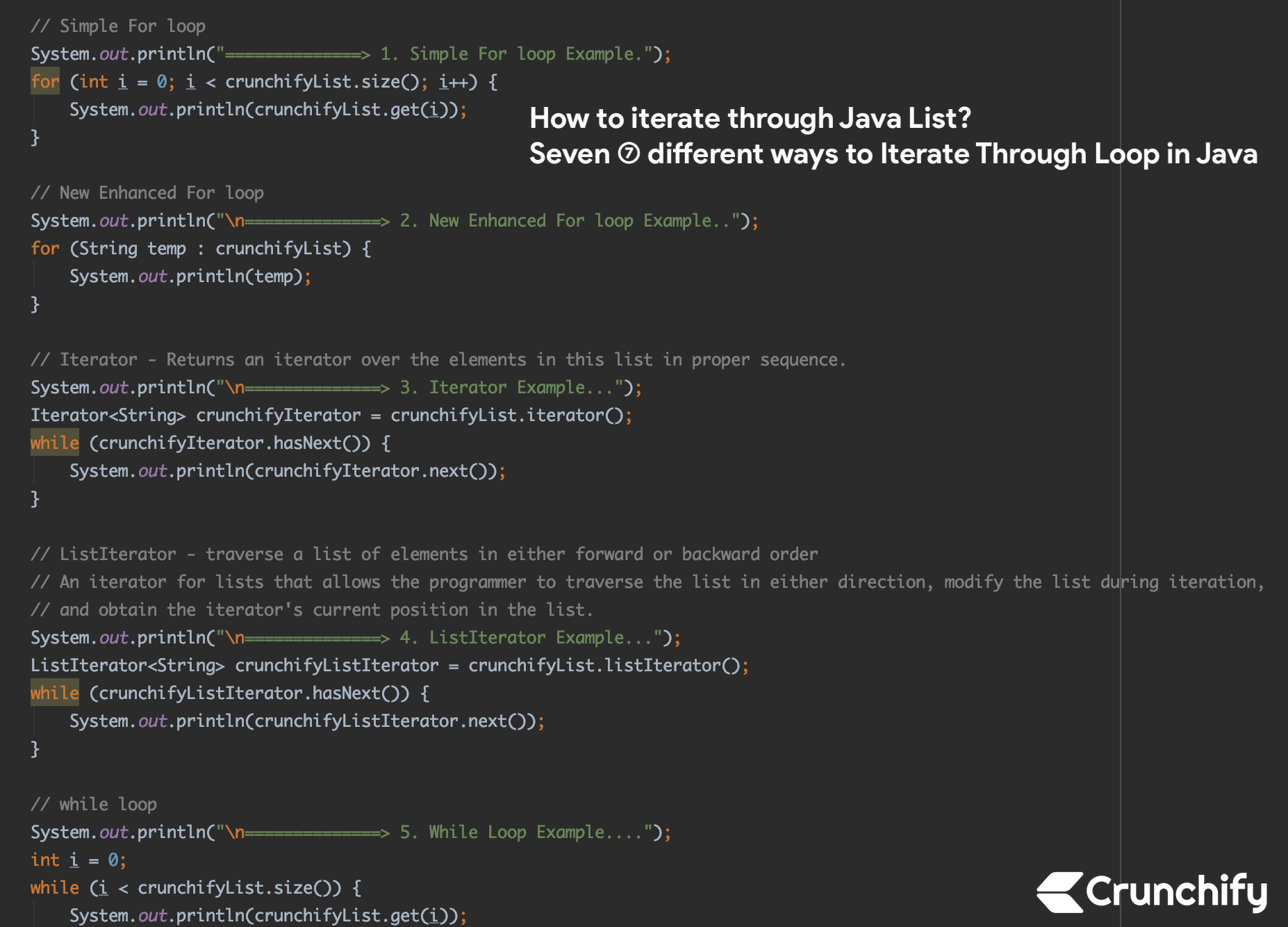
How to iterate through Java List? Seven (7) ways to Iterate Through Loop in Java
How to iterate through Java List? This tutorial demonstrates the use of ArrayList, Iterator and a List.
There are 7 ways you can iterate through List.
- Simple For loop
- Enhanced For loop
- Iterator
- ListIterator
- While loop
- Iterable.forEach() util
- Stream.forEach() util
Java Example:
You need JDK 13 to run below program as point-5 above uses stream() util.
void java.util.stream.Stream.forEach (Consumer action) p erforms an action for each element of this stream.
package crunchify.com.tutorials; import java.util.*; /** * @author Crunchify.com * How to iterate through Java List? Seven (7) ways to Iterate Through Loop in Java. * 1. Simple For loop * 2. Enhanced For loop * 3. Iterator * 4. ListIterator * 5. While loop * 6. Iterable.forEach() util * 7. Stream.forEach() util */ public class CrunchifyIterateThroughList < public static void main(String[] argv) < // create list ListcrunchifyList = new ArrayList(); // add 4 different values to list crunchifyList.add("Facebook"); crunchifyList.add("Paypal"); crunchifyList.add("Google"); crunchifyList.add("Yahoo"); // Other way to define list is - we will not use this list :) List crunchifyListNew = Arrays.asList("Facebook", "Paypal", "Google", "Yahoo"); // Simple For loop System.out.println("==============> 1. Simple For loop Example."); for (int i = 0; i < crunchifyList.size(); i++) < System.out.println(crunchifyList.get(i)); >// New Enhanced For loop System.out.println("\n==============> 2. New Enhanced For loop Example.."); for (String temp : crunchifyList) < System.out.println(temp); >// Iterator - Returns an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence. System.out.println("\n==============> 3. Iterator Example. "); Iterator crunchifyIterator = crunchifyList.iterator(); while (crunchifyIterator.hasNext()) < System.out.println(crunchifyIterator.next()); >// ListIterator - traverse a list of elements in either forward or backward order // An iterator for lists that allows the programmer to traverse the list in either direction, modify the list during iteration, // and obtain the iterator's current position in the list. System.out.println("\n==============> 4. ListIterator Example. "); ListIterator crunchifyListIterator = crunchifyList.listIterator(); while (crunchifyListIterator.hasNext()) < System.out.println(crunchifyListIterator.next()); >// while loop System.out.println("\n==============> 5. While Loop Example. "); int i = 0; while (i < crunchifyList.size()) < System.out.println(crunchifyList.get(i)); i++; >// Iterable.forEach() util: Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source System.out.println("\n==============> 6. Iterable.forEach() Example. "); crunchifyList.forEach((temp) -> < System.out.println(temp); >); // collection Stream.forEach() util: Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source System.out.println("\n==============> 7. Stream.forEach() Example. "); crunchifyList.stream().forEach((crunchifyTemp) -> System.out.println(crunchifyTemp)); > > Output:
==============> 1. Simple For loop Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 2. New Enhanced For loop Example.. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 3. Iterator Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 4. ListIterator Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 5. While Loop Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 6. Iterable.forEach() Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo ==============> 7. Stream.forEach() Example. Facebook Paypal Google Yahoo Process finished with exit code 0
If you liked this article, then please share it on social media. Have a question or suggestion? Please leave a comment to start the discussion. 👋
Suggested Articles.
How to loop ArrayList in Java
Earlier we shared ArrayList example and how to initialize ArrayList in Java. In this post we are sharing how to iterate (loop) ArrayList in Java.
There are four ways to loop ArrayList:
Lets have a look at the below example – I have used all of the mentioned methods for iterating list.
import java.util.*; public class LoopExample < public static void main(String[] args) < ArrayListarrlist = new ArrayList(); arrlist.add(14); arrlist.add(7); arrlist.add(39); arrlist.add(40); /* For Loop for iterating ArrayList */ System.out.println("For Loop"); for (int counter = 0; counter < arrlist.size(); counter++) < System.out.println(arrlist.get(counter)); >/* Advanced For Loop*/ System.out.println("Advanced For Loop"); for (Integer num : arrlist) < System.out.println(num); >/* While Loop for iterating ArrayList*/ System.out.println("While Loop"); int count = 0; while (arrlist.size() > count) < System.out.println(arrlist.get(count)); count++; >/*Looping Array List using Iterator*/ System.out.println("Iterator"); Iterator iter = arrlist.iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) < System.out.println(iter.next()); >> > For Loop 14 7 39 40 Advanced For Loop 14 7 39 40 While Loop 14 7 39 40 Iterator 14 7 39 40
In the comment section below, Govardhan asked a question: He asked, how to iterate an ArrayList using Enumeration. Govardhan here is the code:
How to iterate arraylist elements using Enumeration interface
import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; public class EnumExample < public static void main(String[] args) < //create an ArrayList object ArrayListarrayList = new ArrayList(); //Add elements to ArrayList arrayList.add("C"); arrayList.add("C++"); arrayList.add("Java"); arrayList.add("DotNet"); arrayList.add("Perl"); // Get the Enumeration object Enumeration e = Collections.enumeration(arrayList); // Enumerate through the ArrayList elements System.out.println("ArrayList elements: "); while(e.hasMoreElements()) System.out.println(e.nextElement()); > > ArrayList elements: C C++ Java DotNet Perl
Top Related Articles:
About the Author
I have 15 years of experience in the IT industry, working with renowned multinational corporations. Additionally, I have dedicated over a decade to teaching, allowing me to refine my skills in delivering information in a simple and easily understandable manner.
Comments
Hi Govardhan, I have updated the post and added the code. You can find your answer above in the post. Let me know if you have any further question.
Use two variable, lets call them fastVariable and slowVariable. Move the fastVariable twice the speed of slowVariable. By the time fastVariable reach end of the list slowVariable will be at middle of the list. Thanks.
Hello! So I have two seperate arraylists. I am trying to display both of them on a form, but only one of them is showing up. Is it possible to loop to arrayLists and display them at the same time?
Melly, You can join both the arraylists and then loop the combined arraylist to display all the elements. Refer this: How to join ArrayList?
How to traverse iterate or loop ArrayList in Java
Iterating, traversing or Looping ArrayList in Java means accessing every object stored in ArrayList and performing some operations like printing them. There are many ways to iterate, traverse or Loop ArrayList in Java e.g. advanced for loop, traditional for loop with size(), By using Iterator and ListIterator along with while loop etc. All the method of Looping List in Java also applicable to ArrayList because ArrayList is an essentially List. In next section we will see a code example of Looping ArrayList in Java.
Now we know that there are multiple ways to traverse, iterate or loop ArrayList in Java, let’s see some concrete code example to know exactly How to loop ArrayList in Java. I prefer advanced for loop added in Java 1.5 along with Autoboxing, Java Enum, Generics, Varargs and static import, also known as foreach loop if I have to just iterate over Array List in Java. If I have to remove elements while iterating than using Iterator or ListIterator is the best solution.
import java.util.ArrayList ;
import java.util.Iterator ;
/**
* Java program which shows How to loop over ArrayList in Java using advanced for loop,
* traditional for loop and How to iterate ArrayList using Iterator in Java
* advantage of using Iterator for traversing ArrayList is that you can remove
* elements from Iterator while iterating.
* @author
*/
public class ArrayListLoopExample
public static void main ( String args [])
//Creating ArrayList to demonstrate How to loop and iterate over ArrayList
ArrayList < String > games = new ArrayList < String > ( 10 ) ;
games. add ( «Cricket» ) ;
games. add ( «Soccer» ) ;
games. add ( «Hockey» ) ;
games. add ( «Chess» ) ;
System. out . println ( «original Size of ArrayList : » + games. size ()) ;
//Looping over ArrayList in Java using advanced for loop
System. out . println ( «Looping over ArrayList in Java using advanced for loop» ) ;
for ( String game: games ) <
//print each element from ArrayList
System. out . println ( game ) ;
>
//You can also Loop over ArrayList using traditional for loop
System. out . println ( «Looping ArrayList in Java using simple for loop» ) ;
for ( int i = 0 ; i < games. size () ; i++ )<
String game = games. get ( i ) ;
>
//Iterating over ArrayList in Java
Iterator < String > itr = games. iterator () ;
System. out . println ( «Iterating over ArrayList in Java using Iterator» ) ;
while ( itr. hasNext ()) <
System. out . println ( «removing » + itr. next () + » from ArrayList in Java» ) ;
itr. remove () ;
>
System. out . println ( «final Size of ArrayList : » + games. size ()) ;
Output:
original Size of ArrayList : 4
Looping over ArrayList in Java using advanced for loop
Cricket
Soccer
Hockey
Chess
Looping ArrayList in Java using simple for loop
Iterating over ArrayList in Java using Iterator
removing Cricket from ArrayList in Java
removing Soccer from ArrayList in Java
removing Hockey from ArrayList in Java
removing Chess from ArrayList in Java
final Size of ArrayList : 0
That’s all on How to iterate, traverse or loop ArrayList in Java. In summary use advance for loop to loop over ArrayList in Java, its short, clean and fast but if you need to remove elements while looping use Iterator to avoid ConcurrentModificationException .