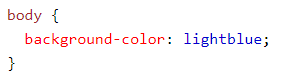- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- EtaiG/css-functions-list
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- About
- CSS Functions Reference
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- CSS Commands
- Basic CSS Commands
- Intermediate CSS Commands
- Advanced CSS Commands
- Tips And Tricks
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
A list of all css functions
License
EtaiG/css-functions-list
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
Just a list of all css functions. Based off of the MDN css reference
All css functions, copy-paste with ease:
["annotation", "attr", "blur", "brightness", "calc", "character-variant", "circle", "contrast", "cubic-bezier", "dir", "drop-shadow", "element", "ellipse", "grayscale", "hsl", "hsla", "hue-rotate", "image", "inset", "invert", "lang", "linear-gradient", "matrix", "matrix3d", "minmax", "not", "nth-child", "nth-last-child", "nth-last-of-type", "nth-of-type", "opacity", "ornaments", "perspective", "polygon", "radial-gradient", "rect", "repeat", "repeating-linear-gradient", "repeating-radial-gradient", "rgb", "rgba", "rotate", "rotatex", "rotatey", "rotatez", "rotate3d", "saturate", "scale", "scalex", "scaley", "scalez", "scale3d", "sepia", "skew", "skewx", "skewy", "steps", "styleset", "stylistic", "swash", "symbols", "translate", "translatex", "translatey", "translatez", "translate3d", "url", "var"]
About
A list of all css functions
CSS Functions Reference
CSS functions are used as a value for various CSS properties.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| attr() | Returns the value of an attribute of the selected element |
| calc() | Allows you to perform calculations to determine CSS property values |
| conic-gradient() | Creates a conic gradient |
| counter() | Returns the current value of the named counter |
| cubic-bezier() | Defines a Cubic Bezier curve |
| hsl() | Defines colors using the Hue-Saturation-Lightness model (HSL) |
| hsla() | Defines colors using the Hue-Saturation-Lightness-Alpha model (HSLA) |
| linear-gradient() | Creates a linear gradient |
| max() | Uses the largest value, from a comma-separated list of values, as the property value |
| min() | Uses the smallest value, from a comma-separated list of values, as the property value |
| radial-gradient() | Creates a radial gradient |
| repeating-conic-gradient() | Repeats a conic gradient |
| repeating-linear-gradient() | Repeats a linear gradient |
| repeating-radial-gradient() | Repeats a radial gradient |
| rgb() | Defines colors using the Red-Green-Blue model (RGB) |
| rgba() | Defines colors using the Red-Green-Blue-Alpha model (RGBA) |
| var() | Inserts the value of a custom property |
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
CSS Commands
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It describes the presentation of the document, which is written in a markup language like HTML. It does the work of separation of presentation and content, which includes different layouts, colors, and fonts. The separation provides flexibility and control in the different characteristics, enabling multiple web pages to share formatting by specifying relevant CSS. World Web Consortium maintains the CSS specifications. Additionally, When accessing the content from a mobile device, it also enables alternate formatting by providing specific rules.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
Basic CSS Commands
Here are some of the basic commands:
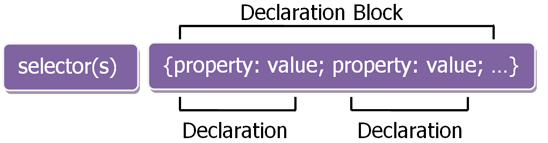
1. CSS Syntax: There are a set of rules which need to be followed in CSS Command. The CSS rule set consists of a selector and a declaration block. The selector points to the HTML element the user wants to style. The declaration block can contain one or more declarations that semicolons can separate. Every declaration should include a property name with its value, and colons should separate these.
2. ID Selector: The id selector can use the id of an HTML element attribute and help select a particular element. To select a unique component on a page, you can use the ‘#’ symbol followed by the id of the element. The id should be unique for that specific element.
3. Class Selector: To select a particular class attribute, the class selector is used to select the elements from that class. You use a period (.) character to target elements in a specific class. The name of the class follows it. With this, if the user wants to use only specific elements, they can specify those elements by using a class.
4. Grouping Selectors: There are times when elements have the same style definitions. To have them together grouped and minimize the code is a better option. To the group, the selector’s user can make use of a comma and separate each selector
5. Comments: These CSS commands should be used when writing code. They clarify what the code is doing and help you or someone else who is new to the code to work on it accordingly. Browsers ignore comments. A CSS comment starts and ends with /* */.
6. Display: Block – Many HTML elements are set to this display mode. By default, the block-level elements take as much space and cannot be placed on the same line as any other display mode. It is possible to gain the ability to change the element’s height and width as per your wish.
7. Colors in CSS: In this CSS command, colors can be specified in the RGB formula. Each parameter defines the intensity of these colors and defines a new color. For example, you need to set all color parameters to RGB(0,0,0) to display black.
8. Background Color: The background-color property defines the color to be set for the background of an element. Color can easily be defined by giving a color name, adding a Hex value, or setting the RGB value
9. Background image: The background image can be set to any particular image you choose. Once you set the image, it repeats and covers the entire element.
10. CSS Margins: CSS Command has different margin properties, which can help create space around different elements and define these outside borders. CSS can have properties like margin-top, margin-right, margin-bottom, and margin-left.
Intermediate CSS Commands
Here are some of the intermediate commands:
1. Class and ID selectors: In addition to the HTML tag, users can define their own selectors, which can be class or ID. These commands primarily style the same HTML element differently based on the assigned ID or class.
2. Pseudo-class: These classes specify a particular state or relation to a given selector. These classes can also take the form of selector:pseudo_class < property: value; >. To define a class, you simply place a colon between the selector and the pseudo-class.
3. Text Formatting: The added texts can be customized and formatted using the formatting properties. You can change the color by using the keyword ‘color.’ You can also change the alignment of text. Using text decoration, you can set and remove decorations. You can perform transformations with respect to cases.
4. CSS Fonts: Fonts in CSS have different families, like generic and font families. The font family is a family of texts. The generic one has a group of families having similar looks, and the font one has a specific font.
5. Icons: Using the icon library and adding the name of specified icon class icons can be easily used in CSS.
6. Tables: CSS can also display tables and help in customization with borders, their width, and height. A user can quickly have tables on a web page using keywords like ‘border’, ‘width’ and height.
7. Positioning: This property specifies the type of positioning method used for any element. The position can be static, relative, fixed, absolute, or sticky.
8. Overflow: This property helps control the content too big to fit into an area.
9. Float: The float property lets the element know how to float. It specifies which elements can float beside the cleared elements.
10. Opacity: This property defines the opacity or transparency of any element.
Advanced CSS Commands
Here are some of the advanced commands:
1. CSS Rounded Corners: An element can be given rounded corners using the’ border-radius’ property. You can also specify a particular corner out of the four corners and make the changes you choose.
2. Border Images: You can set an image as the border around any element. This is possible by making use of a border-image property. It takes the image, slices it into nine sections, and then places the corners at corners and middle sections repeated or stretched.
Tips And Tricks
- Make use of reset.css and reset all fundamental styles.
- Use Shorthand CSS to have a shorter way of writing Command CSS codes.
- Use CSS debugging tools to tweak, understand and debug the CSS command styles.
Conclusion
CSS Command helps you keep a document’s informational content separate and helps display it. It helps avoid duplication, maintain the code easily, and use the same content with different styles.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CSS Commands” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
38+ Hours of HD Videos
9 Courses
5 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
149+ Hours of HD Videos
28 Courses
5 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
253+ Hours of HD Videos
51 Courses
6 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
CSS Course Bundle — 19 Courses in 1 | 3 Mock Tests
82+ Hours of HD Videos
19 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5