Python program to create a class which performs basic calculator operations
In this module, we will learn to create a class which performs basic calculator operations in Python.
Being an object-oriented programming language, python stresses on concepts like classes and objects. Classes are required to create objects. They act like a blueprint or template for the creation of objects. Similar types of variables and functions are collected and are placed into a class. We can hence reuse this class to build different objects. Classes make the code more efficient to use. As related data are grouped together, code looks clear and simple enough to understand. Classes are defined with a keyword class.
To create an object we simply use the syntax:
Create a basic calculator using class in python
Problem statement: Write a python program to create a class which performs basic calculator operations.
Let us solve this step by step,
STEP 1: Create a class Calculator and define all the functions of a basic calculator like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
class Calculator: def addition(self): print(a + b) def subtraction(self): print(a - b) def multiplication(self): print(a * b) def division(self): print(a / b)
Here, self is used because while calling function using obj.function() (in the following steps), the function will call itself.
STEP 2: Next, take inputs from the user and create an object.
a = int(input("Enter first number:")) b = int(input("Enter first number:")) obj = Calculator() STEP 3: Lastly, create choices for the user to perform which operation they need and print out the solution.
choice = 1 while choice != 0: print("1. ADD") print("2. SUB") print("3. MUL") print("4. DIV") choice = int(input("Enter your choice:")) if choice == 1: print(obj.addition()) elif choice == 2: print(obj.subtraction()) elif choice == 3: print(obj.multiplication()) elif choice == 4: print(obj.division()) else: print("Invalid choice") class Calculator: def addition(self): print(a + b) def subtraction(self): print(a - b) def multiplication(self): print(a * b) def division(self): print(a / b) a = int(input("Enter first number:")) b = int(input("Enter first number:")) obj = Calculator() choice = 1 while choice != 0: print("1. ADDITION") print("2. SUBTRACTION") print("3. MULTIPLICATION") print("4. DIVISION") choice = int(input("Enter your choice:")) if choice == 1: print(obj.addition()) elif choice == 2: print(obj.subtraction()) elif choice == 3: print(obj.multiplication()) elif choice == 4: print(obj.division()) else: print("Invalid choice") Enter first number:3 Enter first number:2 1. ADDITION 2. SUBTRACTION 3. MULTIPLICATION 4. DIVISION Enter your choice:1 5 1. ADDITION 2. SUBTRACTION 3. MULTIPLICATION 4. DIVISION Enter your choice:2 1 1. ADDITION 2. SUBTRACTION 3. MULTIPLICATION 4. DIVISION Enter your choice:3 6 1. ADDITION 2. SUBTRACTION 3. MULTIPLICATION 4. DIVISION Enter your choice:4 1.5 1. ADDITION 2. SUBTRACTION 3. MULTIPLICATION 4. DIVISION Enter your choice:5 Invalid choice
Hence, we have successfully created a class of basic calculator in python.
NOTE: There may be other possible methods to solve this problem.
Python Program to Build a Calculator using OOP
Problem: Write a Python program to create a simple calculator i.e a calculator with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division functionality using object-oriented programming (OOP).
To create a basic calculator in python we first need to create a class and define different functionalities like addition, subtraction, etc into separate methods.
After that, we will ask the user to choose what functionality they want to execute through an input, then the user will input the required variables and the respective function will be called to compute the result.
Let’s try to implement it in python.
Source Code:
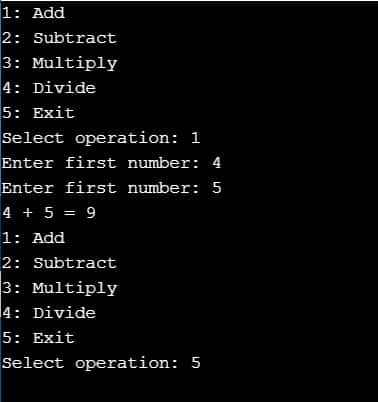
class Calculator: def add(self, a, b): return a+b def subtract(self, a, b): return a-b def multiply(self, a, b): return a*b def divide(self, a, b): return a/b #create a calculator object my_cl = Calculator() while True: print("1: Add") print("2: Subtract") print("3: Multiply") print("4: Divide") print("5: Exit") ch = int(input("Select operation: ")) #Make sure the user have entered the valid choice if ch in (1, 2, 3, 4, 5): #first check whether user want to exit if(ch == 5): break #If not then ask fo the input and call appropiate methods a = int(input("Enter first number: ")) b = int(input("Enter second number: ")) if(ch == 1): print(a, "+", b, "=", my_cl.add(a, b)) elif(ch == 2): print(a, "-", b, "=", my_cl.subtract(a, b)) elif(ch == 3): print(a, "*", b, "=", my_cl.multiply(a, b)) elif(ch == 4): print(a, "/", b, "=", my_cl.divide(a, b)) else: print("Invalid Input")In the above program we have used OOP (i.e class and object) to create a basic python calculator.
Make sure that you typecast the inputs into an integer before using them and also check for invalid inputs prior to calling appropriate methods.
If you have any doubts or suggestions then please comment below.
Классы. Калькулятор
Подскажите ,пожалуйста, как сделать так, что бы значение last записывалось в атрибут класса, а не в атрибут объекта.
class Calculator: last = None def __init__(self): self.history_array = [] def sum(self, a, b): self.history_array.append( a + b) self.last = self.history_array[-1] return a + b def sub(self, a, b): self.history_array.append( a - b) self.last = self.history_array[-1] return a - b def mul(self, a, b): self.history_array.append(a * b) self.last = self.history_array[-1] return a * b def div(self, a, b, mod=False): if mod: self.history_array.append( a % b) self.last = self.history_array[-1] return a % b else: self.history_array.append(a / b) self.last = self.history_array[-1] return a / b def history(self, n): try: result = self.history_array[-n] except IndexError: result = None return result def clear(self): self.last = None @Евгений проблема в том, что эта задача проверяется на яндекс.контесте, для проверки просят в конце добавить две строчки ‘from classes1_tests import Test Test(Calculator).run_all()’ и после проверки выходит ошибка, что last не записывается
3 ответа 3
Пишите соответственно в поле класса, а не в поле объекта:
# яндекс это принял class Calculator: history_array = None def __init__(self): self.history_array = [] last_operation = None @property def last(self): return Calculator.last_operation def sum(self, a, b): self.history_array.append('sum(<>, <>) == <>'.format(a, b, a + b)) Calculator.last_operation = self.history_array[-1] return a + b def sub(self, a, b): self.history_array.append('sub(<>, <>) == <>'.format(a, b, a - b)) Calculator.last_operation = self.history_array[-1] return a - b def mul(self, a, b): self.history_array.append('mul(<>, <>) == <>'.format(a, b, a * b)) Calculator.last_operation = self.history_array[-1] return a * b def div(self, a, b, mod=False): if mod: self.history_array.append('div(<>, <>) == <>'.format(a, b, a % b)) Calculator.last_operation = self.history_array[-1] return a % b else: self.history_array.append('div(<>, <>) == <>'.format(a, b, a / b)) Calculator.last_operation = self.history_array[-1] return a / b def history(self, n): try: result = self.history_array[-n] except IndexError: result = None return result def clear(self): Calculator.last_operation = None from classes1_tests import Test Test(Calculator).run_all() Так как Вы явно не до конца понимаете что такое классы и их атрибуты, поля, методы и т.д.
Переменные, принадлежащие объекту или классу, называют полями. Объекты могут также обладать функционалом, т.е. иметь функции, принадлежащие классу. Такие функции принято называть методами класса. Эта терминология важна, так как она помогает нам отличать независимые функции и переменные от тех, что принадлежат классу или объекту. Всё вместе (поля и методы) принято называть атрибутами класса.
Python Object-Oriented Programming: Calculator class for basic arithmetic
Write a Python program to create a calculator class. Include methods for basic arithmetic operations.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
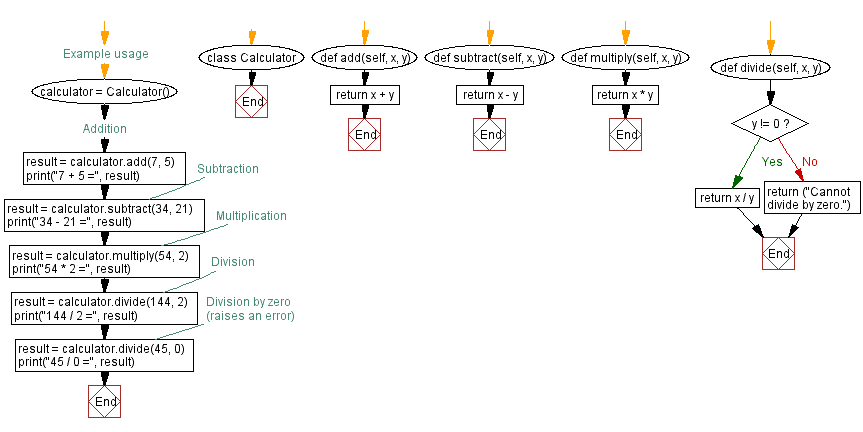
class Calculator: def add(self, x, y): return x + y def subtract(self, x, y): return x - y def multiply(self, x, y): return x * y def divide(self, x, y): if y != 0: return x / y else: return ("Cannot divide by zero.") # Example usage calculator = Calculator() # Addition result = calculator.add(7, 5) print("7 + 5 =", result) # Subtraction result = calculator.subtract(34, 21) print("34 - 21 =", result) # Multiplication result = calculator.multiply(54, 2) print("54 * 2 =", result) # Division result = calculator.divide(144, 2) print("144 / 2 =", result) # Division by zero (raises an error) result = calculator.divide(45, 0) print("45 / 0 output"> 7 + 5 = 12 34 - 21 = 13 54 * 2 = 108 144 / 2 = 72.0 45 / 0 = Cannot divide by zero. Explanation:
In the above exercise, we define a class called Calculator with methods add, subtract, multiply, and divide, representing basic arithmetic operations.
The add method performs addition of two numbers, subtract performs subtraction, multiply performs multiplication, and divide performs division. If the denominator is zero, the divide method returns an error message to avoid division by zero.
As an example, we create a Calculator instance, «calculator», and use it to perform various arithmetic operations.
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource’s quiz.