- Удаление всех пакетов, установленных через pip
- Как удалить все пакеты python
- # Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip in Python
- # Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip using xargs
- # Recreate your virtual environment
- # Additional Resources
- How to Uninstall Python Packages
- Checklist
- How to Uninstall Packages Installed with Pip
- How to Uninstall Packages in a Python Virtual Environment
- How to Globally Uninstall Python Packages
- How to Uninstall Package Dependencies with Pip
- How to Uninstall Package Dependencies with Pipenv
- How to Uninstall a Package Installed With Setuptools
- Next Steps
- How to remove all packages installed by PIP in Python
- How to uninstall the package individually
- How to uninstall all the Python packages
- Latest Posts
Удаление всех пакетов, установленных через pip
Существует множество случаев, когда может возникнуть необходимость удалить все пакеты, установленные через pip в рамках определенного виртуального окружения. Например, это может быть полезно при переходе к новой версии Python или при необходимости «почистить» рабочее пространство для нового проекта.
Чтобы удалить все пакеты, установленные через pip, можно использовать команду pip freeze , которая выводит список всех установленных пакетов, а затем передать вывод этой команды в pip uninstall с использованием параметра -y , который автоматически подтверждает удаление каждого пакета.
В общем виде команда выглядит так:
pip freeze | xargs pip uninstall -y Она работает следующим образом:
- pip freeze создает список всех установленных пакетов.
- xargs берет этот список и передает каждый элемент в качестве аргумента для следующей команды.
- pip uninstall -y удаляет каждый пакет, переданный ей xargs .
Эта команда должна быть выполнена в активированном виртуальном окружении, из которого требуется удалить пакеты. Если виртуальное окружение не активировано, эта команда удалит пакеты из глобального пространства Python, что, скорее всего, не является желаемым действием.
Важно отметить, что эта команда удалит все пакеты, включая pip, поэтому после ее выполнения может потребоваться повторная установка pip или других необходимых пакетов.
Как удалить все пакеты python
Last updated: Feb 20, 2023
Reading time · 4 min
# Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip in Python
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages and uninstalls them without asking for confirmation.
Copied!# 👇️ optionally save the packages that are to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip pip uninstall -y -r (pip freeze)
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages in requirements format and uninstalls the packages.
The -y option is short for -yes and means that pip should not ask for confirmation when uninstalling.
The -r option is short for —requirement and uninstalls all the packages in the given requirements file.
If you need to install the packages again, use the pip install -r command.
Copied!pip install -r to_remove.txt
If you get an error message that setuptools is not installed, e.g. No module named ‘pkg_resources’, run the following command.
Copied!# 👇️ for Linux or MacOS python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ try upgrading pip pip install --upgrade pip setuptools pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools
You can also store the installed packages in a file and uninstall them directly from the file.
Copied!# 👇️ store the installed packages in a file called reqs.txt pip freeze > reqs.txt # 👇️ uninstall packages 1 by 1 pip uninstall -r reqs.txt # 👇️ uninstall all packages without confirmation required pip uninstall -r reqs.txt -y
I used the name reqs.txt because you might not want to override the contents of your existing requirements.txt (if you already have one).
# Remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip using xargs
Alternatively, you can use xargs to remove all packages installed by pip .
Copied!# 👇️ optionally save the packages that are to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ remove/uninstall all packages installed by pip pip freeze | xargs pip uninstall -y
The command uses pip freeze to get a list of the installed packages and then uses xargs to pass the packages as an argument to the pip uninstall command.
We then used the xargs command to pass the installed packages as an argument to the pip uninstall command.
The -y (yes) option makes it so pip doesn’t ask for confirmation when uninstalling packages.
If you need to install the packages again, use the pip install -r command.
Copied!pip install -r to_remove.txt
You might have to install pip , setuptools and wheel after running the command.
Copied!# 👇️ for Linux or MacOS python -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ Windows py -m pip install --upgrade pip setuptools wheel # 👇️ try upgrading pip pip install --upgrade pip setuptools pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools
# Recreate your virtual environment
Alternatively, you can simply recreate your virtual environment.
- Deactivate your virtual environment.
- Delete the folder of your virtual environment.
- Create a new virtual environment.
- Activate the new virtual environment.
Copied!# 👇️ (optional) store the packages to be removed pip freeze > to_remove.txt # 👇️ deactivate deactivate # 👇️ Remove the old virtual environment folder: macOS and Linux rm -rf venv # 👇️ Remove the old virtual environment folder: Windows rd /s /q "venv" # 👇️ initialize a new virtual environment python -m venv venv # 👇️ activate on Unix or MacOS source venv/bin/activate # 👇️ activate on Windows (cmd.exe) venv\Scripts\activate.bat # 👇️ activate on Windows (PowerShell) venv\Scripts\Activate.ps1 # 👇️ (optional) install the modules in your requirements.txt file pip install -r requirements.txt
If running python -m venv venv doesn’t work, try the following commands:
We used the deactivate command to deactivate the virtual environment, deleted the venv folder and created a new virtual environment.
Your virtual environment will use the version of Python that was used to create it.
Make sure to use the correct activation command depending on your operating system.
You might have to upgrade your pip version in the new virtual environment.
Copied!pip install --upgrade pip
You can use the pip install -r requirements.txt command in the new virtual environment if you need to install any packages from a requirements file.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
I wrote a book in which I share everything I know about how to become a better, more efficient programmer.
How to Uninstall Python Packages
All Python package management solutions provide the basic function of uninstalling packages, including pip, pipenv and the ActiveState Platform. However, unless specifically defined in a requirements.txt or pipfile.lock, package managers will not deal with transitive dependencies (ie., dependencies of dependencies).
In this article, we explain how to uninstall Python packages using these popular tools and we also introduce you to the ActiveState Platform. The AS Platform is unique in automatically installing and uninstalling transitive dependencies. Our dependency management system makes it possible to track conflicts between packages, know about platform-specific dependencies, and even track system-level dependencies like C and C++ libraries. Once you are done reading, you can try the ActiveState Platform by signing up for a free account .
Read on to understand how to work with Pip and Pipenv Package Managers to uninstall Python packages.
Checklist
Before packages can be uninstalled, ensure that a Python installation containing the necessary files needed for uninstalling packages is in place. Installation Requirements (for Windows).
How to Uninstall Packages Installed with Pip
How to Uninstall Packages in a Python Virtual Environment
Packages can be uninstalled from a virtual environment using pip or pipenv.
To use pip to uninstall a package locally in a virtual environment:
- Open a command or terminal window (depending on the operating system)
- cd into the project directory
- pip uninstall
To use pipenv to uninstall a package locally in a virtual environment created with venv or virtualenv:
- Open a command or terminal window (depending on the operating system)
- cd into the project directory
- pipenv uninstall
How to Globally Uninstall Python Packages
In some cases, packages may be installed both locally (e.g., for use in a specific project) and system-wide. To ensure a package is completely removed from your system after you’ve uninstalled it locally, you’ll also need to uninstall it globally.
To uninstall a package globally in Windows:
-
- Open a command window by entering ‘cmd’ in the Search Box of the Task bar
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Enter to gain Administration (Admin) privileges
- pip uninstall
To uninstall a package globally in Linux:
How to Uninstall Package Dependencies with Pip
When you install a package with pip, it also installs all of the dependencies the package requires. Unfortunately, pip does not uninstall dependencies when you uninstall the original package. Here are a couple of different procedures that can be used to uninstall dependencies.
- If a package has been installed via a pip requirements file (i.e., pip install requirements.txt ), all of the packages in requirements.txt can be uninstalled with the following command:
pip uninstall requirements.txt- If a requirements.txt file is not available, you can use the pip show command to output all the requirements of a specified package:
Output should be similar to:
These dependencies can then be uninstalled with the pip uninstall command. However before uninstalling, you should ensure that the packages are NOT dependencies for other existing packages.
How to Uninstall Package Dependencies with Pipenv
To uninstall all the dependencies in a Pipenv project:
- Open a command or terminal window
- cd into the project directory
- pipenv uninstall —all
How to Uninstall a Package Installed With Setuptools
Any packages that have been configured and installed with setuptools used the following command:
Unfortunately, there is no python setup.py uninstall command. To uninstall a package installed with setup.py, use the pip command:
Be aware that there are a few exceptions that cannot be uninstalled with pip, including:
- Distutils packages, which do not provide metadata indicating which files were installed.
- Script wrappers installed by the setup.py develop command.
Next Steps
Resolving packages when installing or uninstalling an environment can be an extremely slow (or even manual) process. You can speed things up considerably using the ActiveState Platform, which automatically resolves dependencies for you–fast! Get started free on the ActiveState Platform.
Or just install Python 3.9 and use the included command line interface, the State Tool, to “state install” the packages you need:
>state install numpy ╔════════════════════╗ ║ Installing Package ║ ╚════════════════════╝ Updating Runtime ──────────────── Changes to your runtime may require some dependencies to be rebuilt. numpy includes 2 dependencies, for a combined total of 8 new dependencies. Building 8/8 Installing 8/8 Package added: numpy
How to remove all packages installed by PIP in Python
When you are developing in Python, you will probably use Python packages a lot. If you are not using virtualenv and directly developing with a local Python environment, the number of packages you installed would a lot and at some point, you might want to do some cleanup.
Note: In this demo, I’m using macOS Big Sur (11.0.1) but the method should work on any environment.
How to uninstall the package individually
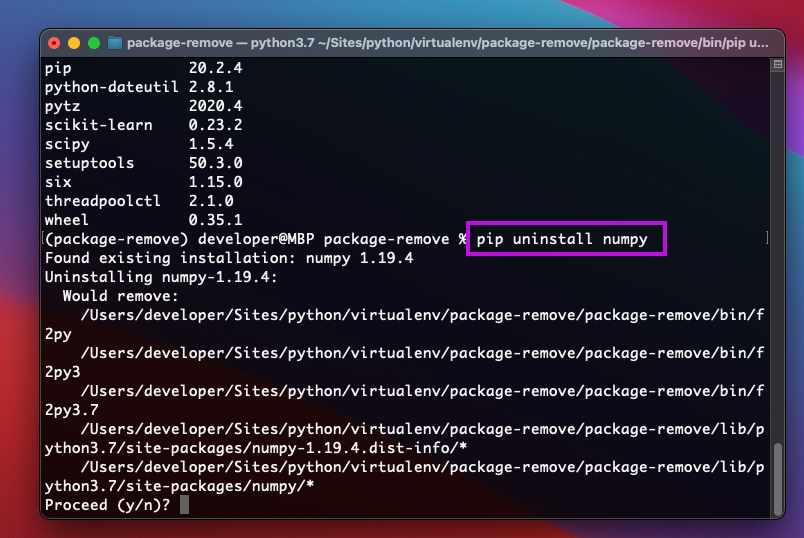
To uninstall individual Python package, you need to execute the below command in the CLI.
pip uninstall [package name]
In the [package name], put the name of the package you want to uninstall.
How to uninstall all the Python packages
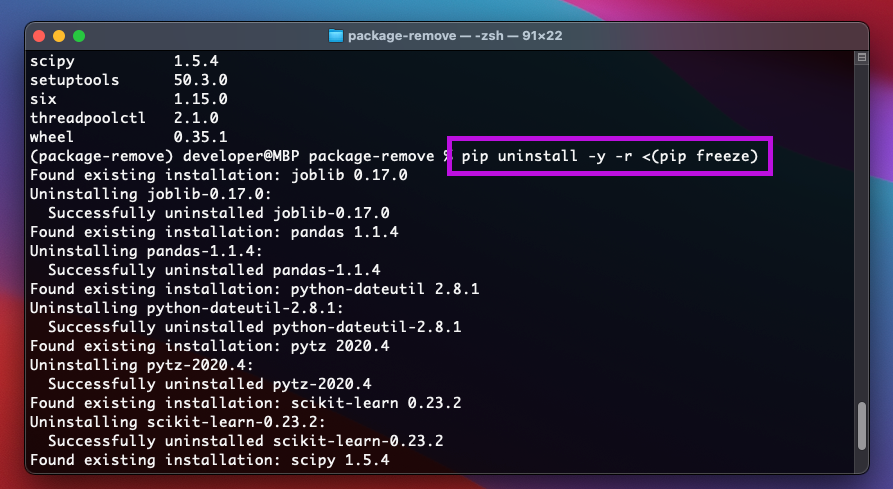
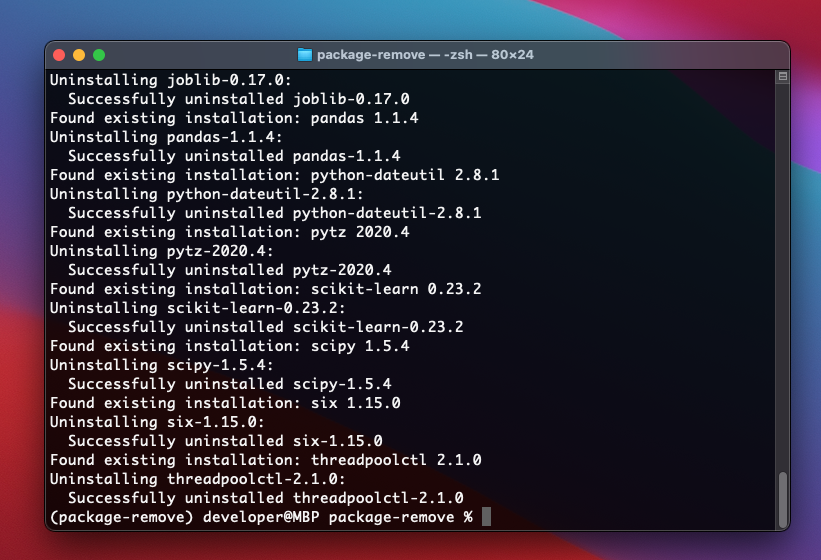
To uninstall all the Python packages, use the below command.
Above command will uninstall all requirement file (by using -r ) and accept all (by using -y ) that is in the freeze list
As you can see the above screenshots, it will uninstall all the packages you have installed.
Please check out also How to use VirtualEnv in Python to learn more about an organized way to develop a Python app.
Latest Posts
Feel free to share this post!