Class ConcurrentHashMap
A hash table supporting full concurrency of retrievals and high expected concurrency for updates. This class obeys the same functional specification as Hashtable , and includes versions of methods corresponding to each method of Hashtable . However, even though all operations are thread-safe, retrieval operations do not entail locking, and there is not any support for locking the entire table in a way that prevents all access. This class is fully interoperable with Hashtable in programs that rely on its thread safety but not on its synchronization details.
Retrieval operations (including get ) generally do not block, so may overlap with update operations (including put and remove ). Retrievals reflect the results of the most recently completed update operations holding upon their onset. (More formally, an update operation for a given key bears a happens-before relation with any (non-null) retrieval for that key reporting the updated value.) For aggregate operations such as putAll and clear , concurrent retrievals may reflect insertion or removal of only some entries. Similarly, Iterators, Spliterators and Enumerations return elements reflecting the state of the hash table at some point at or since the creation of the iterator/enumeration. They do not throw ConcurrentModificationException . However, iterators are designed to be used by only one thread at a time. Bear in mind that the results of aggregate status methods including size , isEmpty , and containsValue are typically useful only when a map is not undergoing concurrent updates in other threads. Otherwise the results of these methods reflect transient states that may be adequate for monitoring or estimation purposes, but not for program control.
The table is dynamically expanded when there are too many collisions (i.e., keys that have distinct hash codes but fall into the same slot modulo the table size), with the expected average effect of maintaining roughly two bins per mapping (corresponding to a 0.75 load factor threshold for resizing). There may be much variance around this average as mappings are added and removed, but overall, this maintains a commonly accepted time/space tradeoff for hash tables. However, resizing this or any other kind of hash table may be a relatively slow operation. When possible, it is a good idea to provide a size estimate as an optional initialCapacity constructor argument. An additional optional loadFactor constructor argument provides a further means of customizing initial table capacity by specifying the table density to be used in calculating the amount of space to allocate for the given number of elements. Also, for compatibility with previous versions of this class, constructors may optionally specify an expected concurrencyLevel as an additional hint for internal sizing. Note that using many keys with exactly the same hashCode() is a sure way to slow down performance of any hash table. To ameliorate impact, when keys are Comparable , this class may use comparison order among keys to help break ties.
A Set projection of a ConcurrentHashMap may be created (using newKeySet() or newKeySet(int) ), or viewed (using keySet(Object) when only keys are of interest, and the mapped values are (perhaps transiently) not used or all take the same mapping value.
A ConcurrentHashMap can be used as a scalable frequency map (a form of histogram or multiset) by using LongAdder values and initializing via computeIfAbsent . For example, to add a count to a ConcurrentHashMap freqs , you can use freqs.computeIfAbsent(key, k -> new LongAdder()).increment();
This class and its views and iterators implement all of the optional methods of the Map and Iterator interfaces.
Like Hashtable but unlike HashMap , this class does not allow null to be used as a key or value.
- forEach: Performs a given action on each element. A variant form applies a given transformation on each element before performing the action.
- search: Returns the first available non-null result of applying a given function on each element; skipping further search when a result is found.
- reduce: Accumulates each element. The supplied reduction function cannot rely on ordering (more formally, it should be both associative and commutative). There are five variants:
- Plain reductions. (There is not a form of this method for (key, value) function arguments since there is no corresponding return type.)
- Mapped reductions that accumulate the results of a given function applied to each element.
- Reductions to scalar doubles, longs, and ints, using a given basis value.
These bulk operations accept a parallelismThreshold argument. Methods proceed sequentially if the current map size is estimated to be less than the given threshold. Using a value of Long.MAX_VALUE suppresses all parallelism. Using a value of 1 results in maximal parallelism by partitioning into enough subtasks to fully utilize the ForkJoinPool.commonPool() that is used for all parallel computations. Normally, you would initially choose one of these extreme values, and then measure performance of using in-between values that trade off overhead versus throughput.
The concurrency properties of bulk operations follow from those of ConcurrentHashMap: Any non-null result returned from get(key) and related access methods bears a happens-before relation with the associated insertion or update. The result of any bulk operation reflects the composition of these per-element relations (but is not necessarily atomic with respect to the map as a whole unless it is somehow known to be quiescent). Conversely, because keys and values in the map are never null, null serves as a reliable atomic indicator of the current lack of any result. To maintain this property, null serves as an implicit basis for all non-scalar reduction operations. For the double, long, and int versions, the basis should be one that, when combined with any other value, returns that other value (more formally, it should be the identity element for the reduction). Most common reductions have these properties; for example, computing a sum with basis 0 or a minimum with basis MAX_VALUE.
Search and transformation functions provided as arguments should similarly return null to indicate the lack of any result (in which case it is not used). In the case of mapped reductions, this also enables transformations to serve as filters, returning null (or, in the case of primitive specializations, the identity basis) if the element should not be combined. You can create compound transformations and filterings by composing them yourself under this «null means there is nothing there now» rule before using them in search or reduce operations.
Methods accepting and/or returning Entry arguments maintain key-value associations. They may be useful for example when finding the key for the greatest value. Note that «plain» Entry arguments can be supplied using new AbstractMap.SimpleEntry(k,v) .
Bulk operations may complete abruptly, throwing an exception encountered in the application of a supplied function. Bear in mind when handling such exceptions that other concurrently executing functions could also have thrown exceptions, or would have done so if the first exception had not occurred.
Speedups for parallel compared to sequential forms are common but not guaranteed. Parallel operations involving brief functions on small maps may execute more slowly than sequential forms if the underlying work to parallelize the computation is more expensive than the computation itself. Similarly, parallelization may not lead to much actual parallelism if all processors are busy performing unrelated tasks.
All arguments to all task methods must be non-null.
This class is a member of the Java Collections Framework.
СодержаниеКак работает ConcurrentHashMap
В октябре на хабре появилась замечательная статья про работу HashMap. Продолжая данную тему, я собираюсь рассказать о реализации java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap.
Итак, как же появился ConcurrentHashMap, какие у него есть преимущества и как он был реализован.Предпосылки к созданию ConcurrentHashMap
- Не каждый программист и не каждое решение нуждались в использовании потокобезопасной хэш-таблицы
- Программисту необходимо было дать выбор, какой вариант ему удобно использовать
ConcurrentHashMap
- Потокобезопасность
- Отсутствие блокировок всей таблицы на время доступа к ней
- Желательно, чтобы отсутствовали блокировки таблицы при выполнении операции чтения
1. Элементы карты
В отличие от элементов HashMap, Entry в ConcurrentHashMap объявлены как volatile. Это важная особенность, также связанная с изменениями в JMM. Ответ Doug Lea о необходимости использования volatile и возможных race condition можно прочитать здесь.
static final class HashEntry < final K key; final int hash; volatile V value; final HashEntrynext; HashEntry(K key, int hash, HashEntry next, V value) < this .key = key; this .hash = hash; this .next = next; this .value = value; >@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") static final HashEntry[] newArray(int i) < return new HashEntry[i]; >>2. Хэш-функция
В ConcurrentHashMap также используется улучшенная функция хэширования.
Напомню, какой она была в HashMap из JDK 1.2:static int hash(int h) < h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); >
Версия из ConcurrentHashMap JDK 1.5:
private static int hash(int h) < h += (h >> 10); h += (h >> 6); h += (h >> 16); >
В чём необходимость усложнения хэш-функции? Таблицы в хэш-карте имеют длину, определяемую степенью двойки. Для хэш-кодов, двоичные представления которых не различаются в младшей и старшей позиции, мы будем иметь коллизии. Усложнение хэш-функции как раз решает данную проблему, уменьшая вероятность коллизий в карте.
3. Сегменты
Карта делится на N различных сегментов (16 по умолчанию, максимальное значение может быть 16-битным и представлять собой степень двойки). Каждый сегмент представляет собой потокобезопасную таблицу элементов карты.
Между хэш-кодами ключей и соответствующими им сегментами устанавливается зависимость на основе применения к старшим разрядам хэш-кода битовой маски.
Вот как в карте хранятся элементы:final Segment[] segments; transient Set keySet; transient Set
entrySet; transient Collection values; Рассмотрим, что же представляет из себя класс сегмента:
static final class Segment extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable < private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L; transient volatile int count; transient int modCount; transient int threshold; transient volatile HashEntry[] table; final float loadFactor; Segment(int initialCapacity, float lf) < loadFactor = lf; setTable(HashEntry.newArray(initialCapacity)); > . >
Учитывая псевдослучайное распределение хэшей ключей внутри таблицы, можно понять, что увеличение количества сегментов будет способствовать тому, что операции модификации будут затрагивать различные сегменты, что уменьшит вероятность блокировок во время выполнения.
4. ConcurrencyLevel
Данный параметр влияет на использование картой памяти и количество сегментов в карте.
Посмотрим на создание карты и на то, как влияет заданный в качестве парамента конструктора concurrencyLevel:public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) < if (!(loadFactor >0) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; // Find power-of-two sizes best matching arguments int sshift = 0; int ssize = 1; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) < ++sshift; ssize segmentShift = 32 - sshift; segmentMask = ssize - 1; this .segments = Segment.newArray(ssize); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = 1; while (cap < c) cap (cap, loadFactor); >
Количество сегментов будет выбрано как ближайшая степень двойки, большая чем concurrencyLevel. Ёмкость каждого сегмента, соответственно, будет определяться как отношение округлённого до ближайшей большей степени двойки значения ёмкости карты по умолчанию, к полученному количеству сегментов.
Очень важно понимать две следующие вещи. Занижение concurrencyLevel ведёт к тому, что более вероятны блокировки потоками сегментов карты при записи. Завышение показателя ведёт к неэффективному использованию памяти.Как же выбрать concurrencyLevel?
Если лишь один поток будет изменять карту, а остальные будут производить чтение — рекомендуется использовать значение 1.
Необходимо помнить, что resize таблиц для хранения внутри карти — опреация, требующая дополнительного времени (и, зачастую, выполняемая не быстро). Поэтому при создании карты требуется иметь некоторые приблизительные оценки по статистике выполнения возможных операций чтения и записи.
Оценки масштабируемости
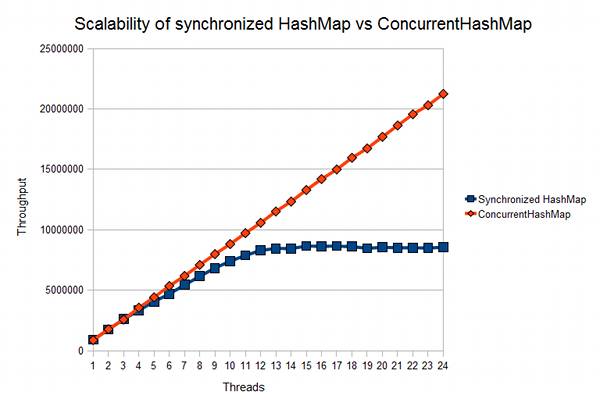
На javamex можно найти статью о сравнении масштабируемости synchronizedMap и ConcurrentHashMap:
Как видно из графика, между 5 и 10 миллионами операций доступа к карте заметно серьёзное расхождение, что обуславливает эффективность применения ConcurrentHashMap в случае с высоким количеством хранимых данных и операций доступа к ним.
Итого
- Карта имеет схожий с hashmap интерфейс взаимодействия
- Операции чтения не требуют блокировок и выполняются параллельно
- Операции записи зачастую также могут выполняться параллельно без блокировок
- При создании указывается требуемый concurrencyLevel, определяемый по статистике чтения и записи
- Элементы карты имеют значение value, объявленное как volatile