- Использование интерактивной консоли Python
- Доступ к интерактивной консоли
- Работа с интерактивной консолью Python
- Многострочный код Python в консоли
- Импорт модулей
- Выход из интерактивной консоли Python
- История консоли Python
- Заключение
- Python console
- Actions available in the Python Console
- Working with Python console
- Preview a variable as an array
- Run source code from the editor in console
- Run asyncio coroutines
- Configure Python console settings
- Run several Python consoles
- Manage the command execution queue
Использование интерактивной консоли Python
Интерактивная консоль Python (также интерпретатор или оболочка Python) предоставляет программистам быстрый способ выполнить команды и протестировать код, не создавая файл.
Интерактивная консоль предоставляет доступ к истории команд, всем встроенным функциям и установленным модулям Python. Она позволяет использовать автозаполнение, исследовать возможности Python и вставлять код в файлы программирования после проверки.
Этот мануал научит вас работать с интерактивной консолью Python.
Доступ к интерактивной консоли
Доступ к интерактивной консоли Python можно получить с любого локального компьютера или сервера, на котором установлен Python.
Для входа в интерактивную консоль Python используйте команду:
Если вы настроили среду разработки, вы можете получить доступ к консоли внутри этой среды. Сначала запустите среду:
cd environments
my_env/bin/activate
Читайте также:
В этом случае по умолчанию используется версия Python 3.5.2, которая отображается на выходе вместе с уведомлением об авторских правах и командами для дополнительной информации:
Python 3.5.2 (default, Nov 17 2016, 17:05:23)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
>>>
Поле для ввода следующей команды – три знака больше:
Вы можете указать определенную версию Python, добавив номер версии в команду без пробелов:
$ python2.7
Python 2.7.12 (default, Nov 19 2016, 06:48:10)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux2
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
>>>
Вывод сообщает, что теперь будет использоваться версия Python 2.7.12. Если бы она была версией Python по умолчанию, открыть её интерактивную консоль можно было бы с помощью команды python2.
Чтобы вызвать интерактивную консоль версии Python 3 по умолчанию, нужно ввести:
$ python3
Python 3.5.2 (default, Nov 17 2016, 17:05:23)
[GCC 5.4.0 20160609] on linux
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
>>>
Также консоль этой версии можно вызвать с помощью команды:
Работа с интерактивной консолью Python
Интерактивный интерпретатор Python принимает синтаксис Python, который находится после префикса >>>.
Например, он позволяет присваивать значения переменным:
Вы можете присвоить значения нескольким переменным, чтобы обрабатывать математические операции.
>>> birth_year = 1868
>>> death_year = 1921
>>> age_at_death = death_year — birth_year
>>> print(age_at_death)
53
>>>
Как и в файле, в консоли можно задать значения переменных, выполнить математическую операцию и запросить результат.
Интерактивную консоль можно использовать как калькулятор.
Многострочный код Python в консоли
При создании многострочного кода в консоли интерпретатор Python использует троеточие (…) в качестве вспомогательной строки.
Чтобы выйти из вспомогательной строки, нужно дважды нажать Enter.
Чтобы понять, как это работает, рассмотрите этот код, который задает значения двум переменным и использует условное выражение, чтобы определить вывод.
>>> 8host = ‘8host’
>>> blog = ‘blog’
>>> if len(8host) > len(blog):
. print(‘8host codes in Java.’)
. else:
. print(‘8host codes in Python.’)
.
8host codes in Java.
>>>
В данном случае первая строка длиннее, чем вторая, потому срабатывает первое условие и программа выводит соответствующую строку.
Обратите внимание, при этом нужно соблюдать соглашение об отступах Python (четыре пробела), иначе вы получите сообщение об ошибке:
>>> if len(8host) > len(blog):
. print(‘8host codes in Java.’)
File «», line 2
print(‘8host codes in Java.’)
^
IndentationError: expected an indented block
>>>
Импорт модулей
Интерпретатор Python позволяет быстро проверить, доступны ли те или иные модули в определенной среде программирования. Для этого существует оператор import:
>>> import matplotlib
Traceback (most recent call last):
File «», line 1, in
ImportError: No module named ‘matplotlib’
В данном случае библиотека matplotlib недоступна в текущей среде.
Чтобы установить эту библиотеку, используйте pip.
pip install matplotlib
Collecting matplotlib
Downloading matplotlib-2.0.2-cp35-cp35m-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (14.6MB)
.
Installing collected packages: pyparsing, cycler, python-dateutil, numpy, pytz, matplotlib
Successfully installed cycler-0.10.0 matplotlib-2.0.2 numpy-1.13.0 pyparsing-2.2.0 python-dateutil-2.6.0 pytz-2017.2
Установив модуль matplotlib и его зависимости, вы можете вернуться в интерактивный интерпретатор.
(my_env) 8host@ubuntu:~/environments$ python
>>>import matplotlib
>>>
Теперь вы можете использовать импортированный модуль в этой среде.
Выход из интерактивной консоли Python
Закрыть консоль Python можно двумя способами: с помощью клавиатуры или с помощью функции Python.
Чтобы закрыть консоль, можно нажать на клавиатуре Ctrl + D в *nix-подобных системах или Ctrl + Z + Ctrl в Windows.
>>> age_at_death = death_year — birth_year
gt;>> print(age_at_death)
53
>>>
8host@ubuntu:~/environments$
Также в Python есть функция quit(), которая закрывает консоль и возвращает вас в стандартный терминал.
>>> octopus = ‘Ollie’
>>> quit()
8host@PythonUbuntu:~/environments$
Функция quit() записывается в историю, а комбинации клавиш – нет. Это следует учитывать при выходе из консоли. Откройте файл истории /home/8host /.python_history
.
age_at_death = death_year — birth_year
print(age_at_death)
octopus = ‘Ollie’
quit()
История консоли Python
Еще одним преимуществом интерактивной консоли Python является история. Все команды регистрируются в файле .python_history (в *nix-подобных системах).
На данный момент файл истории Python выглядит так:
import pygame
quit()
if 10 > 5:
print(«hello, world»)
else:
print(«nope»)
8host = ‘8host’
blog = ‘blog’
.
Чтобы закрыть файл, нажмите Ctrl + X.
Отслеживая историю, вы можете вернуться к предыдущим командам, скопировать, вставить или изменить этот код, а затем использовать его в файлах программы или Jupyter Notebook.
Заключение
Интерактивная консоль Python предоставляет пространство для экспериментов с кодом Python. Вы можете использовать ее как инструмент для тестирования, разработки логики программы и многого другого.
Для отладки файлов программы Python вы можете использовать модуль code и открыть интерактивный интерпретатор внутри файла.
Python console
Python console enables executing Python commands and scripts line by line, similar to your experience with Python Shell.
Actions available in the Python Console
- Type commands and press Enter to execute them. Results are displayed in the same console.
- Use basic code completion Control+Space and tab completion.
- Use the await keyword to run asyncio coroutines.
- Use Up and Down arrow keys to scroll through the history of commands, and execute the required ones.
- Load source code from the editor into console.
- Use the context menu to copy the contents of the console to the clipboard, compare it with the clipboard, or clear the console.
- Use the toolbar buttons to control your session in the console.
- Configure color scheme of the console to meet your preferences. Refer to the section Configure color schemes for consoles for details.
Working with Python console
The console appears as a tool window every time you choose the corresponding command on the Tools menu. You can assign a shortcut to open Python console: press Control+Alt+S , navigate to Keymap , specify a shortcut for Main menu | Tools | Python or Debug Console .
The main reason for using the Python console within PyCharm is to benefit from the main IDE features, such as code completion, code analysis, and quick fixes.
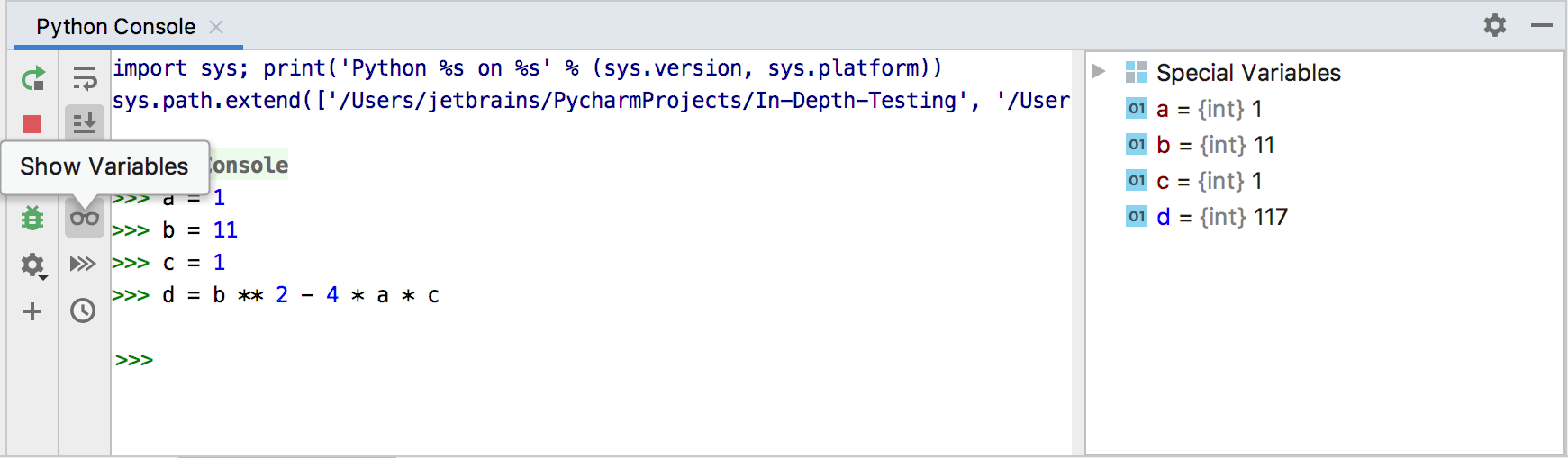
You can use up and down arrow keys to browse through the history of executed commands, and repeat the desired ones. To preview the variable values calculated in the course of the execution, click and check the Special Variables list.
The console is available for all types of Python interpreters and virtual environments, both local and remote.
Preview a variable as an array
When your variables are numpy arrays or dataframes, you can preview them as an array in a separate window. To try it, do one of the following:
- Click the link View as Array / View as DataFrame :
- From the context menu of a variable, choose View as Array / View as DataFrame :
The variable will be opened in the Data tab of the SciView window.
Run source code from the editor in console
- Open file in the editor, and select a fragment of code to be executed.
- From the context menu of the selection, choose Execute Selection in Python Console , or press Alt+Shift+E :
With no selection, the command changes to Execute line in console . Choose this command from the context menu, or press Alt+Shift+E . The line at caret loads into the Python console, and runs.
- Watch the code selection execution:
By default, the Python console executes Python commands using the Python interpreter defined for the project. However, you can assign an alternative Python interpreter.
Run asyncio coroutines
- In the editor, select a fragment of code which contains the definition of an asyncio coroutine.
- From the context menu, select Execute Selection in Python Console , or press Alt+Shift+E :
- After the code is executed on the Python console, run the coroutine by using the await keyword:
Configure Python console settings
- In the Settings dialog ( Control+Alt+S ), select Build, Execution, Deployment | Console | Python Console .
- Select any available interpreter from the Python interpreter list. Note that you cannot introduce a new interpreter here. If you want to come up with the new interpreter, you need to create it first.
- In needed, click the Configure Interpreters link to inspect the list of the installed packages and add new ones. Mind the code in the Starting script area. It contains the script that will be executed after you open the Python console. Use it to pre-code some required Python commands.
When working on several Python scripts, you might want to execute each in a separate Python console.
Run several Python consoles
- Click to add a new Python console.
- By default, each console has the name Python Console with an index. To make a console reflect the script you’re running, right-click the console tab, select Rename Console , and enter any meaningful name.
All the commands you’re running in the Python console are executed one by one. If the commands require substantial time to get executed, you might want to preview and manage the execution queue.
Manage the command execution queue
- Go to Settings | Build, Execution, Deployment | Console and enable the Command queue for Python Console checkbox.
- Click on the console toolbar to open the queue.
- In the Python Console Command Queue dialog, review the list of commands. If needed, click to delete the command from the queue.
Note, once the command is executed, it disappears from the queue. To preview all previously executed commands browse the console history ().