- How to terminate Scanner when input is complete?
- 8 Answers 8
- How to Close a Scanner in Java
- How to Close a Scanner in Java?
- Syntax
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Farah Batool
- Close a Scanner in Java
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing the Standard Input From the User
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing a Specified String That Has New Line Characters in Between
- Use the close() Method to Close Scanner in Java After Reading the Contents of a File
- Related Article — Java Scanner
- In this tutorial, we will learn how to close a scanner in Java, and when we should use it. The Scanner class has a method close() that is especially available to close the opened scanner. Even if we don’t call the close() method explicitly, the interface Closeable will be invoked, closing the stream. It is a good practice to close a scanner explicitly.
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing the Standard Input From the User
- Also Read: How to Cancel, Close or Pause Your Shopify Store
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing a Specified String That Has New Line Characters in Between
- Also Read: How To Close Apps On Apple TV
- Use the close() Method to Close Scanner in Java After Reading the Contents of a File
- How to close scanner in java?
How to terminate Scanner when input is complete?
Just wondering how I can terminate the program after I have completed entering the inputs? As the scanner would still continue after several «Enter» assuming I am going to continue entering inputs. I tried:
if (scan.nextLine() == null) System.exit(0); if (scan.nextLine() == "") System.exit(0); 8 Answers 8
The problem is that a program (like yours) does not know that the user has completed entering inputs unless the user . somehow . tells it so.
There are two ways that the user could do this:
- Enter an «end of file» marker. On UNIX and Mac OS that is (typically) CTRL + D , and on Windows CTRL + Z . That will result in hasNextLine() returning false .
- Enter some special input that is recognized by the program as meaning «I’m done». For instance, it could be an empty line, or some special value like «exit». The program needs to test for this specifically.
(You could also conceivably use a timer, and assume that the user has finished if they don’t enter any input for N seconds, or N minutes. But that is not a user-friendly way, and in many cases it would be dangerous.)
The reason your current version is failing is that you are using == to test for an empty String. You should use either the equals or isEmpty methods. (See How do I compare strings in Java?)
Other things to consider are case sensitivity (e.g. «exit» versus «Exit») and the effects of leading or trailing whitespace (e.g. » exit» versus «exit»).
How to Close a Scanner in Java
Java Scanner is a class used to read data from files, strings, and users. This class belongs to the java.util package. More specifically, the close() method of the Scanner class is used to close the opened Scanner object. It is recommended to close the Scanner after performing any tasks on the Scanner instance; otherwise, the Scanner will be activated and potentially cause data leaks.
This article will discuss how to close a scanner in Java with a detailed example.
How to Close a Scanner in Java?
In Java, the close() method of the Scanner class is utilized for closing a Scanner. This method accepts no arguments and returns nothing. It just terminates the current Scanner instance.
Syntax
The syntax of the close() method is given as:
Here, sc is an instance of the Scanner class that invokes the close() method.
Note: If the Scanner has already been closed, the close() method will not perform any operation. Similarly, after closing the Scanner, if you want to access something or execute some lines of code, it will throw an IllegalStateException.
Example
In this example, we will print out a string using the Scanner class, then close the Scanner using the close() method, and again try to print another string which will throw an exception.
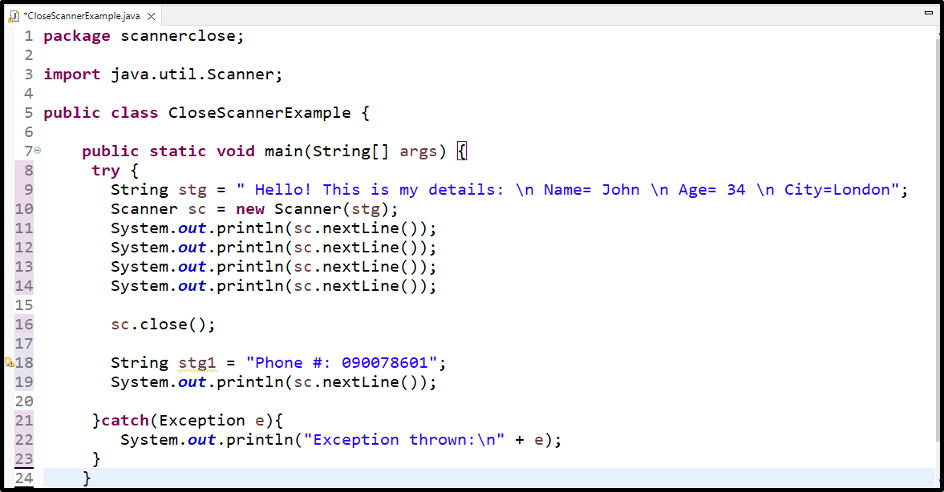
First, we will store a string in the variable stg. Here \n indicates a new line:
Create a new object sc of the Scanner Class and pass the string stg to it as an argument:
Print the string by using the nextLine() method with object sc. This method will detect a new line, move to that line, and then print it. We call the nextLine() method four times to print all the lines of the string stg:
System . out . println ( sc. nextLine ( ) ) ;
System . out . println ( sc. nextLine ( ) ) ;
System . out . println ( sc. nextLine ( ) ) ;
System . out . println ( sc. nextLine ( ) ) ;
After printing the string, we will close the Scanner object sc by using the close() method:
After closing the Scanner, we will again create one more string named stg1 and execute it by using the same object sc:
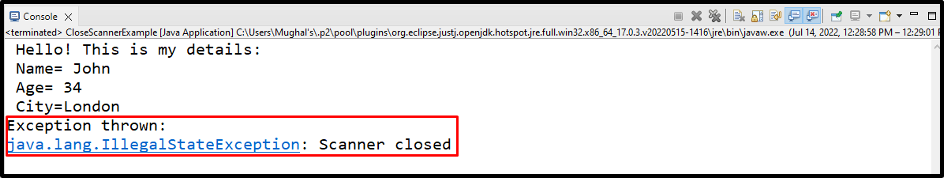
The given output indicates that we have successfully closed the Scanner at first, and re-accessing it throws an IllegalStateException:
We have provided the guidelines related to closing a Scanner in Java.
Conclusion
To close a Scanner in Java, you can use a close() method of the Scanner class. This method takes no arguments, returns nothing, and terminates the current Scanner instance. To utilize the close() method, create an object of the Java Scanner class and invoke the close() method with it. Also, re-accessing a closed Scanner throws an IllegalStateException. This article discussed the procedure of closing a Scanner in Java.
About the author
Farah Batool
I completed my master’s degree in computer science. I am an academic researcher and love to learn and write about new technologies. I am passionate about writing and sharing my experience with the world.
Close a Scanner in Java
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing the Standard Input From the User
- Close a Scanner in Java After Printing a Specified String That Has New Line Characters in Between
- Use the close() Method to Close Scanner in Java After Reading the Contents of a File
In this tutorial, we will learn how to close a scanner in Java, and when we should use it. The Scanner class has a method close() that is especially available to close the opened scanner. Even if we don’t call the close() method explicitly, the interface Closeable will be invoked, closing the stream. It is a good practice to close a scanner explicitly.
Below are the examples that show how and when we can use the Scanner.close() method.
Close a Scanner in Java After Printing the Standard Input From the User
In the code below, we have created a Scanner object in that takes the System.in standard input from the user in the constructor. The method nextLine() returns the input that was skipped. It reads the entire line of input till the end of the line, including spaces and line separators.
The input is printed, and then we close the Scanner by calling the close() method on the Scanner object in . After the Scanner is closed, if we want to use in like we are doing below with myString2 , it will throw an exception because the stream or Scanner has been closed.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CloseScanner public static void main (String [] args) Scanner in = new Scanner (System.in); System.out.print ("Enter a String: "); String mystring = in.nextLine(); System.out.println("The String you entered is: " + mystring); in.close(); String myString2 = in.nextLine(); System.out.println(myString2); > > Enter a String: the cat is white The String you entered is: the cat is white Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Scanner closed at java.base/java.util.Scanner.ensureOpen(Scanner.java:1150) at java.base/java.util.Scanner.findWithinHorizon(Scanner.java:1781) at java.base/java.util.Scanner.nextLine(Scanner.java:1649) at com.company.Main.main(Main.java:20) Close a Scanner in Java After Printing a Specified String That Has New Line Characters in Between
In this example, we will separate the string s into different lines using \n and nextLine() . \n is used to indicate a new line, and as the scanner.nextLine() notices a new line, it goes to a new line and then prints it. Thus the output has all the three subjects in s in different lines.
This is one of the situations when we might want to call the close() method as we don’t want the scanner to scan any further new lines.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CloseScanner public static void main (String [] args) try String s = " English \n Maths \n Science "; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(s); System.out.println(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println(scanner.nextLine()); System.out.println(scanner.nextLine()); scanner.close(); >catch(Exception e) System.out.println(e.getMessage()); > > > Use the close() Method to Close Scanner in Java After Reading the Contents of a File
It is recommended to always close the Scanner when we are reading a file. It ensures that no input or output stream is opened, which is not in use. The following example shows how we can read a string from the file and then close the scanner once the operation has been done.
import java.io.File; import java.util.Scanner; public class CloseScanner public static void main (String [] args) try File file = new File("/Users/john/Documents/Example.txt"); Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); while (scanner.hasNext()) sb.append(" " + scanner.nextLine()); > System.out.println(sb); scanner.close(); > catch(Exception e) System.out.println(e.getMessage()); > > > Hello, You are in a text file. Rupam Saini is an android developer, who also works sometimes as a web developer., He likes to read books and write about various things.
Related Article — Java Scanner
Copyright © 2023. All right reserved
In this tutorial, we will learn how to close a scanner in Java, and when we should use it. The Scanner class has a method close() that is especially available to close the opened scanner. Even if we don’t call the close() method explicitly, the interface Closeable will be invoked, closing the stream. It is a good practice to close a scanner explicitly.
Below are the examples that show how and when we can use the Scanner.close() method.
Close a Scanner in Java After Printing the Standard Input From the User
In the code below, we have created a Scanner object in that takes the System.in standard input from the user in the constructor. The method nextLine() returns the input that was skipped. It reads the entire line of input till the end of the line, including spaces and line separators.
The input is printed, and then we close the Scanner by calling the close() method on the Scanner object in . After the Scanner is closed, if we want to use in like we are doing below with myString2 , it will throw an exception because the stream or Scanner has been closed.
import java . util . Scanner ;
public class CloseScanner
public static void main ( String [] args )
Scanner in = new Scanner ( System . in );
System . out . print ( “Enter a String: “ );
String mystring = in . nextLine ();
System . out . println ( “The String you entered is: “ + mystring );
String myString2 = in . nextLine ();
System . out . println ( myString2 );
Enter a String: the cat is white
The String you entered is: the cat is white
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.IllegalStateException: Scanner closed
Also Read: How to Cancel, Close or Pause Your Shopify Store
Close a Scanner in Java After Printing a Specified String That Has New Line Characters in Between
In this example, we will separate the string s into different lines using \n and nextLine() . \n is used to indicate a new line, and as the scanner.nextLine() notices a new line, it goes to a new line and then prints it. Thus the output has all the three subjects in s in different lines.
This is one of the situations when we might want to call the close() method as we don’t want the scanner to scan any further new lines.
import java . util . Scanner ;
public class CloseScanner
public static void main ( String [] args )
String s = ” English \n Maths \n Science “ ;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( s );
System . out . println ( scanner . nextLine ());
System . out . println ( scanner . nextLine ());
System . out . println ( scanner . nextLine ());
System . out . println ( e . getMessage ());
Also Read: How To Close Apps On Apple TV
Use the close() Method to Close Scanner in Java After Reading the Contents of a File
It is recommended to always close the Scanner when we are reading a file. It ensures that no input or output stream is opened, which is not in use. The following example shows how we can read a string from the file and then close the scanner once the operation has been done.
import java . io . File ; import java . util . Scanner ;
public class CloseScanner
public static void main ( String [] args )
File file = new File ( “/Users/john/Documents/Example.txt” );
Scanner scanner = new Scanner ( file );
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer ();
sb . append ( ” “ + scanner . nextLine ());
System . out . println ( e . getMessage ());
Hello, You are in a text file.
How to close scanner in java?
The close() method of java.util.Scanner class is used to close the scanner. If the scanner is already closed then invoking this method will have no effect.
If the scanner is not closed then if its readable also implements the closeable interface then the readable’s close method will be invoked.
If the user does not close the Scanner then the Java will not garbage collect the Scanner object which will lead to a memory leak in the program.
If the user tries to use the Scanner after closing, an IllegalStateException is thrown.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Example < public static void main(String args[]) < String s = "Java is a object oriented programming"; Scanner sc = new Scanner(s); System.out.println("" + sc.nextLine()); //Close the scanner sc.close(); System.out.println("Scanner Closed."); >>Java is a object oriented programming Scanner Closed.Another way to close the scanner automatically is using try-with-resources. When we use try-with, it automatically closes the underlying Scanner, which automatically closes the underlying stream that is System.in.
import java.util.Scanner; public class Example < public static void main(String args[]) < String s = "Cloud Computing"; try (Scanner sc = new Scanner(s)) < System.out.println("" + sc.nextLine()); System.out.println("Scanner Closed"); >> >Cloud Computing Scanner Closed