- Join Two Lists Python – Learn Joining Two Lists With Examples
- Join Two Lists Python Tutorial – An Easy Way To Join Lists
- Meaning of Joining Lists
- Ways Of Joining Lists
- Using + Operator
- Using extend() method
- Taking Inputs From Users
- What We Did ?
- Dealing With Strings
- Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Popular Posts
- About
- 6 Ways to Concatenate Lists in Python
- 1. Concatenation operator (+) for List Concatenation
- 2. Naive Method for List Concatenation
- 3. List Comprehension to concatenate lists
- 4.Python extend() method for List Concatenation
- 5. Python ‘*’ operator for List Concatenation
- 6. Python itertools.chain() method to concatenate lists
- Conclusion
- Python Join Two Lists
- Example
- Example
- Example
- Related Pages
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
Join Two Lists Python – Learn Joining Two Lists With Examples
Hello everyone, in Join Two Lists Python tutorial, we will learn how to join two lists in python. Already, we know list is an important data structure of python. Joining two lists in python is very easy. So let’s see how to do them. But before proceeding further check the previous tutorial that explain you how to create a list in python and everything related to lists.
Join Two Lists Python Tutorial – An Easy Way To Join Lists
Meaning of Joining Lists
- Joining lists means, we combine the items of two lists into a list.
- It is also called merging or concatenation of lists.
Ways Of Joining Lists
In python, there is two ways by using that you can join two lists.
Using + Operator
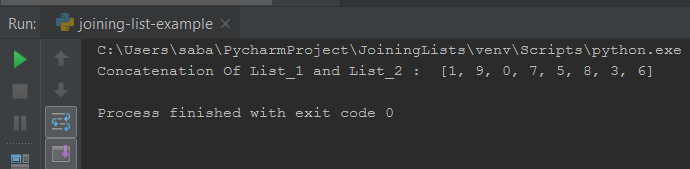
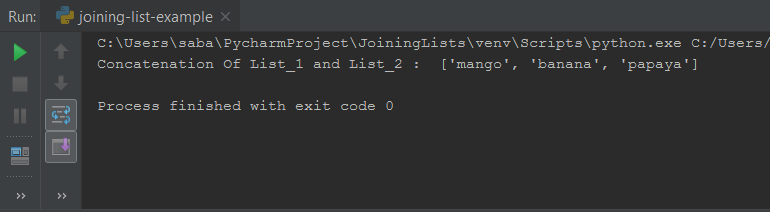
Let’s take an example, where lists are as follows –
- Here we have taken two lists.
- Then we have joined these two lists and stored the result into an another list.
Now, if you don’t want to store the joined lists into a separate list then what will have you to do, let’s see.
So the result is as follows.
Using extend() method
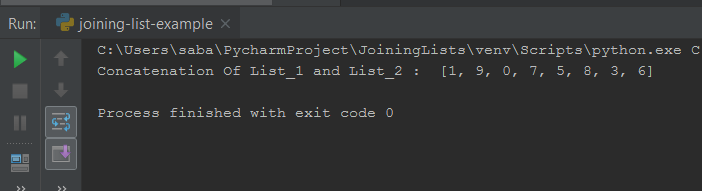
Now we will see how to join two lists using extend() method. So understanding this we are taking an example. So let’s write the code for this.
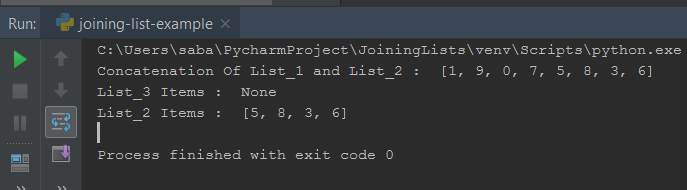
- Using extend() method, we can’t store the concatenation of two lists into a third list.
- We can store the result only in an existing list.
Now see the output of this code.
Here you can see List_3 has no items because using extend() method, we can’t store the concatenation of two lists into a third list.
Taking Inputs From Users
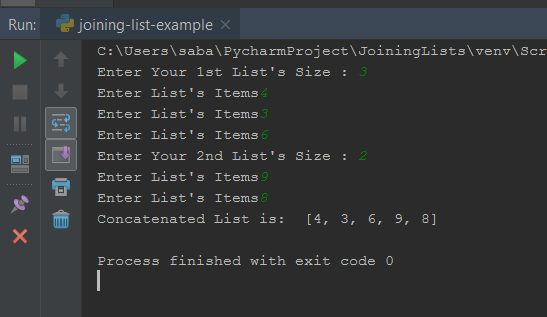
Now we will see an example where we will take inputs from users.
So, for this we have to write the below code.
What We Did ?
- First of all we have initialized an empty list.
- Then we have asked the user to enter size of their list1.
- We have cast it to integer so user can only enter integers.
- Now we will need to ask the user to enter those numbers so for this we have started a for loop.
- Next, we have asked the user to enter items into list1.
- And then these numbers into list.
- We have repeated same procedure for second list.
- Then we have joined these two lists using + operator.
- And last simply printed the concatenated list.
And now, the output of this example is –
Dealing With Strings
Till now we have seen only examples of integers items of a list. And now we will see how to concatenate two lists if they contain string items. So for implementing this concept we have to write the following code.
- If we are joining two lists that contain string then we have to the follow same process as we do in the case of integers.
So that’s all for this Join Two Lists Python tutorial . You can leave your queries below in comment section to have a discussion about that. And please share this tutorial with your friends. Thank You.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Hi my name is Belal Khan.
I am the creator of this blog. By profession I am a software engineer and I love to share my knowledge over the internet. You can read more about me here.
Popular Posts
About
If you just started learning Python then this blog is for you. When I started learning about Python; I though I should create a blog to share my Python Knowledge, and hence I’ve created Simplified Python.
Click Here if you want to know the man behind Simplified Coding.
6 Ways to Concatenate Lists in Python
While we believe that this content benefits our community, we have not yet thoroughly reviewed it. If you have any suggestions for improvements, please let us know by clicking the “report an issue“ button at the bottom of the tutorial.
- concatenation (+) operator
- Naive Method
- List Comprehension
- extend() method
- ‘*’ operator
- itertools.chain() method
1. Concatenation operator (+) for List Concatenation
The ‘+’ operator can be used to concatenate two lists. It appends one list at the end of the other list and results in a new list as output.
list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] res = list1 + list2 print ("Concatenated list:\n" + str(res)) Concatenated list: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] 2. Naive Method for List Concatenation
In the Naive method, a for loop is used to traverse the second list. After this, the elements from the second list get appended to the first list. The first list results out to be the concatenation of the first and the second list.
list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] print("List1 before Concatenation:\n" + str(list1)) for x in list2 : list1.append(x) print ("Concatenated list i.e. list1 after concatenation:\n" + str(list1)) List1 before Concatenation: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] Concatenated list i.e. list1 after concatenation: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] 3. List Comprehension to concatenate lists
Python List Comprehension is an alternative method to concatenate two lists in Python. List Comprehension is basically the process of building/generating a list of elements based on an existing list.
It uses for loop to process and traverses the list in an element-wise fashion. The below inline for-loop is equivalent to a nested for loop.
list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] res = [j for i in [list1, list2] for j in i] print ("Concatenated list:\n"+ str(res)) Concatenated list: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] 4.Python extend() method for List Concatenation
Python’s extend() method can be used to concatenate two lists in Python. The extend() function does iterate over the passed parameter and adds the item to the list thus, extending the list in a linear fashion.
list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] print("list1 before concatenation:\n" + str(list1)) list1.extend(list2) print ("Concatenated list i.e ,ist1 after concatenation:\n"+ str(list1)) All the elements of the list2 get appended to list1 and thus the list1 gets updated and results as output.
list1 before concatenation: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] Concatenated list i.e ,ist1 after concatenation: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] 5. Python ‘*’ operator for List Concatenation
Python’s ‘*’ operator can be used to easily concatenate two lists in Python.
The ‘*’ operator in Python basically unpacks the collection of items at the index arguments.
For example: Consider a list my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4].
The statement *my_list would replace the list with its elements at the index positions. Thus, it unpacks the items of the lists.
list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] res = [*list1, *list2] print ("Concatenated list:\n " + str(res)) In the above snippet of code, the statement res = [*list1, *list2] replaces the list1 and list2 with the items in the given order i.e. elements of list1 after elements of list2. This performs concatenation and results in the below output.
Concatenated list: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] 6. Python itertools.chain() method to concatenate lists
Python itertools modules’ itertools.chain() function can also be used to concatenate lists in Python.
The itertools.chain() function accepts different iterables such as lists, string, tuples, etc as parameters and gives a sequence of them as output.
It results out to be a linear sequence. The data type of the elements doesn’t affect the functioning of the chain() method.
For example: The statement itertools.chain([1, 2], [‘John’, ‘Bunny’]) would produce the following output: 1 2 John Bunny
import itertools list1 = [10, 11, 12, 13, 14] list2 = [20, 30, 42] res = list(itertools.chain(list1, list2)) print ("Concatenated list:\n " + str(res)) Concatenated list: [10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 20, 30, 42] Conclusion
Thus, in this article, we have understood and implemented different ways of Concatenating lists in Python.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases.
Python Join Two Lists
There are several ways to join, or concatenate, two or more lists in Python.
One of the easiest ways are by using the + operator.
Example
list1 = [«a», «b» , «c»]list2 = [1, 2, 3]
list3 = list1 + list2
print(list3)
Another way to join two lists are by appending all the items from list2 into list1, one by one:
Example
list1 = [«a», «b» , «c»]list2 = [1, 2, 3]
for x in list2:
list1.append(x)
Or you can use the extend() method, which purpose is to add elements from one list to another list:
Example
Use the extend() method to add list2 at the end of list1:
list1 = [«a», «b» , «c»]list2 = [1, 2, 3]
Related Pages
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.