JavaScript read JSON from URL
JavaScript read JSON from URL tutorial shows how to read data in JSON format from the provided URL. We use JQuery, Fetch API, and XMLHttpRequest.
URL
A , is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A web resource is any data that can be obtained via web, such as HTML documents, PDF files, PNG images, JSON data, or plain text.
A generic URL has the following form:
scheme:[//[user:password@]host[:port]][/]path[?query][#fragment]
The square brackets indicate that the part is optional. A scheme is a way of addressing resources, such as http, ftp, mailto, or file.
The part following two slashes is called the authority part. The authority part contains 1) an optional authentication section of a user name and password, separated by a colon, followed by an at symbol (@) 2) a host, which is either a host name of or an IP address, 3) an optional port number, separated from the host by a colon.
A path is a road to the resource on the host. It may or may not resemble or map exactly to a file system path. Query string is used to add some criteria to the request for the resource. It is often a sequence of key/value pairs. The final part is an optional fragment, which points to a secondary resource, such as a heading. It is separated from the query string by a hash (#).
JSON
is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write and for machines to parse and generate. The official Internet media type for JSON is application/json . The JSON filename extension is .json .
In our examples, we use JSON data from http://time.jsontest.com .
The GET request returns this JSON string.
Reading JSON with JQuery
is a JavaScript library which is used to manipulate DOM. With jQuery, we can find, select, traverse, and manipulate parts of a HTML document.
The JQuery $.getJSON method loads JSON-encoded data from a server using a GET HTTP request.
jQuery.getJSON( url [, data ] [, success ] )
This is the method signature. The url parameter is a string containing the URL to which the request is sent. The data is a plain object or string that is sent to the server with the request. The success is a callback function that is executed if the request succeeds.
$.getJSON is a shorthand for the above call.
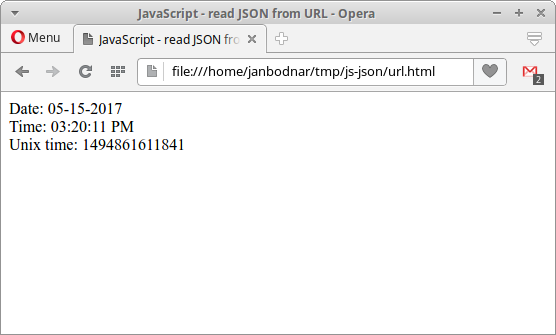
$.getJSON('http://time.jsontest.com', function(data) < var text = `Date: $
Time: $
Unix time: $` $(".mypanel").html(text); >); In the example, we read JSON data from http://time.jsontest.com . The returned object has three attributes: date, time, and unix epoch.
var text = `Date: $
Time: $
Unix time: $`
We build the message using the JavaScript template string.
With JQuery’s html method, we append the text to the div tag. Figure: Reading JSON from URL with JQuery
In the figure we can see the current date, time, and Unix time.
Reading JSON with Fetch API
is interface for fetching resources. It is similar to XMLHttpRequest but its API provides a more powerful and flexible feature set.
The example reads JSON data with Fetch API and prints the returned data to the console. To see the output, we need to activate the developer console of our browser.
The fetch method takes one mandatory argument, the path to the resource we want to fetch. It returns a promise that resolves to the response of the request.
Reading JSON with XMLHttpRequest
API provides client functionality for transferring data between a client and a server. It allows an easy way to retrieve data from a URL without having to do a full page refresh. As a consequence, a web page has to update just a part of the page without disrupting what the user is doing. XMLHttpRequest is used heavily in AJAX programming.
This example reads JSON data with XMLHttpRequest .
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
A new instance of XMLHttpRequest is created.
The open method initializes a request.
The responseType value defines the response type.
In the onload method, we wait for the response from the server.
The send method sends the request; the request is asynchronous by default.
In this article we have read JSON data in JavaScript with JQuery, Fetch API, and XMLHttpRequest.
Author
My name is Jan Bodnar and I am a passionate programmer with many years of programming experience. I have been writing programming articles since 2007. So far, I have written over 1400 articles and 8 e-books. I have over eight years of experience in teaching programming.
jQuery.getJSON()
jQuery.getJSON( url [, data ] [, success ] ) Returns: jqXHR
Description: Load JSON-encoded data from the server using a GET HTTP request.
version added: 1.0 jQuery.getJSON( url [, data ] [, success ] )
This is a shorthand Ajax function, which is equivalent to:
$.ajax(dataType: "json",url: url,data: data,success: success>);
Data that is sent to the server is appended to the URL as a query string. If the value of the data parameter is a plain object, it is converted to a string and url-encoded before it is appended to the URL.
Most implementations will specify a success handler:
This example, of course, relies on the structure of the JSON file:
"one": "Singular sensation","two": "Beady little eyes","three": "Little birds pitch by my doorstep">
Using this structure, the example loops through the requested data, builds an unordered list, and appends it to the body.
The success callback is passed the returned data, which is typically a JavaScript object or array as defined by the JSON structure and parsed using the $.parseJSON() method. It is also passed the text status of the response.
As of jQuery 1.5, the success callback function receives a "jqXHR" object (in jQuery 1.4, it received the XMLHttpRequest object). However, since JSONP and cross-domain GET requests do not use XHR , in those cases the jqXHR and textStatus parameters passed to the success callback are undefined.
Important: As of jQuery 1.4, if the JSON file contains a syntax error, the request will usually fail silently. Avoid frequent hand-editing of JSON data for this reason. JSON is a data-interchange format with syntax rules that are stricter than those of JavaScript's object literal notation. For example, all strings represented in JSON, whether they are properties or values, must be enclosed in double-quotes. For details on the JSON format, see https://json.org/.
JSONP
If the URL includes the string "callback=?" (or similar, as defined by the server-side API), the request is treated as JSONP instead. See the discussion of the jsonp data type in $.ajax() for more details.
The jqXHR Object
As of jQuery 1.5, all of jQuery's Ajax methods return a superset of the XMLHTTPRequest object. This jQuery XHR object, or "jqXHR," returned by $.getJSON() implements the Promise interface, giving it all the properties, methods, and behavior of a Promise (see Deferred object for more information). The jqXHR.done() (for success), jqXHR.fail() (for error), and jqXHR.always() (for completion, whether success or error; added in jQuery 1.6) methods take a function argument that is called when the request terminates. For information about the arguments this function receives, see the jqXHR Object section of the $.ajax() documentation.
The Promise interface in jQuery 1.5 also allows jQuery's Ajax methods, including $.getJSON() , to chain multiple .done() , .always() , and .fail() callbacks on a single request, and even to assign these callbacks after the request may have completed. If the request is already complete, the callback is fired immediately.