- Javascript: Path to the current script
- SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]
- Different methods to get script directory path in Node.js
- Method-1: Using __dirname and __filename objects
- Method-2: Using the process object
- Method-3: Using the path module
- Setup Lab Environment
- Some practical examples to get script directory in Node.js
- Example~1: Node.js get script directory using __dirname
- Example~2: Node.js get script directory using __filename
- Example~3: Node.js get absolute directory path using process.cwd() method
- Example~4: Node.js get script directory using path.basename()
- Conclusion
- Get the path of executed Javascript file
Javascript: Path to the current script
If–within a javascript file–you wish to find the path to this file, how’s it done?
Javascript provides helpful objects like self.location that can be used to find the URL of the page running the script but I was completely unable to find an object representing the path to the current script. This is useful when creating a plugin for distribution to other users in which there is no control over the folder the user will put the plugin in. It’s a lot easier to say to people “put all these files in the same folder” than it is to say “put all these files in a folder /scripts/foo/bar/ ” because your user might not have that much control.
Assume we have a file script.js that needs to load some other resources flash.swf and image.png . The file script.js is in the directory foo/bar appearing therefore at the URL http://www.example.com/foo/bar/script.js . Also, we assume this script is loaded via a from an HTML file that could be anywhere in the website. We can use the following function to extract the /foo/bar/ from the above script statement:
var scriptPath = function () var scripts = document.getElementsByTagName('SCRIPT'); var path = ''; if(scripts && scripts.length>0) for(var i in scripts) if(scripts[i].src && scripts[i].src.match(/\/script\.js$/)) path = scripts[i].src.replace(/(.*)\/script\.js$/, '$1'); break; > > > return path; >; This function basically scans the DOM tree for all the script tags and looks for the one with the same name as the script we’re currently executing. This has to be hard-coded, unfortunately, because if Javascript provided an object containing the name of the current script then it’d probably provide an object containing the current script’s path and this whole code would be redundant.
To use this reliably, ensure the script file has a unique name, such as .init.js or similar. Then, within the file .init.js , you can load the other resources using scriptPath()+» such as scriptPath()+’/flash.swf’ or scriptPath()+’/image.png’ .
Because the above function scans the DOM every time it’s called, it’s sensible for performance reasons to store the result in a variable if it’s going to be called more than a couple of times.
Incidentally, script.aculo.us uses a variant of the above to load other resources but because their codebase depends on prototype they can write less code for this function. If your code depends on a library ( jquery , mootools , prototype , etc…) then use what it provides; mine doesn’t, so I needed the above library independent method.
UPDATE March 2014: Thanks to Shawn who has been in touch to suggest an improvement to the above that allows for the query strings caching services typically add to the URLs such as ?v=3.8.1 or similar. In that case, the above will fail because the filename of the javascript file is expected to be the last component of the URL. To solve this problem you could use match(/\/script\.js($|\?.*$)/) and replace(/(.*)\/script\.js($|\?.*$)/, ‘$1’) which makes the query string optional.
SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]
Different methods to get script directory path in Node.js
We can classify the four main ways of handling a Node.js get script directory according to the path returned.
Methods returning the absolute path
Methods to return the directory name
console.log(require('path').basename(__dirname)) Here is an in-depth explanation of how each method works.
Method-1: Using __dirname and __filename objects
Node.js wraps the script file with an immediately invoked function expression (IIFE) with file arguments: exports , require , module , __dirname , and __filename .
exports is a mutable object. It is where you attach file contents before exporting them to another file. module.exports is an alias to exports .
// moduleA.js const cube = (number) => number * number * number; module.exports.customFunction = cube;module refers to the (current) file you are modifying/running. It imports another module’s content using the require method.
// moduleB.js const < customFunction >= require('./moduleA.js'); const cubeOfThree = customFunction(3); console.log(cubeOfThree); // 27__dirname returns the absolute path of the script directory.
const absolutePathWithoutFilename = __dirname; console.log(absolutePathWithoutFilename);Lastly, the __filename object attaches the script name to the absolute path of the script directory.
const absolutePathWithFilename = __filename; console.log(absolutePathWithFilename);Method-2: Using the process object
The process object is involved in (almost) all script and operating system interactions. It creates an interface for your Node.js script to read from the operating system or write to it. You can import or use it without importing it.
The process object exposes multiple properties and methods for your script to communicate with the operating system. For example, the env property reads environment variables, while the cwd() method helps during a Node.js get script directory.
// env property if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") console.log("Node.js get script directory in development mode!"); // cwd() method console.log(process.cwd());cwd is the short form of the Current Working Directory. So, console-logging the process.cwd() method reveals the absolute path of the current script directory.
Method-3: Using the path module
The path module provides utilities to work with directory and file paths. You can import and utilize its methods like join() and basename() .
const path = require('path'); // join() const customPath = path.join('Users', 'doe', 'moduleA.js'); console.log(customPath); // basename() const scriptDirectory = path.basename(__dirname); console.log(scriptDirectory);path.basename() returns the script directory’s name, not the absolute path. We can use it to get the script directory, as shown in the subsequent sections of this tutorial.
Setup Lab Environment
This section prepares a simple directory structure to practice getting the script directory. We will set up a lab for
a Linux workflow using the Vim Editor and the terminal
a Windows workflow using Visual Studio Code and its integrated terminal.
You should have installed Node.js. Better yet, follow this link to install and use Node.js and Visual Studio Code on Ubuntu.
Launch the terminal by simultaneously pressing the ctrl+alt+t keys. Make the script directory and cd into it. Next, create and open the script file using the Vim Editor.
mkdir getScriptDirectory && cd getScriptDirectory vim index.jsOpen the terminal by searching cmd . Make the project directory and open it with Visual Studio Code. I am using Git Bash, a terminal emulator you get after a Git installation on Windows, and runs most Linux commands on Windows.
mkdir getScriptDirectory cd getScriptDirectory code .Lastly, create an index.js script file in readiness for Node.js get script directory examples.
Some practical examples to get script directory in Node.js
Update the script file with code for each example (1 to 4 below), then save and run the file on the terminal using the node command.
Example~1: Node.js get script directory using __dirname
const filePath = __dirname console.log(filePath)We store __dirname in the filePath variable before printing the variable.
/home/[username]/getScriptDirectoryWe get the script directory’s path from the /home directory.
C:\Users\[username]\getScriptDirectoryThe system returns the script directory’s absolute path from the C:\ root directory.
Example~2: Node.js get script directory using __filename
const filePath = __filename console.log(filePath)/home/[username]/getScriptDirectory/index.jsc:\Users\[username]\getScriptDirectory\index.jsThis time around, the system appends the index.js file’s name to the script directory’s absolute path.
Example~3: Node.js get absolute directory path using process.cwd() method
const filePath = process.cwd() console.log(filePath)/home/[username]/getScriptDirectoryc:\Users\[username]\getScriptDirectoryLike __dirname , process.cwd() returns the absolute path of the script directory.
Example~4: Node.js get script directory using path.basename()
Assume we want to get the script directory’s name and NOT its absolute path. We can use the basename() method of the path module.
// import the path module const path = require('path') // Node.js get script directory const currentScriptDirectory = path.basename(__dirname) // print the output console.log(currentScriptDirectory)We dissect the last portion of __dirname using the basename( ) method and store the result in currentScriptDirectory variable. Lastly, we console-log the result.
And voila, we get the script directory’s name getScriptDirectory we created in the lab setup section!
Additionally, we can use the path.basename() method with process.cwd() and get similar results.
// import the path module const path = require('path') // Node.js get script directory const currentScriptDirectory = path.basename(process.cwd()) // print the output console.log(currentScriptDirectory)Conclusion
You can Node.js get script directory’s absolute path by console-logging the __dirname , __filename , and process.cwd() .
Besides, you can get the exclusive directory name by running __dirname and process.cwd() objects inside the path.basename() method, as shown in this tutorial.
Related Keywords: Node.js get script directory, node.js get current directory, node.js get absolute path, node.js get absolute directory path
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!
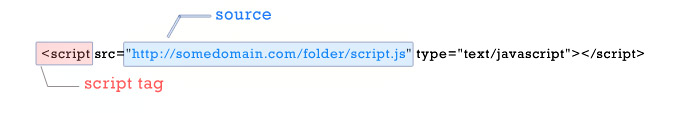
Get the path of executed Javascript file
fetches the url of the current page. But to fetch the url of the path from where the Javascript is executed, is not possible with pure jQuery method unless you use some jQuery plugin or write your own function. Let us take an example, my Javascript file is executed from here – http://somedomain/folder/script.js , but when I use the above jQuery method the url returned will be http://somedomain . But I need the url path http://somedomain/folder , the actual location from where the jQuery or Javascript is executed.
In case of php it is lot easier to get the current directory from where the php script is executed. Also jQuery is executed at the client side, that is in the browser window, so no way to get the path of the Javascript file from the server. So I wrote my own function with jQuery, here it is.
function urlofdoc ( jsfile ) < var scriptElements = document.getElementsByTagName('script'); var i, element, myfile; for( i = 0; element = scriptElements[i]; i++ ) < myfile = element.src; if( myfile.indexOf( jsfile ) >= 0 ) < var myurl = myfile.substring( 0, myfile.indexOf( jsfile ) ); >> return myurl; > A bit of explanation – Our function urlofdoc ( jsfile ) takes the file name as argument, so lets us call the function like this
var myurl = urlofdoc ( "script.js" );
getElementsByTagName will fetch all the script tags and store it in an array, which will contain the whole string from opening script tag to close tag
after that every element source is checked for the occurrence of our file.
if( myfile.indexOf( jsfile ) >= 0 )
if the file is found, then we trim the filename using substring from the full url and return the path, in our example if we call the urlofdoc function with script.js as argument, it will return http://somedomain/folder.
![SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]](https://www.golinuxcloud.com/wp-content/uploads/lab-setup-in-Windows.jpg)
![SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]](https://www.golinuxcloud.com/wp-content/uploads/use-dirname.jpg)
![SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]](https://www.golinuxcloud.com/wp-content/uploads/use-process.cwd_-1.jpg)

![SOLVED: Get script directory path in Node.js [4 Methods]](https://www.golinuxcloud.com/wp-content/uploads/output-3-4.jpg)