- What is Validate.notNull in Java?
- How to import Validate
- Syntax
- Parameters
- Return value
- Code
- Output
- Explanation
- Example 1
- Example 2
- Java verify not null
- Learn Latest Tutorials
- Preparation
- Trending Technologies
- B.Tech / MCA
- Javatpoint Services
- Training For College Campus
- Java — How to check if a variable or object is not null
- Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
- About
- Search
- How to Check if an Object is Null in Java
- How to Check if an Object is null in Java?
- Method 1: Check if an Object is null in Java Using Comparison Operator
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 2: Check if an Object is null in Java Using isNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 3: Check if an Object is null in Java Using nonNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 4: Check if an Object is null in Java Using requireNonNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Farah Batool
What is Validate.notNull in Java?
Many candidates are rejected or down-leveled due to poor performance in their System Design Interview. Stand out in System Design Interviews and get hired in 2023 with this popular free course.
notNull() is a static the methods in Java that can be called without creating an object of the class. method of the Validate class that is used to check whether the passed object is null or not.
- If the passed object is null , then the method raises an exception with a formatted message.
- If the passed object is not null , then the method returns the input as it is.
How to import Validate
The definition of Validate can be found in the Apache Commons Lang package, which we can add to the Maven project by adding the following dependency to the pom.xml file:
org.apache.commons commons-lang3 3.12.0 For other versions of the commons-lang package, refer to the Maven Repository.
You can import the Validate class as follows.
import org.apache.commons.lang3.Validate; Syntax
public static T notNull(T object, String message, Object. values) Parameters
- object : The object to check if it is null .
- message : The exception message if the object is invalid.
- values : The optional values for the formatted exception message.
Return value
This method throws a NullPointerException if the object is null . Otherwise, it doesn’t return anything.
Code
import org.apache.commons.lang3.Validate;public class Mainpublic static void main(String[] args)String stringToValidate = "hello";System.out.printf("Validate.notNull(%s) = %s", stringToValidate, Validate.notNull(stringToValidate));System.out.println();String exceptionMessageFormat = "Argument should not be null";stringToValidate = null;System.out.printf("Validate.notNull(%s) = %s", stringToValidate, Validate.notNull(stringToValidate, exceptionMessageFormat));System.out.println();>>Output
The output of the code will be as follows:
Validate.notNull(hello) = hello Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException: Argument should not be null at java.base/java.util.Objects.requireNonNull(Objects.java:347) at org.apache.commons.lang3.Validate.notNull(Validate.java:224) at Main.main(Main.java:12)Explanation
Example 1
The method returns the input value hello as it is not a null value.
Example 2
The method throws a NullPointerException as the input value is null .
Java verify not null
Learn Latest Tutorials
Preparation
Trending Technologies
B.Tech / MCA
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on h[email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected].
Duration: 1 week to 2 weekLike/Subscribe us for latest updates or newsletter





Java — How to check if a variable or object is not null
Java will throw the NullPointerException error when you call a method on an object with the value of null .
This frequently happens when you call methods from an object returned from a function as follows:
The call to the response.length() in the code above is done on a String variable with a null value, causing Java to throw the NullPointerException error:To avoid the error and make the code run without any error, you can perform an if check on the returned value response and see if the value is null.
You can do so using the not equal operator ( != ) like this:
When the value of response is not null , then Java will run the println() method inside the if block above.You can also use the Objects.nonNull() method to check whether a variable is not null .
You need to import the Objects class and use the nonNull() static method as follows:
Finally, you can also add an else condition to define code that will be executed when the result is null:The full code for is not null check is as shown below:Checking for null values before executing further operations will help you to avoid the NullPointerException error.
And that’s how you check if a variable or object is not null in Java. I hope this tutorial has been useful for you 🙏
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I’m sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I’ll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
About
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials.
Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.Search
Type the keyword below and hit enter
How to Check if an Object is Null in Java
Java is a dynamic object-oriented programming language that implements classes and objects. A unique instance of a class defines an object of the class. It is a self-contained entity with a state and behavior that facilitates mapping real-world entities while coding. The class defines the data and methods, and its object can utilize them to represent a specific entity.
This article will demonstrate the methods to check if the object is null in Java.
How to Check if an Object is null in Java?
For checking whether the object is null or not, you can use:
We will now implement each of the mentioned methods, one by one!
Method 1: Check if an Object is null in Java Using Comparison Operator
In Java, the comparison operator “==” is mostly used to compare two entities. It returns true or false after performing the comparison. This operator can also be utilized to determine whether an object is null or not.
Syntax
The syntax for verifying an object is null using the Comparison Operator is given below:
Example
In this example, we have two classes named “myFirstClass” and “objectCheckExample”. The “myFirstClass” contains an empty constructor, that is called when the object or instance of the class is instantiated:
Here, we will create an instance of the “myFirstClass” in the main() method of “objectCheckExample” class and then we will check either the object is null or not by adding the comparison operator “==” in the “if” statement:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
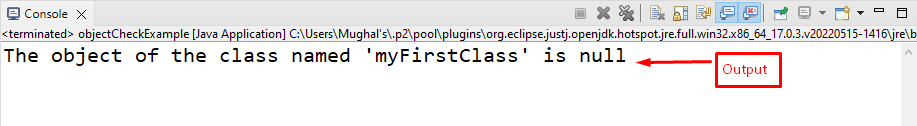
if ( myClass1 == null )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
The output shows the object “myClass1” is null because we have only declared it. Without instantiation, the object is considered null:
Now, let’s confirm whether the object is null or not when it is instantiated.
Method 2: Check if an Object is null in Java Using isNull() Method
Another method to check whether an object is null or not is the “isNull()” method. It is a static method of the Objects class. It receives an object as an argument and outputs the boolean value true or false.
Syntax
Follow the below given syntax for “isNull()” method:
Here, “myClass1” object will be validated using the “isNull()” method.
Example
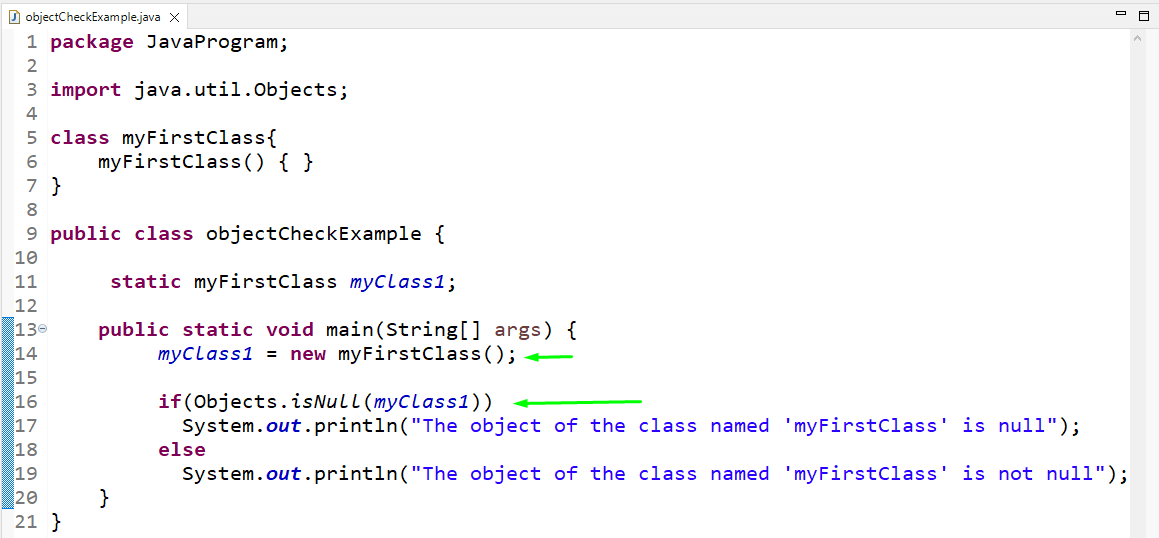
We will create an instance of “myFirstClass” in the main() method of the class named “objectCheckExample”. Using the “new” keyword, the object will be declared and instantiated simultaneously. After that, check whether the object is null or not with the help of the “isNull()” method. As this is a static method so, it will be called by using the class name “Objects”:
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( ) ;
if ( Objects. isNull ( myClass1 ) )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
— else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
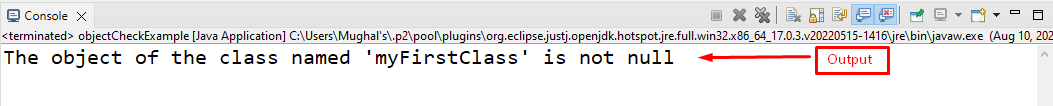
The output indicates that the object of class “myFirstClass” is not null because the object is instantiated:
Let’s check the other ways to verify the object is null or not.
Method 3: Check if an Object is null in Java Using nonNull() Method
We can also verify whether the object is null or not with the help of the “nonNull()” method. It is also a static method belonging to the Objects class. It also takes an object as a parameter and returns a boolean value where true means the object is not null.
Syntax
Here, the syntax for the method is given:
The negation (!) operator is used to convert the result of the “nonNull()” method so that it returns false if the object is not null.
Example
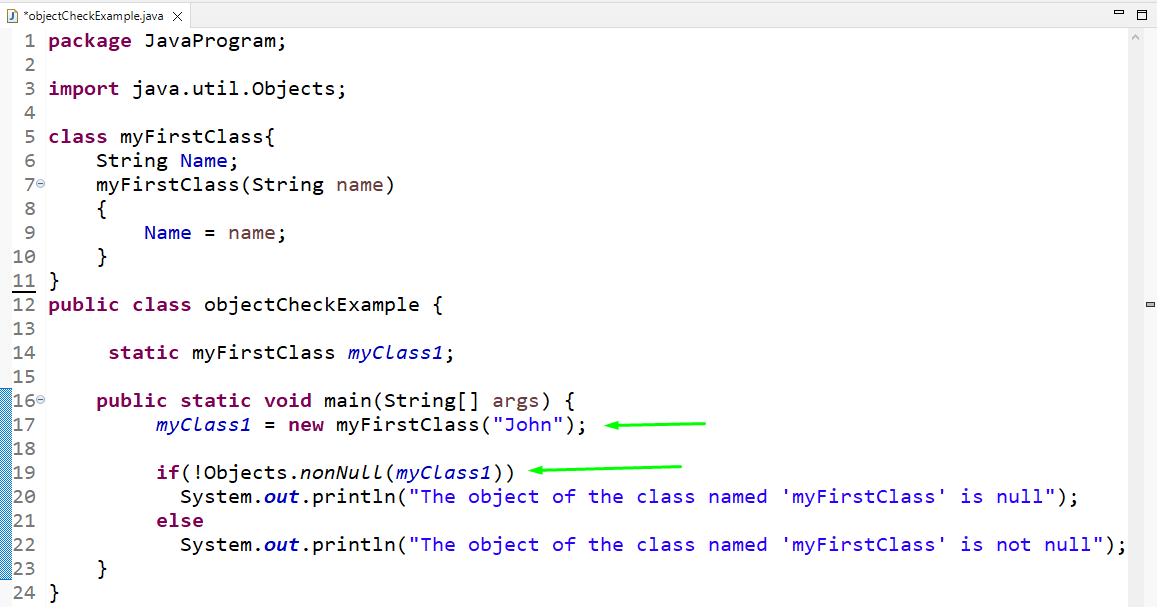
In our “myFirstClass”, we will now create a String type variable “Name” and a parameterized constructor that takes “name” as a parameter:
In the main() method of the “objectCheckExample” class, pass the name “John” as an argument to the created object. After that we will verify the object by using the “nonNull()” method:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( «John» ) ;
if ( ! Objects. nonNull ( myClass1 ) )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
As you can see, the object is not null because we have assigned value to its “Name” property:
Let’s check one more method to verify the object is null or not.
Method 4: Check if an Object is null in Java Using requireNonNull() Method
The “requireNonNull()” method is a static method and belongs to the Objects class. It takes the class object as an input in the method. If the object is null, an exception is thrown.
Syntax
Following described syntax is used for the “requireNonNull()” method:
Example
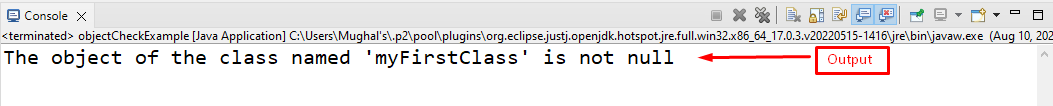
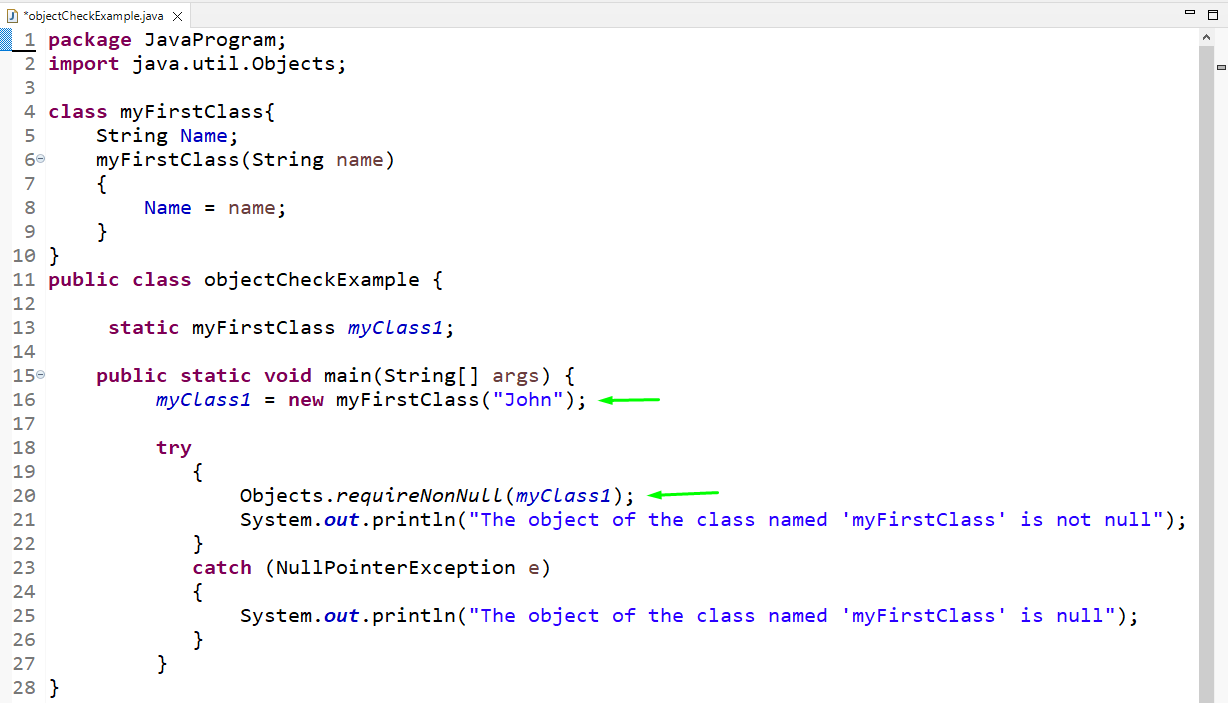
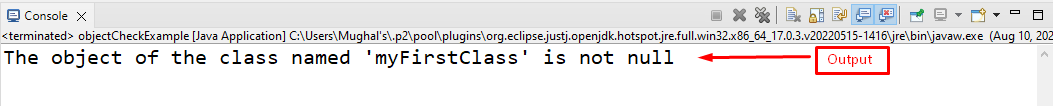
We will verify whether the created object “myClass1” is null or not by using the “requireNonNull()” method. Here, we will add a try-catch block to handle the exception.
In the try block, we call the “requireNonNull()” method and pass the “myClass1” object to it. It will print the specified line if the object is not null. Otherwise, it goes to the catch block and throw a null exception by printing the given statement:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( «John» ) ;
try
{
Objects. requireNonNull ( myClass1 ) ;
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
catch ( NullPointerException e )
{
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
}
}
}
The resultant output shows that the object is not null because it contains a value:
We have provided all the essential information about how to check an Object is null in Java.
Conclusion
To verify if the object in Java is null or not, you can use different methods: Comparison Operator, isNull() method, nonNull() method, and requireNonNull() method. It is a good practice to verify whether the object is null or not while coding; otherwise, you can face failures and unexpected outputs. This article demonstrated the methods to determine if an object is null in Java.
About the author
Farah Batool
I completed my master’s degree in computer science. I am an academic researcher and love to learn and write about new technologies. I am passionate about writing and sharing my experience with the world.