Java Program to Use Exceptions with Thread
Exceptions are the events that occur due to the programmer error or machine error which causes a disturbance in the normal flow of execution of the program. When a method encounters an abnormal condition that it can not handle, an exception is thrown as an exception statement. Exceptions are caught by handlers(here catch block). Exceptions are caught by handlers positioned along with the thread’s method invocation stack. If the calling method is not prepared to catch the exception, it throws the exception up to its calling method and so on. So in the java program exception handlers should be positioned strategically, so the program catches all the exception from which the program want to recover.
Lifecycle of a thread: The class implements a Thread class or Runnable interface then the extended class has start() method run the thread, sleep() methods cause the currently executing thread to sleep for the specified number of milliseconds, and many more.
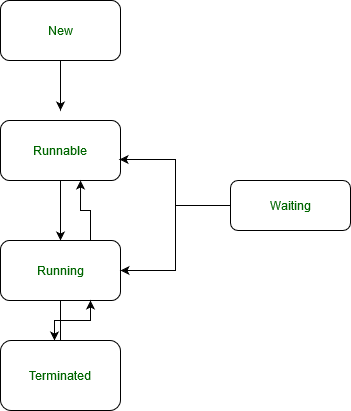
Prior to discussing the approaches, state. transactions of thread should be known to further deal with exceptions for better understanding. A thread in Java at any point in time exists in any one of the following states. A thread lies only in one of the shown states at any instant:
- New
- Runnable
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting
- Terminated
1. A class name RunnableThread implements the Runnable interface which gives the run( ) method executed by the thread. The object of this class is now runnable
2. The Thread constructor is used to create an object of RunnableThread class by passing the runnable object as a parameter.
3. The start() method is invoked on the Thread object as it returns immediately once a thread has been spawned.
4. The thread ends when the run( ) method ends which is to be normal termination or caught exception.
5. Now in order to create a new thread
runner = new Thread(this,threadName) ;
6. In order to start the new thread.
7. public void run( ) is an overridable method used to display the information of a particular thread.
8. Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000) is used to deactivate the thread until the next thread started execution or used to delay the current thread.
Uncaught exception handler will be used to demonstrate the use of exception with thread. It is a specific interface provided by Java to handle exception in the thread run method.
There are two methods to create a thread:
- Extend the thread Class (java.lang.thread)
- Implement Runnable Interface (java.lang.thread)
1. Exception and Exception handling with threads
Here, a new thread is created in the class which is extending the thread class in which run() method is overridden. This invokes the entry point of the new thread created in the class which was extending the thread class. Further, start() method is used to start and run the thread in the program.
Restarting threads using UncaughtExceptionHandler
Java applications have two kind of exceptions – checked exceptions and unchecked exceptions. Checked exceptions must be specified in the throws clause of a method or caught inside them. Unchecked exceptions don’t have to be specified or caught.
When a checked exception is thrown inside the run() method of a Thread object, we have to catch and handle it accordingly, because the run() method doesn’t accept a throws clause. But when an unchecked exception is thrown inside the run() method of a Thread object, the default behavior is to write the stack trace in the console (or log it inside error log file) and exit the program.
Fortunately, Java provides us with a mechanism to catch and treat the unchecked exceptions thrown in a Thread instance to avoid the program crashing. This can be done using UncaughtExceptionHandler .
2. UncaughtExceptionHandler example
In this example, we have created a thread which tries to parse few strings which are supposed to be integers. We have written the run() method such that it throws a “ java.lang.NumberFormatException ” during it’s execution.
As program does not try to catch this exception, exception floats through JVM level and thread gets killed. This is absolutely normal behavior but it MAY NOT be desired behavior.
2.1. Without UncaughtExceptionHandler
In real life application, you would like to try more than once to perform a critical task even if it failed couple of times. Our example below demonstrate the usecase, first without use of UncaughtExceptionHandler ; which causes the thread to die immediately after failure.
class Task implements Runnable < @Override public void run() < System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("234")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("345")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("XYZ")); //This will cause NumberFormatException System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("456")); >> public class DemoThreadExample < public static void main(String[] args) < Task task = new Task(); Thread thread = new Thread(task); thread.start(); >>
Below is output we get when we run the thread:
123 234 345 Exception in thread "Thread-0" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "XYZ" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at examples.algorithms.sleepingbarber.Task.run(DemoThreadExample.java:24) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)
2.2. With UncaughtExceptionHandler
Let’s add one UncaughtExceptionHandler implementation to catch any unchecked exception during runtime.
class ExceptionHandler implements UncaughtExceptionHandler < public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) < System.out.printf("An exception has been captured\n"); System.out.printf("Thread: %s\n", t.getId()); System.out.printf("Exception: %s: %s\n", e.getClass().getName(), e.getMessage()); System.out.printf("Stack Trace: \n"); e.printStackTrace(System.out); System.out.printf("Thread status: %s\n", t.getState()); new Thread(new Task()).start(); >> Now add this exception handler to the thread.
class Task implements Runnable < @Override public void run() < Thread.currentThread().setUncaughtExceptionHandler(new ExceptionHandler()); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("123")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("234")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("345")); System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("XYZ")); //This will cause NumberFormatException System.out.println(Integer.parseInt("456")); >> Now run the above example once again. This will run continuously. In real life, if this task is able to complete it’s task then it will exit without throwing any exception and will complete it’s life cycle.
123 234 345 An exception has been captured Thread: 1394 Exception: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "XYZ" Stack Trace: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "XYZ" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at examples.algorithms.sleepingbarber.Task.run(DemoThreadExample.java:24) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source) Thread status: RUNNABLE 123 234 345 An exception has been captured Thread: 1395 Exception: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "XYZ" Stack Trace: java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "XYZ" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Unknown Source) at examples.algorithms.sleepingbarber.Task.run(DemoThreadExample.java:24) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source) Thread status: RUNNABLE 123 234 345
UncaughtExceptionHandler helps you to run a thread in a way such that it will run until it’s task is done. This can be achieved through other multi-threading concepts as well.
Please note that UncaughtExceptionHandler can be used for making logging more robust only as well without restarting the thread because often default logs don’t provide enough information about the context when thread execution failed.