- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- ehsk/sqlite-jdbc-tutorial
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.md
- Java Connect to SQLite with JDBC Example
- 1. Download SQLite JDBC driver
- 2. SQLite JDBC database connection URL
- 3. Loading SQLite JDBC driver
- 4. Making SQLite JDBC connection
- JDBC API References:
- Related JDBC Tutorials:
- About the Author:
- SQLite Java: Connect To SQLite Database Using SQLite JDBC Driver
- Download SQLite JDBC Driver
- SQLite connection strings
- Connect to an SQLite database via JDBC
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Troubleshooting
- How the program works
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
License
ehsk/sqlite-jdbc-tutorial
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.md
The goal of this tutorial is to learn how to write a program in Java to work with SQLite database. This tutorial covers the basics of JDBC and SQLite-JDBC. An example code is also provided to practice on JDBC. Here is the outline of this tutorial:
The Java Database Connectivity, or JDBC in short, is a standard for dealing with a relational database in Java. JDBC APIs enable developers to interact with a database regradless of the vendor. These functionalities entail [1]:
- Creating and managing data source connections
- Integrating SQL with Java programs, i.e. sending SQL queries to data source
- Processing retrieved results from data source
Now, let’s see how to use JDBC APIs in programs. In the following, the key classes in JDBC are introduced:
- DriverManager: Applications can establish a connection to a data source via this class. DriverManager requires a Driver class typically implemented by third parties. These drivers can be determined using Java dynamic loading mechanism Class.forName(«a.b.Class») . We also need to specify a data source URL. The Driver class and the URL are provided by database vendors. Depending on the database, you may need to pass other information such as credentials and configuration properties.
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:myDriver:myDatabase", username, password);
The following Table lists required JDBC information for some well-known open-source databases.
Statement stmt = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT column1 FROM Table1"); stmt.executeUpdate("INSERT INTO Table1 VALUES (value1,value2)");
- ResultSet class represents results returned by the data source. ResultSet operates like an iterator, i.e. it points to the current row of data and its pointer should be moved forward to read the data.
while (rs.next()) < System.out.println(rs.getString("column1")); >
All JDBC APIs are provided in java.sql and javax.sql packages.
SQLite-JDBC [2] is the JDBC Driver we’re using for SQLite in this tutorial.
SQLite supports in-memory data management. In order to SQLite without any files, JDBC URL should be defined as jdbc:sqlite::memory: . Also, for storing data in a file, JDBC URL must be jdbc:sqlite:/path/myfile.db (UNIX-style) or jdbc:sqlite:C:/path/myfile.db (Windows-style).
Here is an example code to acquire an in-memory SQLite connection:
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC"); try (Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite::memory:")) < Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); > catch (SQLException e) < System.err.println(e.getMessage()); >
SQLite-JDBC library provides SQLiteConfig object to configure connections. SQLiteConfig offers a wide of range configurations, most of which requires detailed knowledge on SQLite. Here, we leverage it to enforce foreign key constraints (which is not enabled by default):
SQLiteConfig config = new SQLiteConfig(); config.enforceForeignKeys(true); Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:sqlite::memory:", config.toProperties());
Let’s put what we discussed into practice. Consider the following schema:
The goal here is to write a program that is able to perform two tasks:
First, the program must support enrolling a student to a course. In order to do that, it prompts user for student id and course id. Then, after performing preliminary validations, the program must insert a row to take table and update seats_available in course table.
The second task is defined to work with ResultSet class. In this task, the program retrieves information of students, but not all in once. The program must load information page by page, called pagination, because the number of students may be so large that it does’nt fit into memory. The details of pagination in SQLite is provided in [3].
Before running the code, you need to compile the code. The code is located in src and depends on SQLite-JDBC library, located in lib.
You can compile the code using the following command:
mkdir target javac -cp "lib/sqlite-jdbc-3.20.0.jar" -d target src/SQLiteJDBCExample.java The class file is generated in target folder. The following command can be used to run the code:
java -cp "lib/sqlite-jdbc-3.20.0.jar:target" SQLiteJDBCExample
The argument can be either paginate or enroll.
Java Connect to SQLite with JDBC Example
SQLite is a simple, small, fast, reliable, server-less, zero-configuration and no-installation SQL database library which is running in-process with the client application. Although there is no official JDBC driver library from www.sqlite.org, there is one provided by www.xerial.org – an XML Database Management System project.
1. Download SQLite JDBC driver
You can download the latest version of JDBC driver for SQLite here. The download is categorized by versions, so browse a directory for a specific version you want: 3.5.9, 3.6.16, 3.7.2, etc. As of this writing, the latest version is 3.7.2 which corresponds to the jar file sqlite-jdbc-3.7.2.jar .
Beside Java class files, the jar file includes SQLite binaries for Windows, Linux and Mac (for both 32-bit and 64-bit).
Place the sqlite-jdbc-VERSION.jar into your classpath.
2. SQLite JDBC database connection URL
Here is the syntax of database connection URL for file system database:
jdbc:sqlite:database_file_path
Where database_file_path can be either relative or absolute path. For example:
jdbc:sqlite:C:/work/product.db
And here is the syntax of database connection URL for memory database:
3. Loading SQLite JDBC driver
Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC"); DriverManager.registerDriver(new org.sqlite.JDBC());
4. Making SQLite JDBC connection
The following example program creates a connection to a SQLite database file product.db which is in the same directory as the program, prints some database metadata information, and closes the connection:
package net.codejava.jdbc; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * This program demonstrates making JDBC connection to a SQLite database. * @author www.codejava.net * */ public class JdbcSQLiteConnection < public static void main(String[] args) < try < Class.forName("org.sqlite.JDBC"); String dbURL = "jdbc:sqlite:product.db"; Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL); if (conn != null) < System.out.println("Connected to the database"); DatabaseMetaData dm = (DatabaseMetaData) conn.getMetaData(); System.out.println("Driver name: " + dm.getDriverName()); System.out.println("Driver version: " + dm.getDriverVersion()); System.out.println("Product name: " + dm.getDatabaseProductName()); System.out.println("Product version: " + dm.getDatabaseProductVersion()); conn.close(); >> catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) < ex.printStackTrace(); >catch (SQLException ex) < ex.printStackTrace(); >> > To see the coding in action, I recommend you to watch the video below:
JDBC API References:
Related JDBC Tutorials:
About the Author:
Nam Ha Minh is certified Java programmer (SCJP and SCWCD). He started programming with Java in the time of Java 1.4 and has been falling in love with Java since then. Make friend with him on Facebook and watch his Java videos you YouTube.
SQLite Java: Connect To SQLite Database Using SQLite JDBC Driver
Summary: in this tutorial, we will show you how to download SQLite JDBC Driver and connect to the SQLite database via JDBC.
Download SQLite JDBC Driver
To download the latest version of SQLite JDBC Driver, you go to the download page. You should download the latest version of the driver. At the time of this writing, the latest version is sqlite-jdbc-3.27.2.1.jar .
The JAR file includes both Java class files and SQLite binaries for Mac OX S, Linux, and Windows, Both 32-bit and 64-bit.
SQLite connection strings
The SQLite JDBC driver allows you to load an SQLite database from the file system using the following connection string:
jdbc:sqlite:sqlite_database_file_pathCode language: Java (java)The sqlite_data_file_path is the path to the SQLite database file, which is either relative or absolute path as follows:
jdbc:sqlite:sample.dbCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)jdbc:sqlite:C:/sqlite/db/chinook.dbCode language: Java (java)To connect to an in-memory database, you use the following connection string:
jdbc:sqlite::memory:Code language: Java (java)Connect to an SQLite database via JDBC
Step 1
Create a new directory called java under c:\sqlite
Step 2
Inside the java folder create a new folder called connect .
Step 3
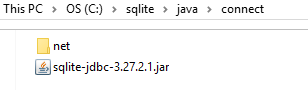
Copy the jar file sqlite-jdbc-3.27.2.1.jar to the c:\sqlite\connect folder.
Step 4
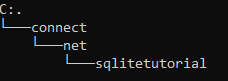
Create a new subfolder called net inside c:\sqlite\connect\ and another subfolder called sqlitetutorial inside the net folder.
Step 5
Create a new file named Connect.java in the sqlitetutorial folder with the following contents. The program will connect to the chinook.db database located in the c:\sqlite\db\ folder.
package net.sqlitetutorial; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.SQLException; /** * * @author sqlitetutorial.net */ public class Connect < /** * Connect to a sample database */ public static void connect() < Connection conn = null; try < // db parameters String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C:/sqlite/db/chinook.db"; // create a connection to the database conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url); System.out.println("Connection to SQLite has been established."); > catch (SQLException e) < System.out.println(e.getMessage()); >finally < try < if (conn != null) < conn.close(); >> catch (SQLException ex) < System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); >> > /** * @param args the command line arguments */ public static void main(String[] args) < connect(); >>Code language: Java (java)Note that you should have the chinook.db file downloaded and copied to the C:/sqlite/db/ folder.
Step 6
Launch the command line window and navigate to the sqlitetutorial subfolder created above using the following command:
cd c:\sqlite\java\connect\net\sqlitetutorialCode language: Shell Session (shell)Step 7
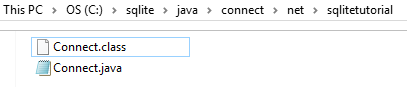
Compile the Connect.java file using the following command:
javac Connect.javaCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)You will see a new class file generated:
Note that your JDK must be on the PATH, otherwise you will get an error.
Step 8
Change the current directory to the connect directory:
c:\sqlite\java\connect\net\sqlitetutorial>cd.. c:\sqlite\java\connect\net>cd..Code language: Shell Session (shell)Step 9
Run the net.sqlitetutorial.Connect class using the following command:
java -classpath ".;sqlite-jdbc-3.27.2.1.jar" net.sqlitetutorial.ConnectCode language: Shell Session (shell)Connection to SQLite has been established.Code language: Shell Session (shell)Troubleshooting
If you receive the following message, you should have missed step 8:
Error: Could not find or load main class net.sqlitetutorial.ConnectCode language: Shell Session (shell)How the program works
First, declare a variable that holds a connecting string to the sqlite database c:\sqlite\db\chinook.db
String url = "jdbc:sqlite:C:/sqlite/db/chinook.db";Code language: Java (java)Next, use the DriverManager class to get a database connection based on the connection string.
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);Code language: Java (java)Then, trap any SQLException in the try catch block and display the error message.
After that, close the database connection in the finally block.
Finally, call the connect() method in the main() method of the Connect class.
In this tutorial, you have learned step by step how to use the SQLite JDBC driver to connect to an SQLite database from a Java program.