- Manipulating Characters in a String
- Getting Characters and Substrings by Index
- Other Methods for Manipulating Strings
- Searching for Characters and Substrings in a String
- Replacing Characters and Substrings into a String
- An Example
- Java Replace Char in String
- Examples of Java Replace Char in String
- Example #1
- Example #2
- Example #3
- Example #4
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
Manipulating Characters in a String
The String class has a number of methods for examining the contents of strings, finding characters or substrings within a string, changing case, and other tasks.
Getting Characters and Substrings by Index
You can get the character at a particular index within a string by invoking the charAt() accessor method. The index of the first character is 0, while the index of the last character is length()-1 . For example, the following code gets the character at index 9 in a string:
String anotherPalindrome = "Niagara. O roar again!"; char aChar = anotherPalindrome.charAt(9);
Indices begin at 0, so the character at index 9 is ‘O’, as illustrated in the following figure:
If you want to get more than one consecutive character from a string, you can use the substring method. The substring method has two versions, as shown in the following table:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The substring begins at the specified beginIndex and extends to the character at index endIndex — 1 . |
| String substring(int beginIndex) | Returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The integer argument specifies the index of the first character. Here, the returned substring extends to the end of the original string. |
The following code gets from the Niagara palindrome the substring that extends from index 11 up to, but not including, index 15, which is the word «roar»:
String anotherPalindrome = "Niagara. O roar again!"; String roar = anotherPalindrome.substring(11, 15);
Other Methods for Manipulating Strings
Here are several other String methods for manipulating strings:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) String[] split(String regex, int limit) | Searches for a match as specified by the string argument (which contains a regular expression) and splits this string into an array of strings accordingly. The optional integer argument specifies the maximum size of the returned array. Regular expressions are covered in the lesson titled «Regular Expressions.» |
| CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a new character sequence constructed from beginIndex index up until endIndex — 1. |
| String trim() | Returns a copy of this string with leading and trailing white space removed. |
| String toLowerCase() String toUpperCase() | Returns a copy of this string converted to lowercase or uppercase. If no conversions are necessary, these methods return the original string. |
Searching for Characters and Substrings in a String
Here are some other String methods for finding characters or substrings within a string. The String class provides accessor methods that return the position within the string of a specific character or substring: indexOf() and lastIndexOf() . The indexOf() methods search forward from the beginning of the string, and the lastIndexOf() methods search backward from the end of the string. If a character or substring is not found, indexOf() and lastIndexOf() return -1.
The String class also provides a search method, contains , that returns true if the string contains a particular character sequence. Use this method when you only need to know that the string contains a character sequence, but the precise location isn’t important.
The following table describes the various string search methods.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| int indexOf(int ch) int lastIndexOf(int ch) | Returns the index of the first (last) occurrence of the specified character. |
| int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | Returns the index of the first (last) occurrence of the specified character, searching forward (backward) from the specified index. |
| int indexOf(String str) int lastIndexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the first (last) occurrence of the specified substring. |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | Returns the index of the first (last) occurrence of the specified substring, searching forward (backward) from the specified index. |
| boolean contains(CharSequence s) | Returns true if the string contains the specified character sequence. |
Note: CharSequence is an interface that is implemented by the String class. Therefore, you can use a string as an argument for the contains() method.
Replacing Characters and Substrings into a String
The String class has very few methods for inserting characters or substrings into a string. In general, they are not needed: You can create a new string by concatenation of substrings you have removed from a string with the substring that you want to insert.
The String class does have four methods for replacing found characters or substrings, however. They are:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) | Returns a new string resulting from replacing all occurrences of oldChar in this string with newChar. |
| String replace(CharSequence target, CharSequence replacement) | Replaces each substring of this string that matches the literal target sequence with the specified literal replacement sequence. |
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | Replaces each substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement. |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | Replaces the first substring of this string that matches the given regular expression with the given replacement. |
An Example
The following class, Filename , illustrates the use of lastIndexOf() and substring() to isolate different parts of a file name.
Note: The methods in the following Filename class don’t do any error checking and assume that their argument contains a full directory path and a filename with an extension. If these methods were production code, they would verify that their arguments were properly constructed.
public class Filename < private String fullPath; private char pathSeparator, extensionSeparator; public Filename(String str, char sep, char ext) < fullPath = str; pathSeparator = sep; extensionSeparator = ext; >public String extension() < int dot = fullPath.lastIndexOf(extensionSeparator); return fullPath.substring(dot + 1); >// gets filename without extension public String filename() < int dot = fullPath.lastIndexOf(extensionSeparator); int sep = fullPath.lastIndexOf(pathSeparator); return fullPath.substring(sep + 1, dot); >public String path() < int sep = fullPath.lastIndexOf(pathSeparator); return fullPath.substring(0, sep); >>
Here is a program, FilenameDemo , that constructs a Filename object and calls all of its methods:
public class FilenameDemo < public static void main(String[] args) < final String FPATH = "/home/user/index.html"; Filename myHomePage = new Filename(FPATH, '/', '.'); System.out.println("Extension = " + myHomePage.extension()); System.out.println("Filename = " + myHomePage.filename()); System.out.println("Path = " + myHomePage.path()); >> And here’s the output from the program:
Extension = html Filename = index Path = /home/user
As shown in the following figure, our extension method uses lastIndexOf to locate the last occurrence of the period (.) in the file name. Then substring uses the return value of lastIndexOf to extract the file name extension that is, the substring from the period to the end of the string. This code assumes that the file name has a period in it; if the file name does not have a period, lastIndexOf returns -1, and the substring method throws a StringIndexOutOfBoundsException .
Also, notice that the extension method uses dot + 1 as the argument to substring . If the period character (.) is the last character of the string, dot + 1 is equal to the length of the string, which is one larger than the largest index into the string (because indices start at 0). This is a legal argument to substring because that method accepts an index equal to, but not greater than, the length of the string and interprets it to mean «the end of the string.»
Previous page: Converting Between Numbers and Strings
Next page: Comparing Strings and Portions of Strings
Java Replace Char in String
Replacing a character in a string refers to placing another character at the place of the specified character. An index represents specified characters. In java, the String class is used to replace the character & strings. A string is the class of java.lang packages.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
In programming, developers face many situations where they have to need to replace characters in the string. Java provides multiple methods to replace the characters in the String. Remove is one of the important methods used in replacing the characters. while using the remove method, a few things should be remember
- String in Java is immutable, so after replacing the character, a new string is created.
- The string variable before applying the replace method remains the same after applying the replace method.
- Replace method replaces all the characters in the string with the new character.
In the following syntax, it is given how a character is being replaced. There are two parameters in the replace method: the first parameter is the character to replace & the second one is the character to be replaced with.
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar): //OR String replaceFirst(char oldChar, char newChar): //replaces only the first occurrence of the characterIn the second line of syntax, the replaceFirst method is used to replace only the character’s first occurrence.
Examples of Java Replace Char in String
Below are the examples of Java Replace Char in String:
Example #1
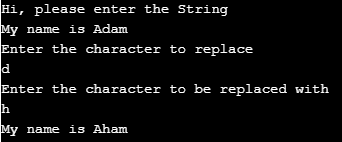
In this example, we can see how a character in the string is replaced with another one.
- In the first line taking input from the user as a string.
- Further asking character as an input to replace in the provided string.
- The replace method creates a new string with the replaced character in the next line because the string in java is immutable.
import java.util.*; public class JavaReplaceCharExample < public static void main(String[] args)< Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Hi, please enter the String"); String str = input.nextLine(); System.out.println("Enter the character to replace"); char ch = input.next().charAt(0); System.out.println("Enter the character to be replaced with"); char newCh = input.next().charAt(0); String newStr = str.replace(ch, newCh); //displaying new string after applying replace method System.out.println(newStr); >>Example #2
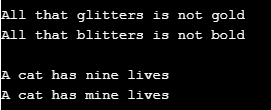
In this example, replaceFirst is used to only replace the first occurrence of the character in this string.
import java.util.*; public class JavaReplaceCharExample2 < public static void main(String[] args)< //second string to replace the character String str = "All that glitters is not gold"; //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + str); //replacing character p from b String newStr = str.replace("g", "b"); //displaying string after replacing the character System.out.println(newStr); //second string to replace the character String sentence = "A cat has nine lives"; //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + sentence); //replacing character n from m String newSentence = sentence.replaceFirst("n", "m"); //displaying new string after applying replace method System.out.println(newSentence); >>The output of the program is given below. In the output screenshot, the first sentence character “g” is replaced by “b”. In the second sentence, only the first occurrence of the syntax “n” is replaced with “m”.
Example #3
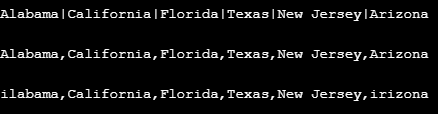
In this example, first replacing a pipe separated value with the comma. After replacing ‘|’ to “,”, in the next line replacing the “A” character to “i” using the replace method.
import java.util.*; public class JavaReplaceCharExample3 < public static void main(String[] args)< //second string to replace the character String str = "Alabama|California|Florida|Texas|New Jersey|Arizona"; //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + str); //replacing | with the comma String newStr = str.replace('|', ','); //displaying string after applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + newStr); //replacing the character A with the i String reNewedStr = newStr.replace('A', 'i'); //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + reNewedStr); >>Output:
Example #4
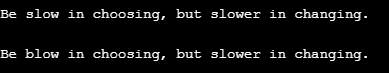
In this example, we can see how a string can be replaced without using the replace method. The string before & after the specified character is stored in a separate variable in the below-given program. Further in the program, it is concatenated with the character to be replaced with.
import java.util.*; public class JavaReplaceCharExample4 < public static void main(String[] args)< //second string to replace the character String str = "Be slow in choosing, but slower in changing."; //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + str); int index = 3; char chToReplacedWith = 'b'; String strBeforeChar = str.substring(0, index); String strAfterChar = str.substring(index + 1); String newStr = strBeforeChar + chToReplacedWith + strAfterChar; //displaying string before applying replace method System.out.println("\n" + newStr); >>Output:
Conclusion
The above-given article describes how to replace char in a string, what methods are provided by java packages to work with the string. In the given examples, it is given how string class methods can be used to replace characters in a string.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java Replace Char in String. Here we discuss how to replace char in a string and its Examples along with its Code Implementation. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
89+ Hours of HD Videos
13 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
97+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Courses
12 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
JAVA Course Bundle — 78 Courses in 1 | 15 Mock Tests
416+ Hours of HD Videos
78 Courses
15 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.8