- A Java MySQL UPDATE example
- A simple MySQL database table
- A Java MySQL UPDATE PreparedStatement example
- Java MySQL UPDATE example — results
- Java MySQL UPDATE example using PreparedStatement — summary
- Java — how to make MySQL update query with JDBC?
- 1. UPDATE query with JDBC example
- 2. Data base preparation
- See also
- Java mysql for update
- Добавление
- Редактирование
- Удаление
- Update MySQL Table using JDBC [Easy Guide]
- Prerequisites
- Create A Table In MySQL
- Create Java Application in Eclipse IDE
- Update MySQL table using JDBC
A Java MySQL UPDATE example
Java MySQL FAQ: Can you share an example of a Java MySQL UPDATE example (using a Java PreparedStatement object)?
Sure. I just worked up a Java MySQL UPDATE example, using the Java PreparedStatement class, and a sample MySQL database table we can work with.
A simple MySQL database table
The first thing we need for our Java UPDATE example is a sample MySQL database table. To keep it simple — but also show several different data types — I’ve created the following MySQL database table:
create table users ( id int unsigned auto_increment not null, first_name varchar(32) not null, last_name varchar(32) not null, date_created timestamp default now(), is_admin boolean, num_points int, primary key (id) ); -- insert some sample records insert into users (first_name, last_name) values ('Fred', 'Flinstone'); insert into users (first_name, last_name) values ('Barney', 'Rubble'); A few of these fields are a little contrived, but I wanted to show several different data types in one table, so this is what I came up with. In particular, the field num_points is a little unusual, but I made it up so I could show an int data type in this table, and I was thinking of those websites where points are awarded for giving correct answers.
Other than that, this MySQL database table is relatively normal, though it is greatly simplified.
A Java MySQL UPDATE PreparedStatement example
Given that MySQL database table design, let’s assume that we just want to update one record in this table. To do so, we just need to follow these steps:
- Create a Java Connection to our MySQL database.
- Create a SQL UPDATE statement, using the Java PreparedStatement syntax.
- Set the fields on our Java PreparedStatement object.
- Execute a Java PreparedStatement .
- Close our Java database connection.
- Catch any exceptions that may come up during the process.
I’ve tried to document the following Java MySQL UPDATE example so you can see these steps. Note that in this example my MySQL database username is «root», my password is blank, and the MySQL database is running on the same computer where this program is run, so the database host name is «localhost».
import java.sql.*; /** * A Java MySQL UPDATE example. * Demonstrates the use of a SQL UPDATE statement against a * MySQL database, called from a Java program. * * Created by Alvin Alexander, http://devdaily.com * */ public class JavaMysqlPreparedStatementUpdateExample < public static void main(String[] args) < try < // create a java mysql database connection String myDriver = "org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver"; String myUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/test"; Class.forName(myDriver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(myUrl, "root", ""); // create the java mysql update preparedstatement String query = "update users set num_points = ? where first_name = ?"; PreparedStatement preparedStmt = conn.prepareStatement(query); preparedStmt.setInt (1, 6000); preparedStmt.setString(2, "Fred"); // execute the java preparedstatement preparedStmt.executeUpdate(); conn.close(); >catch (Exception e) < System.err.println("Got an exception! "); System.err.println(e.getMessage()); >> > Note that this SQL UPDATE query is a little unusual, but not totally uncommon. Typically in a database program like this you’ll end up updating rows based on the primary key of the database table. Specifically, in this example, you’d probably already know the «id» for the user Fred, and when you go to update Fred’s data, you would normally do it like this:
update users set num_points = 6000 where >but because this is a sample program, I decided to show the query this way.
Java MySQL UPDATE example — results
After this Java MySQL UPDATE query runs, you can verify that it worked by looking at the data from the MySQL command prompt, running a SELECT query like this:
where you will see some output like this:
+----+------------+-----------+---------------------+----------+------------+ | id | first_name | last_name | date_created | is_admin | num_points | +----+------------+-----------+---------------------+----------+------------+ | 2 | Fred | Flinstone | 2010-06-23 14:02:00 | 0 | 6000 | +----+------------+-----------+---------------------+----------+------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Java MySQL UPDATE example using PreparedStatement — summary
In «real world» Java database programs I almost always use the Spring JDBC libraries to access a database, but when you’re first getting started, or working on small programs, I think it’s important to see examples like this so you can understand how things work under the covers.
In summary, this example demonstrated:
- How to connect to a MySQL database.
- How to write a MySQL UPDATE query for use with a PreparedStatement .
- How to set the field values for a PreparedStatement .
- How to execute the Java PreparedStatement .
- How to close the MySQL database connection.
- One way to confirm that our data was successfully updated in our MySQL database.
I hope this Java MySQL UPDATE example (using a Java PreparedStatement ) makes sense. As usual, if you have any questions or comments about this example, just use the Comment form below.
Java — how to make MySQL update query with JDBC?
RomanaLittle
In Java it is possible to make SQL UPDATE query with JDBC in following way.
Note: read this article to know how to download and install JDBC driver proper way.
1. UPDATE query with JDBC example
Note: this approach prevents of SQL Injection attack.
package com.dirask.examples; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.SQLException; public class Program < private static final String DB_NAME = "test"; private static final String DB_HOST = "127.0.0.1"; // 'localhost' private static final String DB_USER = "root"; private static final String DB_PASSWORD = "root"; private static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://" + DB_HOST + "/" + DB_NAME + "?serverTimezone=UTC"; public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException < String sql = "UPDATE `users` SET `name` = ?, `role` = ? WHERE `id` = ?"; try ( // gets connection with database Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL, DB_USER, DB_PASSWORD); // sends queries and receives results PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); ) < // this way to prevent sql injection statement.setString(1, "Matt"); statement.setString(2, "admin"); statement.setInt(3, 3); int count= statement.executeUpdate(); System.out.print("Number of updated rows is " + count + "."); >catch (SQLException e) < // some logic depending on scenario // maybe LOGGER.log(e.getMessage()) and "result false" e.printStackTrace(); >> >Number of updated rows is 1.2. Data base preparation
CREATE TABLE `users` ( `id` INT(10) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, `role` VARCHAR(15) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB;INSERT INTO `users` (`name`, `role`) VALUES ('John', 'admin'), ('Chris', 'moderator'), ('Kate', 'user'), ('Denis', 'moderator');See also
Java mysql for update
Для добавления, редактирования и удаления данных мы можем ипользовать рассмотренный в прошлой теме метод executeUpdate . С помощью результата метода мы можем проконтроллировать, сколько строк было добавлено, изменено или удалено.
Добавление
Так, возьмем созданную в прошлой теме таблицу Products:
CREATE TABLE Products ( Id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, ProductName VARCHAR(20), Price INT )
И добавим в эту таблицу несколько объектов:
import java.sql.*; public class Program < public static void main(String[] args) < try< String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/store?serverTimezone=Europe/Moscow&useSSL=false"; String username = "root"; String password = "password"; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver").getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password))< Statement statement = conn.createStatement(); int rows = statement.executeUpdate("INSERT Products(ProductName, Price) VALUES ('iPhone X', 76000)," + "('Galaxy S9', 45000), ('Nokia 9', 36000)"); System.out.printf("Added %d rows", rows); >> catch(Exception ex) < System.out.println("Connection failed. "); System.out.println(ex); >> > Для добавления данных в БД применяется команда INSERT. В данном случае в таблицу Products добавляется три объекта. И после выполнения программы на консоли мы увидим число добавленных объектов:
C:\Java>javac Program.java C:\Java>java -classpath c:\Java\mysql-connector-java-8.0.11.jar;c:\Java Program Added 3 rows C:\Java>
А добавленные строки мы можем увидеть в таблице в бд MySQL:
Редактирование
Изменим строки в таблице, например, уменьшим цену товара на 5000 единиц. Для изменения применяется команда UPDATE:
import java.sql.*; public class Program < public static void main(String[] args) < try< String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/store?serverTimezone=Europe/Moscow&useSSL=false"; String username = "root"; String password = "password"; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver").getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password))< Statement statement = conn.createStatement(); int rows = statement.executeUpdate("UPDATE Products SET Price = Price - 5000"); System.out.printf("Updated %d rows", rows); >> catch(Exception ex) < System.out.println("Connection failed. "); System.out.println(ex); >> > Удаление
Удалим один объект из таблицы с помощью команды DELETE:
import java.sql.*; public class Program < public static void main(String[] args) < try< String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/store?serverTimezone=Europe/Moscow&useSSL=false"; String username = "root"; String password = "password"; Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver").getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance(); try (Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password))< Statement statement = conn.createStatement(); int rows = statement.executeUpdate("DELETE FROM Products WHERE row(s) deleted", rows); >> catch(Exception ex) < System.out.println("Connection failed. "); System.out.println(ex); >> > Как видно из примеров, не так сложно взаимодействовать с базой данных. Достаточно передать в метод executeUpdate нужную команду SQL.
Update MySQL Table using JDBC [Easy Guide]
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to update a table from a java application using JDBC Driver. In SQL, an update statement refers to modifying existing records in a table. For example, You have an employee table, which has columns like name, department, and email.
There was a particular record, where the department was named Textile but it was supposed to be Telecom. In such cases, we use an update statement to modify the record which already exists on our database or table.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, make sure your desktop/laptop is already set up with the following applications:
- MySQL, as we’ll use MySQL RDBMS. https://dev.MySQL.com/downloads/
- MySQL Driver, as we need to connect to the java application and therefore we’ll need JDBC driver: https://dev.MySQL.com/downloads/connector/j/
- Java, as we’ll be coding in a java application: https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/
- Eclipse is an IDE(Integrated Development Environment), we’ll be using Eclipse IDE for the application development today, but if you want to go with any other IDE like VScode, Netbeans, etc, you are welcome. It is recommended that you use IDE as it eases out a lot for you automatically which saves your time: https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/
If you are connecting to JDBC for the first time, We recommend you to follow the previous tutorial on how to connect MySQL database using JDBC.
Now, we are all through with our setup and good to go for the tutorial.
Create A Table In MySQL
For this tutorial, you must have an existing table in your database, if you do have a table that you want to update then you may proceed with the next step. Otherwise, you can follow along.
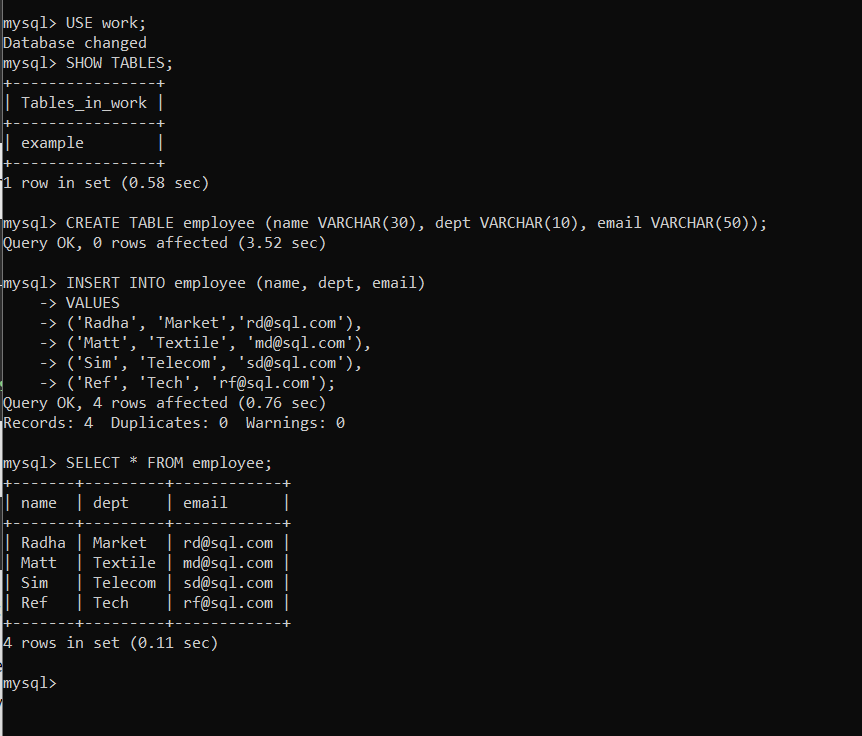
Open MySQL Command-Line client, we’ll be creating an employee table that will have three columns, name, department, and email.
To see view available databases:
SHOW DATABASES;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To create a new table or use an existing table:
CREATE DATABASE databasename; USE tablename;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To view existing tables or to create a new table:
SHOW TABLES; CREATE TABLE tablename (field1 datatype, field2 datatype. );Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To insert values into a table:
INSERT INTO TABLE (field1, field2. ) VALUES (value1, value2, ..);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Create Java Application in Eclipse IDE
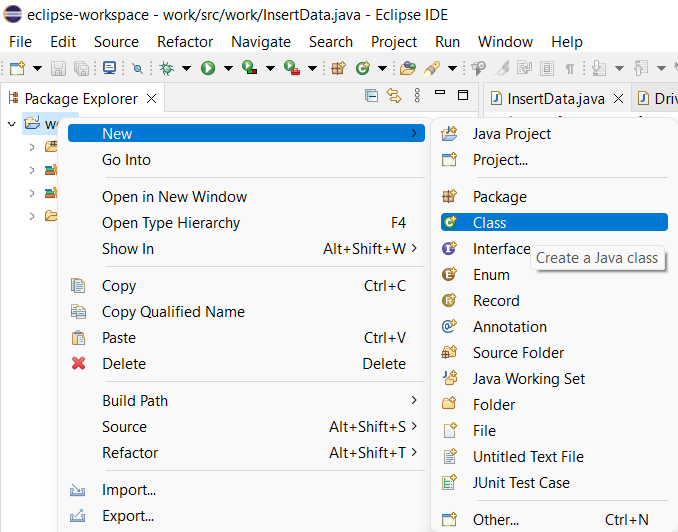
Open Eclipse Workspace, create a java project by clicking on File -> New -> Java Project. If you already have an existing project you can just right-click on it and create a new class. Name the class as UpdateSQL or UpdateData.
Update MySQL table using JDBC
To update a MySQL table from a java application, we use JDBC Driver, there are 4 steps we need to follow:
- Create a Connection
- Create a Statement
- Execute Query
- Close connection
We are using the Employee table, we’ll update the record that has name = ‘Matt’ and we’ll change the department name form ‘Textile’ to ‘Telecom’. The below java code will help you to perform that:
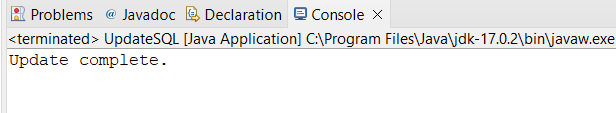
package work; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.Statement; public class UpdateSQL < public static void main(String[] args) < String url = "jdbc:MySQL://localhost:3306/work"; String user ="root"; String password = "root"; try < //1. Create a connection Connection myConn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password); //2. Create a statement Statement myStmt = myConn.createStatement(); //3. Execute Query String sql = "update employee " +"set dept = 'Telecom" + " where name = 'Matt'"; myStmt.executeUpdate(sql); System.out.println("Update complete."); //4. Execute Query myConn.close(); > catch(Exception e) < e.printStackTrace(); >> >Code language: Java (java)After writing the java update code, you can right-click and run the application as Java Application. The application will run successfully and you’ll get the console output as Update complete.
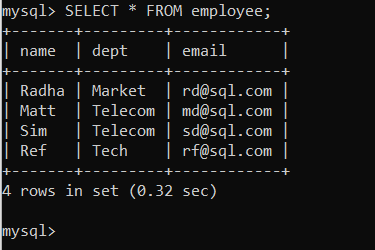
To check if the table is updated, we can check in by writing the select statement for the employee table.
You can see in the above image, that Matt’s department has now been updated from ‘Textile’ to ‘Telecom’ using JDBC.
This is how you can update any record or records in a table through a java application using JDBC.