- Основной метод Java – main method
- Простое объявление класса Java
- main() метод
- Запуск метода main()
- Передача аргументов
- Java main() Method – public static void main(String[] args)
- Syntax of main() Method
- Java
- 1. Public
- Java
- 2. Static
- Java
- 3. Void
- Java
- 4. main
- Java
- 5. String[] args
- Java
- FAQs on Java main() Method
- Q1. Can the main method be int? If not, why?
- Java
- Java
- Explanation of the above programs:
- Q2. Can we execute a Java program without the main method?
- Q3. Can we declare the main() method without String[] args?
Основной метод Java – main method
Программа Java – это последовательность инструкций, которые выполняются в определенном порядке. Поскольку инструкции выполняются в определенном порядке, Java-программа имеет начало и конец.
Для выполнения вашей программы вам необходимо указать виртуальной машине, с чего начать выполнение программы. Все инструкции(код) должны находиться внутри класса. Класс – это способ группировки данных и инструкций, которые принадлежат друг другу. Таким образом, класс может содержать как переменные, так и методы. Переменная может содержать данные, а метод группирует набор операций над данными(инструкции). Не так страшно, если вы еще не до конца поняли это. Начнем разбираться.
Простое объявление класса Java
Объявление простого класса без каких-либо переменных, методов или любых других инструкций выглядит следующим образом:
Этот код Java должен находиться в файле с тем же именем, что и у класса, и заканчиваться суффиксом файла .java. В частности, имя файла должно быть MyClass.java. Как только файл находится в файле, соответствующем его имени класса и оканчивающемся на .java, вы можете скомпилировать его с помощью компилятора из Java SDK или изнутри вашей Java IDE(что гораздо проще).
Рекомендуется размещать свой класс в пакете Java. Пакет Java – это просто каталог в вашей файловой системе, который может содержать один или несколько файлов. Пакеты могут быть вложенными, как каталоги.
Например, вы можете создать пакет с именем myjavacode, который будет соответствовать каталогу на вашем жестком диске с именем myjavacode.
Если вы находите класс внутри пакета, вы должны указать имя пакета в верхней части файла. Вот как выглядит класс с добавлением объявления пакета:
package myjavacode; public class MyClass
Примечание. Файл MyClass.java должен теперь находиться в каталоге myjavacode и содержать объявление пакета package myjavacode; Недостаточно, чтобы файл находился в правильном каталоге. Также недостаточно просто иметь объявление пакета внутри файла. Оба требования должны быть выполнены.
main() метод
Java-программа начинается с выполнения метода main некоторого класса. Вы можете выбрать имя класса для выполнения, но не имя метода. Метод всегда должен называться main . Вот как выглядит объявление основного метода, когда он находится внутри объявления класса:
package myjavacode; public class MyClass < public static void main(String[] args) < >>
Три ключевых слова public, static и void имеют особое значение. Просто помните, что для объявления метода main() нужны эти три ключевых слова.
После трех ключевых слов у вас есть имя метода. Напомним, что метод – это набор инструкций, которые могут быть выполнены, как если бы они были одной операцией. Вызывая(выполняя) метод, вы выполняете все инструкции внутри этого метода.
После имени метода сначала ставится левая скобка, а затем список параметров. Параметры – это переменные(данные / значения), которые мы можем передать методу, который может использоваться инструкциями в методе для настройки его поведения. Основной метод всегда должен принимать массив объектов String. Вы объявляете массив объектов String следующим образом:
Расскажу о том, что такое String или что такое массив в следующих уроках. Не имеет значения, какое имя вы даете параметру. Ранее в примере с методом main() я вызывал параметр аргумента массива String, а во втором – строковый массив. Вы можете выбрать имя любое.
После списка параметров метода следует сначала левая фигурная скобка(<), затем некоторое пустое пространство, а затем правая фигурная скобка(>). Внутри фигурных скобок инструкции, которые должны выполняться при выполнении основного метода. В приведенном выше примере нет никаких инструкций для выполнения. Метод пуст.
Давайте вставим одну инструкцию в основное тело метода. Вот пример:
package myjavacode; public class MyClass < public static void main(String[] args) < System.out.println("Hello World, Java Program"); >> Теперь основной метод содержит эту единственную инструкцию:
System.out.println("Hello World, Java Program"); Эта инструкция выведет текст Hello World, Java Program. Если вы запустите свою программу из командной строки, вы увидите вывод в консоли командной строки. Если вы запускаете из IDE, IDE обычно перехватывает весь вывод на консоль и делает его видимым для вас где-то внутри IDE.
Запуск метода main()
Когда вы запускаете программу, вы обычно делаете это через командную строку(консоль). Вы вызываете команду, которая поставляется вместе с JRE, и указываете, какой класс выполнять и какие аргументы передавать методу main(). Затем Java-приложение выполняется внутри JVM. Вот диаграмма, иллюстрирующая это:
Вот пример командной строки:
java -cp classes myjavacode.MyClass
- Первая часть этой команды запускает JVM. В некоторых случаях вам может потребоваться указать полный путь к папке, в которой находится команда на вашем компьютере(обычно внутри подкаталога bin каталога установки Java).
- Второй и третий аргументы(классы -cp) сообщают JVM, в каком каталоге находятся скомпилированные классы. В этом случае скомпилированные классы расположены в каталоге с именем classes.
- Четвертый аргумент – это имя класса Java, который должна выполнить JVM. Обратите внимание, что имя класса также содержит имя пакета, в котором находится класс(«полное имя класса»).
Передача аргументов
Вы можете передавать аргументы из командной строки в метод main().
java -cp classes myjavacode.MyClass Hello World
Когда JVM выполняет метод main() myjavacode.MyClass, массив String, передаваемый в качестве параметра методу main(), будет содержать две строки: «Hello» и «World».
Метод может получить доступ к аргументам из командной строки следующим образом:
package myjavacode; public class MyClass < public static void main(String[] args) < System.out.println( args[0] ); System.out.println( args[1] ); >>
Обратите внимание на ссылки на элемент 0 и элемент 1 в массиве args(args [0] и args [1]). args [0] будет содержать строку(текст) Hello, а args [1] будет содержать мир строки.
В вашем проекте может быть столько классов, сколько вы хотите, с методом main(). Но виртуальной машине можно поручить запускать только один из них одновременно.
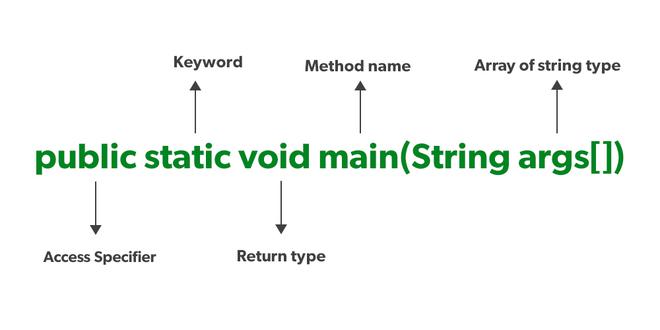
Java main() Method – public static void main(String[] args)
In Java programs, the point from where the program starts its execution or simply the entry point of Java programs is the main() method. Hence, it is one of the most important methods of Java, and having a proper understanding of it is very important.
The Java compiler or JVM looks for the main method when it starts executing a Java program. The signature of the main method needs to be in a specific way for the JVM to recognize that method as its entry point. If we change the signature of the method, the program compiles but does not execute.
The execution of the Java program, the java.exe is called. The Java.exe in turn makes Java Native Interface or JNI calls, and they load the JVM. The java.exe parses the command line, generates a new String array, and invokes the main() method. A daemon thread is attached to the main method, and this thread gets destroyed only when the Java program stops execution.
Syntax of main() Method
The most common in defining the main() method is shown in the below example.
Java
Every word in the public static void main statement has got a meaning in the JVM that is described below:
1. Public
It is an Access modifier, which specifies from where and who can access the method. Making the main() method public makes it globally available. It is made public so that JVM can invoke it from outside the class as it is not present in the current class.
Java
Error: Main method not found in class, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application
2. Static
It is a keyword that is when associated with a method, making it a class-related method. The main() method is static so that JVM can invoke it without instantiating the class. This also saves the unnecessary wastage of memory which would have been used by the object declared only for calling the main() method by the JVM.
Java
Error: Main method is not static in class test, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)
3. Void
It is a keyword and is used to specify that a method doesn’t return anything. As the main() method doesn’t return anything, its return type is void. As soon as the main() method terminates, the java program terminates too. Hence, it doesn’t make any sense to return from the main() method as JVM can’t do anything with the return value of it.
Java
Error: Main method must return a value of type void in class Main, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)
4. main
It is the name of the Java main method. It is the identifier that the JVM looks for as the starting point of the java program. It’s not a keyword.
Java
Error: Main method not found in class, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args) or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application
5. String[] args
It stores Java command-line arguments and is an array of type java.lang.String class. Here, the name of the String array is args but it is not fixed and the user can use any name in place of it.
Java
Apart from the above-mentioned signature of main, you could use public static void main(String args[]) or public static void main(String… args) to call the main function in Java. The main method is called if its formal parameter matches that of an array of Strings.
FAQs on Java main() Method
Q1. Can the main method be int? If not, why?
Java
prg1.java:6: error: missing return statement > ^ 1 error
Java does not return int implicitly, even if we declare the return type of main as int. We will get a compile-time error
Java
Error: Main method must return a value of type void in class GeeksforGeeks, please define the main method as: public static void main(String[] args)
Now, even if we do return 0 or an integer explicitly ourselves, from int main. We get a run time error.
Explanation of the above programs:
The C and C++ programs which return int from main are processes of Operating System. The int value returned from main in C and C++ is exit code or exit status. The exit code of the C or C++ program illustrates, why the program was terminated. Exit code 0 means successful termination. However, the non-zero exit status indicates an error.
For Example exit code 1 depicts Miscellaneous errors, such as “divide by zero”.
The parent process of any child process keeps waiting for the exit status of the child. And after receiving the exit status of the child, cleans up the child process from the process table and free the resources allocated to it. This is why it becomes mandatory for C and C++ programs(which are processes of OS) to pass their exit status from the main explicitly or implicitly.
However, the Java program runs as a ‘main thread’ in JVM. The Java program is not even a process of Operating System directly. There is no direct interaction between the Java program and Operating System. There is no direct allocation of resources to the Java program directly, or the Java program does not occupy any place in the process table. Whom should it return an exit status to, then? This is why the main method of Java is designed not to return an int or exit status.
But JVM is a process of an operating system, and JVM can be terminated with a certain exit status. With help of java.lang.Runtime.exit(int status) or System.exit(int status).
Q2. Can we execute a Java program without the main method?
Yes, we can execute a Java program without a main method by using a static block.
A static block in Java is a group of statements that gets executed only once when the class is loaded into the memory by ClassLoader, It is also known as a static initialization block, and it goes into the stack memory.
Q3. Can we declare the main() method without String[] args?
Yes, we can declare the main() method without String[] args. Although it will generate an error message if we directly try to execute the main method inside the driver class as done in the below example.