- Calculate log base 2 of an integer in Java
- log() in Java
- Java Math log() method
- Syntax of Math log() in Java
- Parameters of Math log() in Java
- Return Value of Math log() in Java
- Exception of Math log() in Java
- Example of Math log() in Java
- Math log() in Java
- Example 1: Radioactive Material Age
- Example 2: Negative Input
- Example 3: Positive Infinity
- Example 4: Zero Input
- Example 5: Custom log() method
- Conclusion
Calculate log base 2 of an integer in Java
This post will discuss how to calculate log base 2 of an integer value in Java.
The java.lang.Math class contains static methods for calculating the logarithms to bases 10 and e . Its log() method returns the natural logarithm (base e ), and the log10() method returns the base 10 logarithms of a double value.
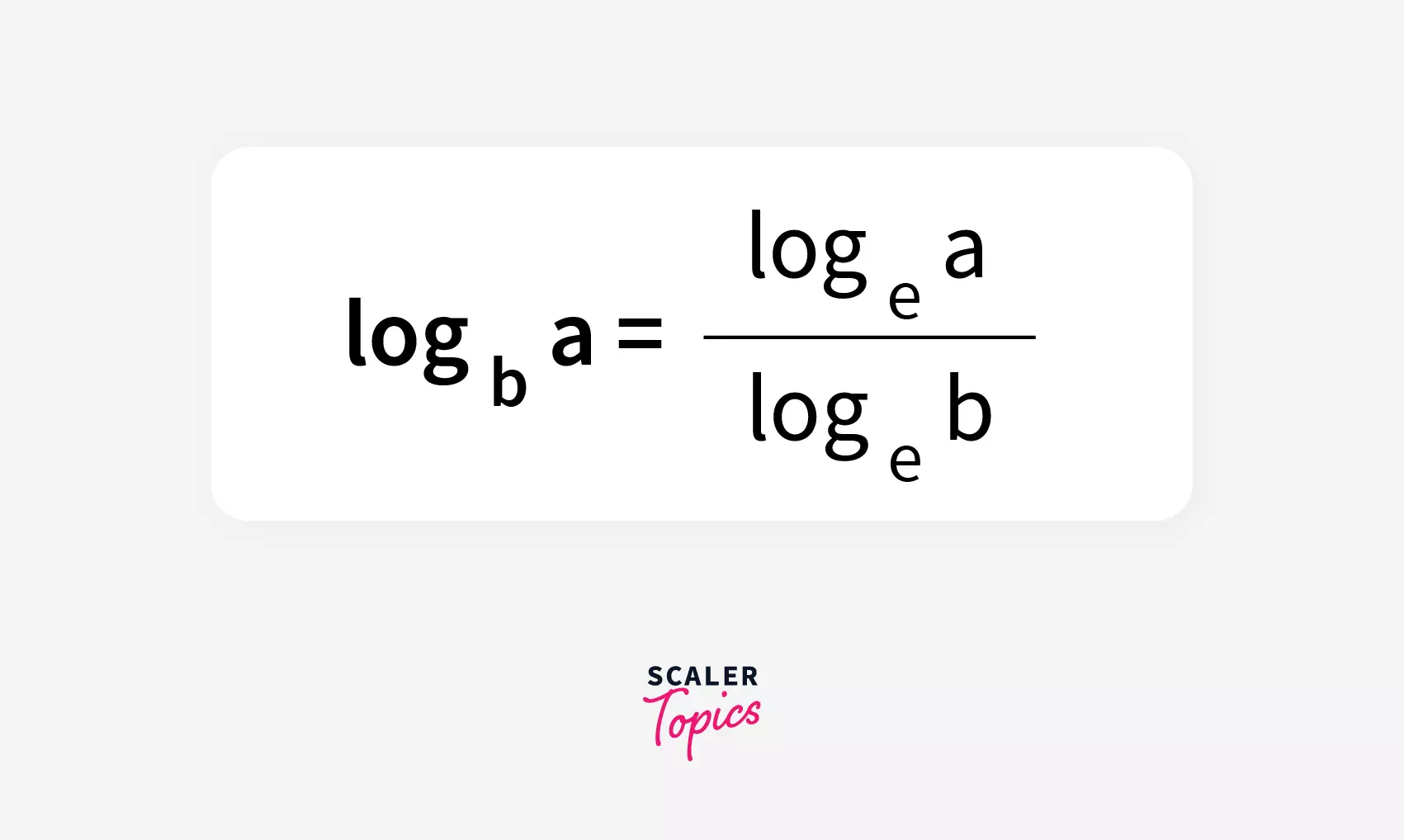
The java.lang.Math class does not provide any method to calculate logarithms with respect to any base b . Mathematically, this can be determined using either of these two logarithms:
Programmatically, this can be done in Java as follows:
To calculate the base 2 logarithm, we can simply use the following function:
Please be aware that miscalculation is a risk due to imprecise floating-point arithmetic, as explained in this StackOverflow post. To completely eliminate errors, add an epsilon between 1e-11 and 1e-14 , as shown below:
That’s all about calculating log base 2 of an integer in Java.
Average rating 4.85 /5. Vote count: 27
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Thanks for reading.
Please use our online compiler to post code in comments using C, C++, Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, PHP, and many more popular programming languages.
Like us? Refer us to your friends and help us grow. Happy coding 🙂
This website uses cookies. By using this site, you agree to the use of cookies, our policies, copyright terms and other conditions. Read our Privacy Policy. Got it
log() in Java
The log() method in Java Math class returns natural logarithm of a value.
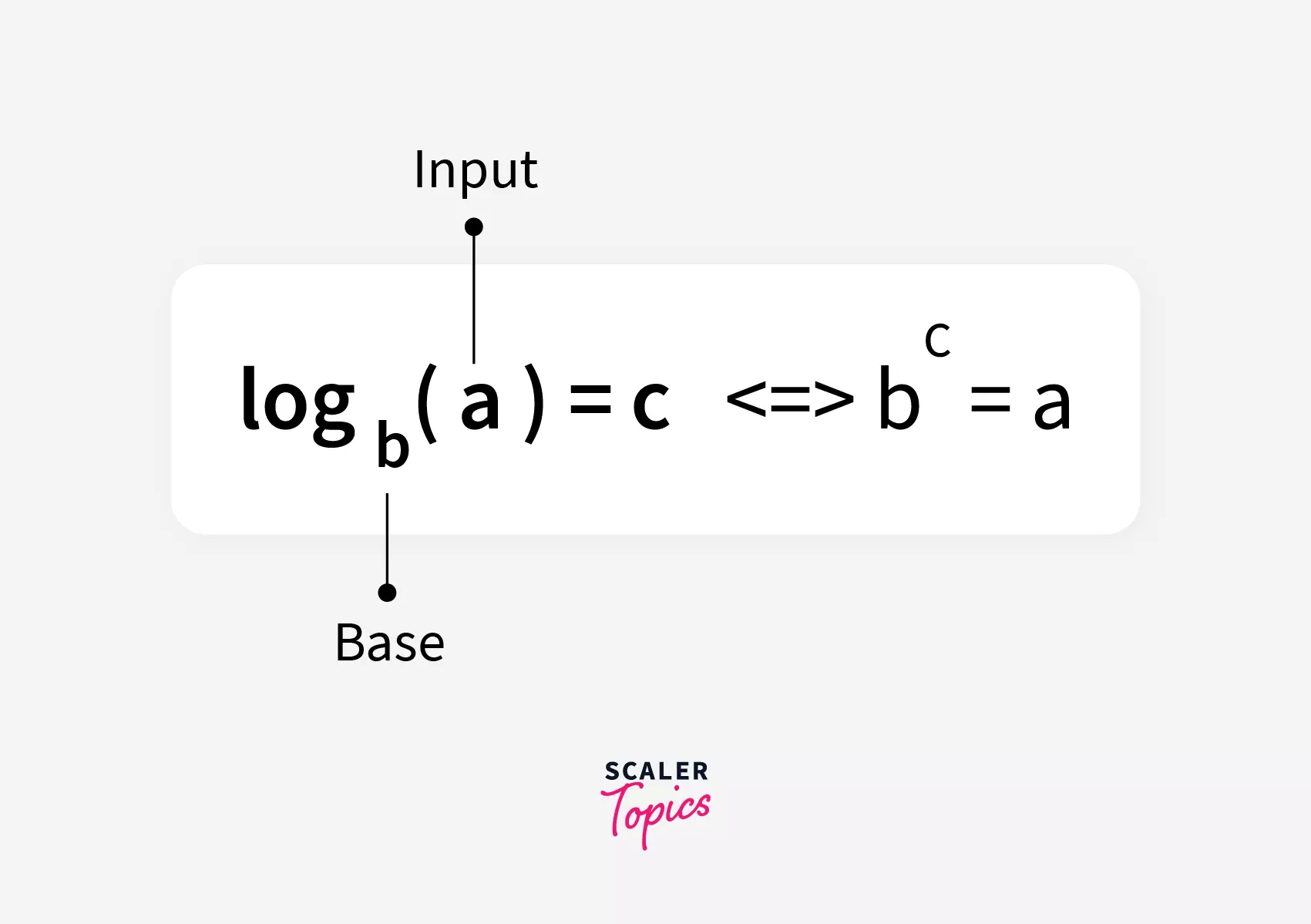
Natural logarithm means the base is fixed as » e e e » and the method returns the value of logarithm of the argument to the base » e e e «. Natural l o g log l o g or l n ln l n means it has a base of » e e e «, where e = 2 . 7 1 8 e=2.718 e = 2 . 7 1 8 .
Mathematically logarithm of a number is given by the equation:
Java Math log() method
The log() method of Math class is used to find the natural logarithm of the given argument i.e. log of the argument to the base e where e is the exponential constant.
Syntax of Math log() in Java
This is a static method so we don’t need an instance of Math class to invoke this method, rather we can use it directly. By default, the base is fixed to «e» .
Parameters of Math log() in Java
It takes a single argument:
If the input is not of double type, the compiler tries to convert the input to double format if possible.
Return Value of Math log() in Java
Java Math log() method returns the value of log of the argument to the base e e e . However, there are some special cases:
| Value of «a» | Return Value |
|---|---|
| NaN | NaN |
| Negative number | NaN |
| Positive Zero or Negative Zero | Negative Infinity |
| Positive Infinity | Positive Infinity |
Exception of Math log() in Java
No exception is thrown by log() method of Math class in Java.
Some special cases of errors:
- If we pass a String as input to the log() function it raises an error of incompatible types as String cannot be converted to double.
- However, if we pass a character to the log() method, it does not throw an error as the A S C I I ASCII A S C I I value of the character is converted to double.
- Example: Maths.log(‘e’) is same as Maths.log(101) and returns a value of 4 . 6 1 4.61 4 . 6 1 but Maths.log(«e») throws an error.
Example of Math log() in Java
Math log() in Java
We’ll check the table of return values given above.
Example 1: Radioactive Material Age
We’ll take a real-life example. The age of radioactive material is given by T = − ( 1 / λ ) ∗ l n ( A / A o ) T = -(1/λ)*ln(A/Ao) T = − ( 1 / λ ) ∗ l n ( A / A o ) , where λ λ λ is a constant for a particular element and A is the present amount while Ao is the initial amount.
The above code computes the age of the sample to be nearly 2 0 20 2 0 years.
Example 2: Negative Input
If the input/argument is negative, the output is N a N NaN N a N because logarithm of negative numbers is not defined.
Example 3: Positive Infinity
If the input is positive infinity, the output is positive infinity because logarithm to any base at positive infinity gives positive infinity.
Example 4: Zero Input
If the input is zero, the output is negative infinity because logarithm to any base at 0 gives negative infinity.
Example 5: Custom log() method
Custom log() method of Java returns a natural logarithm i.e. the base is » e e e «. But what if I’ve to find a logarithm of 2 5 25 2 5 to the base 5 5 5 rather than e e e . For that, we’ll use the change-of-base formula given below.
To get the logarithm of an inputted value to a custom base, we’ll divide the natural logarithm of the inputted value by the natural logarithm of custom base.
Explanation:
- We pass a number and a custom base as input to our custom l o g B logB l o g B (number,custom_base) method.
- l o g B ( ) logB() l o g B ( ) calculates natural logarithms of the number and the custom base.
- Using the change of base formula the method divides the natural logarithms computed in the previous step to get the solution.
Conclusion
- The log() method of Math class in Java returns the natural logarithm of a value, i.e. the base of the logarithm is » e e e «.
- Result is NaN if the input is NaN or negative .
- Result is positive infinity if the input is positive infinity.
- Result is negative infinity if the input is positive zero or negative zero.
- It does NOT throw any exception(s). However, if the input is a String (and not character), it throws an error because a String instance cannot be converted into a double value.