- How to fix java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class files? Example
- Cause of java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file
- java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file
- Solution:
- How to Fix the Unsupported Class Version Runtime Error in Java
- What is the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error and Why Does it Happen?
- How to Fix the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error
- Maven Projects
How to fix java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class files? Example
«java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file» is a common error in Java programming language which comes when you try to run a Java class file which was compiled by different version of Java compiler than then JRE version you are using to run it. In our last article, we discussed that how to resolve Java.lang.UnSupportedClassVersionError and found that it comes when a major and minor version of the class is not supported by Java virtual machine or JRE running the program. Though » java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file » is a little different than that of its manifestation and Cause, both are related to the mismatch in compiler javac and runtime java version.
The UnsupportedClassVersionError is not as difficult as Java.lang.OutOfMemoryError and neither its solution is too complex but what is hard is thinking in the right direction because the cause of different types of UnsupportedClassVersionError is different.
Cause of java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file
» java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file » comes when you compile a Java class in higher version of Java Compiler and run it on a lower version of Java virtual machine or JRE. For example, if you have compiled your Java class using Java SE 17 compiler and then you try to run it on Java SE 11 or Java SE 8 then you will get this error.
Similarly, you can get the Bad Version number in class file error if you compile your Java source file by Java SE 11 compiler, which comes when you install Java 11 JDK in your machine and then you try to run it but there is a lower version of JRE is configured in PATH or it comes first in the PATH if you have multiple JRE installed in your machine.
The key here is you need to run your Java program or class file in the version greater than or equal to the version which is used to compile your Java program. Java is backward compatible which means a JAR file created by Java 1 will still work in Java SE 17 but a JAR File created by Java SE 17 cannot work in Java 1 as it doesn’t have all the new enhancements.
It’s more of a common sense than any rocket science but just finding which version of Java is used to compile and run the program can take time and requires experienced to troubleshoot and think in the right direction.
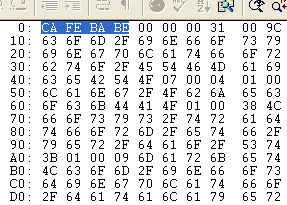
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: Bad version number in .class file
To understand this UnsupportedClassVersionError better let’s reproduce it via a simple example in Java:
2) Run Loan.class with JRE 1.5 or any version lower than Java 17 like Java 8 or Java 11. I have used Java 5 here
Solution:
Now you know that your source is compiled for a higher version of JRE or Java runtime if it doesn’t work in JDK 1.5 then try to run on JDK 1.6 and you will be able to remove «Bad version number in .class file«. The same problem can come to any other Java version for example, a class file compiled by JDK 11 will not run on Java 8 or Java 9 JRE. Similarly, a class file compiled by Java 17 compiler will not run on Java SE 11 JRE.
How to Fix the Unsupported Class Version Runtime Error in Java
Runtime errors occur when a program is being executed and, in the case of compiled languages, after the program has been successfully compiled. Runtime errors are, therefore, harder to detect and prevent than compile-time errors [1]. In Java, some of these runtime errors (namely throwable objects which are not exceptions) are triggered at a very early stage, while the program is basically starting up. Namely, there is a process of dynamic loading, linking, and initializing of classes and interfaces by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) that occurs at the very beginning of execution of any Java application [2]. This allows for a certain category of errors to be captured and dealt with before the program effectively starts.
This category of high level runtime errors in Java is represented by classes which are direct descendants of the java.lang.Error class [3], including the java.lang.LinkageError class which denotes errors occurring during the aforementioned startup process [4]. An instance of the Error class (or any of its subclasses) is a throwable object that a program is not expected or advised to handle, but instead, should cause immediate termination of the program. This is because most of these errors occur as a result of abnormal conditions, often so severe that it is impossible to know or control what further execution of the program might do. LinkageError instances in particular indicate critical class-related errors triggered during the class linking phase of the startup process, usually as a consequence of some post-compilation changes in the bytecode or the Java environment.
What is the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error and Why Does it Happen?
The java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError class extends java.lang.ClassFormatError which is thrown whenever the JVM attempts to read a class file and determines that the file is malformed or otherwise cannot be interpreted as a class file [5][6]. As per Java’s error class hierarchy (Figure 1), an instance of UnsupportedClassVersionError is also a LinkageError which means that the error is identified during the JVM class linking process.
The specific issue that the UnsupportedClassVersionError error raises is the detection of a class file which had been compiled with a newer version of Java than the one used to run it. For instance, if a specific .class file has been compiled with Java Development Kit (JDK) 15, trying to run it with Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 8 will trigger the UnsupportedClassVersionError error. This almost invariably happens when someone attempts to run a program with a JDK or a JRE version that is incompatible with, i.e., lower than the Java version in which the code was compiled.
How to Fix the UnsupportedClassVersionError Error
The solution to the UnsupportedClassVersionError error generally boils down to two options:
- Run the code with a newer version of Java/JRE, or
- Recompile the code with an older Java/JDK compiler.
As a variant of #2, recompiling the code can also be done by specifying the “target” or “release” parameter of a newer Java/JDK compiler to an earlier version of Java, to produce backward-compatible bytecode.
Before recompiling any code, it is important to know the runtime version of both the already compiled code and the environment in which it needs to run on. The message accompanying the UnsupportedClassVersionError error provides this information in the form of class file versions, which can be mapped directly to a specific Java version, using the values from the table below.
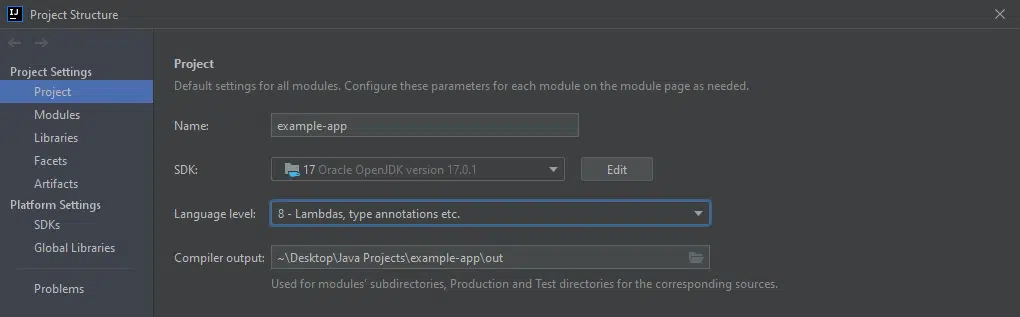
Maven Projects
When dealing with Maven projects, which the majority of both small and large enterprise Java programs are, it is possible to control the Java version targeted by the compilation process from the Maven configuration, i.e. Maven Project Object Model (POM) file. The relevant settings are shown in the Figure below.
Note that while it is possible to control the source and target versions independently, it is recommended to set them to equal values, as backward compatibility of the compiled bytecode cannot be guaranteed [8].
Can Constructors Throw Exceptions in Java
How to Fix and Avoid NullPointerException in Java
How to Fix «Illegal Start of Expression» in Java
«Rollbar allows us to go from alerting to impact analysis and resolution in a matter of minutes. Without it we would be flying blind.»