- FileNotFoundException in Java
- Unhandled exception type FileNotFoundException
- Unreported Exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
- Different Reasons to Get FileNotFoundException in Java
- Java FileNotFoundException
- How FileNotFoundException work in Java?
- Constructors of Java FileNotFoundException
- 1. Constructor with no error message
- 2. Constructor with an error message
- Examples of Java FileNotFoundException
- Example #1
- Example #2
- How to avoid FileNotFoundException?
- Case 1: File is missing
- Case 2: File is inaccessible
- Conclusion
- Recommended Articles
FileNotFoundException in Java
FileNotFoundException is a checked exception therefore we must catch or handle it. It is a subclass of IOException and is defined in the java.io package. Generally, FileNotFoundException will be thrown by the FileInputStream, FileReader, and RandomAccessFile constructors, where file information is the source and must be passed to the constructor. Here we will discuss the different reasons for getting this exception.
Unhandled exception type FileNotFoundException
FileNotFoundException is a checked exception, and at compile time compiler checks whether we are handling FileNotFoundException or not.
It means if there is a chance to raise FileNotFoundException in the statement then we must handle the FileNotFoundException either by using try-catch block or by using the throws keyword.
Unreported Exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
If we don’t handle FileNotFoundException then the compiler gives the compile-time error: unreported exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown.
Example:- FileReader class is used to read character data from the file. The constructor of FileReader class throws FileNotFoundException.
import java.io.FileReader; public class Test < public static void main(String[] args) < FileReader fr = new FileReader("data.txt"); // . >>Since we don’t handle FileNotFoundException therefore we will get the compile-time error:- unreported exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown,
FileReaderDemo.java:6: error: unreported exception
FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
FileReader fr = new FileReader(“data.txt”);
^
1 error
Solution of compile-time error: unreported exception FileNotFoundException; must be caught or declared to be thrown,
But before catching and handling the exception we must import FileNotFoundException or java.io package. While catching or handling the exception we can also use superclass exception, Exception, or Throwable. The Throwable is the superclass for all Exceptions.
// Java program to handle the exception import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class Test < public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException < FileReader fr = new FileReader("data.txt"); // . >>Using throws we are informing the caller method that the called method may throw FileNotFoundException. Now, it’s the responsibility of the caller method to catch or handle the exception.
import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; public class Test < public static void main(String[] args) < try < FileReader fr = new FileReader("data.txt"); // . >catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) < fnfe.printStackTrace(); >> >Using try/catch block we are catching the exception. We can finally block to close the stream also.
Different Reasons to Get FileNotFoundException in Java
We will get runtime exception in the following cases,
- The passed named File is not available.
- Available but it is a directory rather than a normal file.
- The file doesn’t have reading/writing permission.
- Access permission is not there.
If the given name is a directory/folder, not a file then also we will get the same exception with “Access is denied”.
In all Writer and Output classes, we won’t get FileNotFoundException because the file is not available. These classes are made for writing the data and need destination file information, if the file is not available then their constructors can create an empty file with the given name itself, and then write the data into the file. They are FileNotFoundException for another reason like file creation permission is not there, it is available but represents directory/folder, or file is available but writing permission is not there.
Most of the time, Windows C drive doesn’t allow to create a file, it only gives permission to create a directory. In this case, we can get FileNotFoundException. We can get an exception:- Exception in thread “main” java.io.FileNotFoundException: C:\xyz.txt (Access is denied). Similarly, in Linux/Unix OS, we can’t create files in other user directories.
In all Reader and Input classes file is the source from where the Java application will collect the data. And in this case, the file must be available else we will get FileNotFoundException. Other reasons are:- it is a folder rather than a file, access permission is not there.
If you enjoyed this post, share it with your friends. Do you want to share more information about the topic discussed above or do you find anything incorrect? Let us know in the comments. Thank you!
Java FileNotFoundException
Java FileNotFoundException is a type of exception that often occurs while working with File APIs in Java where the path specified for a file for reading or writing purposes in the constructor of classes FileInputStream, FileOutputStream, and RandomAccessFile, either does not exist or inaccessible due to an existing lock or other technical issues. This is a checked exception is a direct subclass of IOException that has been introduced with JDK 1.0. Also, it contains two types of constructors that can be called where one returns an Exception with a null message to display, whereas the other prints the specified message in case the exception occurs.
Web development, programming languages, Software testing & others
public class FileNotFoundExceptionextends IOException- public: The keyword public refers to that the given class is accessible from any class in the project and needs to be inherited to throw an exception.
This class is a direct subclass of IOException, thus inheriting all the class’s methods and variables.
How FileNotFoundException work in Java?
FileNotFoundException is a checked exception is used that occurs when a file path specified for accessing does not exist or is inaccessible. With the checked exception, it means that the java compiler checks at compile time if this exception has been handled or not; otherwise, a compile-time error occurs. Let us see how the exception is thrown at run-time in case it has been handled using try-catch blocks or using throws keyword in its definition at compiler time.
File fileObj = new File("C:/JavaPractice.txt")Suppose we instantiate a File class object as given above with a path of a file, and that file does not exist. In that case, when the compiler attempts to read or write the file and finds such a situation, it throws an exception and create an instance of FileNotFoundExceptionclass. In case it is not specified which constructor needs to be called, the constructor with no error message is thrown.
Thus the application fails with the below error:
Constructors of Java FileNotFoundException
FileNotFoundException is a subclass of IOException that is very useful to trace if the file specified in the file path exists and even accessible. Thus for using this, one needs to instantiate it, and it is a public class; it can be instantiated from any where in the project. And for creating the instance of the class has 2 types of constructors.
Given below are the two types of constructors:
1. Constructor with no error message
This type of constructor is used to create an instance of FileNotFoundException class where it returns null as its error detail message.
public FileNotFoundException()FileNotFoundExceptionexcepObj = new FileNotFoundException()2. Constructor with an error message
This type of constructor is used to create an instance of FileNotFoundException class where it returns a specified string as its error detail message.
public FileNotFoundException(String s)FileNotFoundExceptionexcepObj = new FileNotFoundException("This is a FileNotFoundException")The error message specified can be easily retrieved using the Throwable.getMessage() method since this is one of the superclasses of FileNotFoundException class.
Examples of Java FileNotFoundException
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
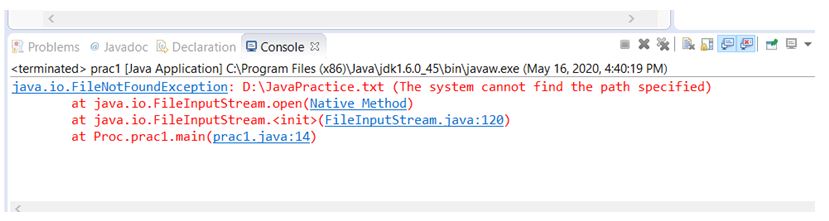
Here we see how an exception is thrown by JVM if one file in inaccessible. In this, the error message displaying in output is one specified by default by JVM.
//package Proc; import java.io.Console; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class prac1 < public static void main(String[] args) < File fileObj = new File("D:/JavaPractice.txt"); FileInputStream fISObj = null; try< fISObj = new FileInputStream(fileObj); while (fISObj.read()!=-1)< System.out.println(fISObj.read()); >>catch (FileNotFoundException e)< e.printStackTrace(); >catch (IOException e) < e.printStackTrace(); >> >Example #2
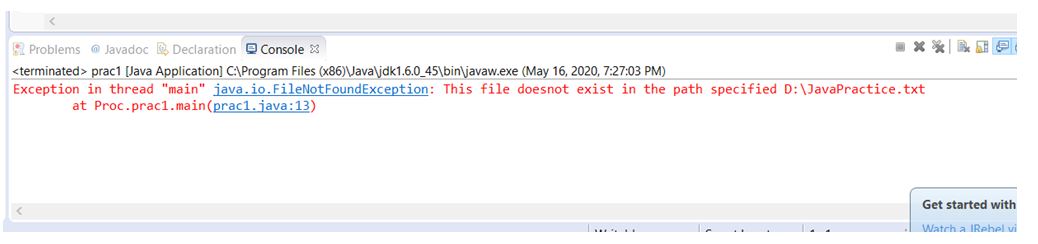
In this example, we will use the constructor with a specified error message to display the error when the file does not exist at the given path. We have used the throw keyword to throw the exception.
//package Proc; import java.io.Console; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; public class prac1 < public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException,IOException< File fileObj = new File("D:/JavaPractice.txt"); if(!fileObj.exists())< throw new FileNotFoundException("This file doesnot exist in the path specified "+fileObj.toString()); >else < System.out.println("Welcome, we got into file "+fileObj.toString()); >> >How to avoid FileNotFoundException?
Getting a FileNotFoundException in an application makes an application inefficient. The first step to avoid this exception is to check if the specified file exists in at the specified path, but still, there might occur a situation in real-time applications that the file is missing or if other processes lock the file to be read to write into it.
Case 1: File is missing
To avoid this, one can use the java.io.File.exists() method to check if the file one attempts to read exist on the path specified or not. Using this, we must make sure if our code is able to handle the FileNotFoundException exception.
Case 2: File is inaccessible
To avoid such cases, one needs to take care if the file we are attempting to read is currently locked by other users writing it. For this we can use canRead() or canWrite() methods of java.io. File class that tells if the specified file is available for reading or writing purposes or not.
Using these 2 precautionary measures, one can easily avoid an attempt by an instance of file class to open a file that can result into a checked exception. This improves the efficiency of an application that includes a program to access files from a specified path.
Conclusion
FileNotFoundException is a type of checked exception that occurs once an attempt is made to the file that either does not exist or not accessible at that moment due to some lock. Since it is a checked exception java compiler ensures it has been handled at compile time. But still, if one needs to avoid it so they can use exist(), canRead() or canWrite() methods present in File class.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Java FileNotFoundException. Here we discuss how FileNotFoundException work in Java along with the constructors and programming examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
89+ Hours of HD Videos
13 Courses
3 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
97+ Hours of HD Videos
15 Courses
12 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.5
JAVA Course Bundle — 78 Courses in 1 | 15 Mock Tests
416+ Hours of HD Videos
78 Courses
15 Mock Tests & Quizzes
Verifiable Certificate of Completion
Lifetime Access
4.8