- How to convert int value to a Long object in Java? Examples
- 2 Examples to convert an int to a long data type in Java
- 1. int to Long in Java — using autoboxing
- 2. int to Long — using Long.valueOf()
- Convert int to Long in Java
- Introduction
- Method 1: Convert int to Long in Java using Implicit Conversion (Simple Assignment Operation)
- Method 2: Convert int to Long in Java Using Explicit Typecasting
- Method 3: Convert int to Long Object in Java Using valueOf() Method
- Conclusion
- Java Convert int to long with examples
- Java int to long using implicit type casting
- Java int to long Example using Long.valueOf() method
- Top Related Articles:
- About the Author
How to convert int value to a Long object in Java? Examples
Suppose you have an int variable but the part of the application is expecting a Long object, how do you convert a primitive int to a Long object in Java? It shouldn’t be a problem, right? after all long is a bigger data type than int , so all int values are acceptable as long, but we also need a Long object, not just the long primitive value. Now, the problem is reduced to converting a long primitive to a Long object, which is not really a problem if you are running on a JRE version higher than Java 5. But, sometimes autoboxing is not efficient like when you have to convert multiple long values into the Long object in a loop.
A better way to convert your long primitive to the Long object is by using static factory methods like Long.valueOf(long l) , which was originally meant to convert long primitive values to a Long object, prior to Java 5, but, also works fine with int primitive.
So, if you have got an int primitive value, just pass it to Long.valueOf() and you will get a Long object with same value.
Btw, This only works well if the method is expecting a long primitive value, if it’s expecting a Long object then you first need to cast an int to long , so that autoboxing can kick-in
Autoboxing also has a disadvantage in terms of converting null back to primitive value e.g. if you have a Long object than it could be null but long primitive cannot be null.
So auto-unboxing will fail with NullPointerException while converting a null Long object to long primitive. So you should beware of that. Now that you know some concepts, let’s see this conversion in action.
2 Examples to convert an int to a long data type in Java
Here is our two main examples for convert an int data type value to a long data type value. Remember, int is a smaller type and long is bigger data type as int require only 4 bytes or 32-bit as compared to 8 bytes and 64-bit required by long data type.
1. int to Long in Java — using autoboxing
In order to leverage autoboxing, you must typecast an int variable to long , otherwise, the compiler will complain about mismatch type, as shown below :
Long one = 10; // Type mismatch : cannot convert from int to Long
Long three = (long) 3; // works fine
Same is true for a method which is expecting a Long object. You cannot pass an int to them because auto-boxing will not be able to convert an int to Long (see The Complete Java Masterclass — Update for Java 11), but, if you cast an int to long, then auto-boxing will take care of converting it to Long object, as shown below :
ListLong> listOfLong = new ArrayListLong>(); for(int i=0; i< 10; i++)< listOfLong.add((long)i); >
So, if you want to use autoboxing, make sure you cast the int value to long first, don’t worry though, if you forget compiler will ensure this 🙂
Another thing to notice in the above code is that we are using auto-boxing in the loop, which can cause performance issue because a lot of Long objects will be created and discarded.
In our case, it is still ok because the loop is running only 10 times, but if have to do this conversion say a million times, this approach will cause a problem, as explained by Joshua Bloch in his classic book, Effective Java 3rd Edition. A must-read for any Java developer.
2. int to Long — using Long.valueOf()
One of the better ways to convert an int primitive to the Long object is by using the valueOf() method of the Long class. If you use Long.valueOf() then you don’t need to explicitly cast an int to long, Why? because you can pass an int value to a method which is accepting primitive long.
Btw, if you are not familiar with such fundamental rules of Java programming, I suggest taking these free Java online training courses from Udemy and Pluralsight.
Since Long.valueOf() does accept a long primitive, passing an int value to it is no problem at all, here you go :
// you can pass an int to method expects long
Long two = Long.valueOf(2); //Ok
It’s seamless, clean and easy. It is also efficient because valueOf() method implement Flyweight pattern (see Design Patterns courses) and maintains a pool of frequently used Long values, particularly in the range of -128 to 127, as shown below.
Since Long is also immutable in Java, it’s no harm sharing same Long instance between multiple clients.
The Long.vlaueOf() method from JDK 8:
public static Long valueOf(long l) < final int offset = 128; if (l >= -128 && l 127) < // will cache return LongCache.cache[(int)l + offset]; > return new Long(l); >
You can see it caches the Long instances with values in the rage of -128 to 127. This means same Long instance is returned to multiple clients and this work because like String, Long is also Immutable in Java. So, it’s safe to share the same instance of the Long object between multiple clients.
That’s all about how to convert a primitive int value to a Long object in Java. It’s easy but worth knowing the subtleties involved. Prefer Long.valueOf() to take advantage of caching it provides as well as to avoid casting.
Also, remember that auto-boxing will throw NPE if you want to convert a Long object back to long primitive value and it happened to be null. This kind of NPE is sometimes not obvious and takes a long time to reveal itself.
- How to convert Map to List in Java (tutorial)
- How to convert Double to Long in Java? (tutorial)
- How to convert Array to String in Java? (tutorial)
- 5 Ways to convert Java 8 Stream to List? (solution)
- How to convert a binary number to decimal in Java? (tutorial)
- 5 examples of converting InputStream to String in Java? (tutorial)
- How to convert Character to String in Java? (tutorial
Thanks for reading this tutorial, if you like this article then please share with your friends and colleagues, it makes a lot of difference.
Convert int to Long in Java
Typecasting refers to the process of conversion of one data type to another. Several times, it is required to convert a String to int , double to long , int to long , etc.
The int data-type can be converted to long data-type using both implicit and explicit conversions. We can perform implicit conversion because lower data type can be converted to higher data type without any loss.
Introduction
To understand the conversion of an int variable to a long variable, we first have to understand typecasting in Java.
Casting means to treat or convert a variable/expression from one data type to another and it is used to avoid the loss of data as a result of mathematical expression.
There exist two types of casting in Java:
- Widening Casting: This is an automatic/implicit conversion of a small data type to a large data type by the compiler without the loss of any data.
- This is possible because the conversion of a smaller data type to a larger data type is highly compatible with Java programming.
- Widening Casting cannot lead to any loss of data under any circumstances.
- We can use explicit conversion in widening casting also, but explicit conversions are not necessarily required here.
- It is also called implicit casting.
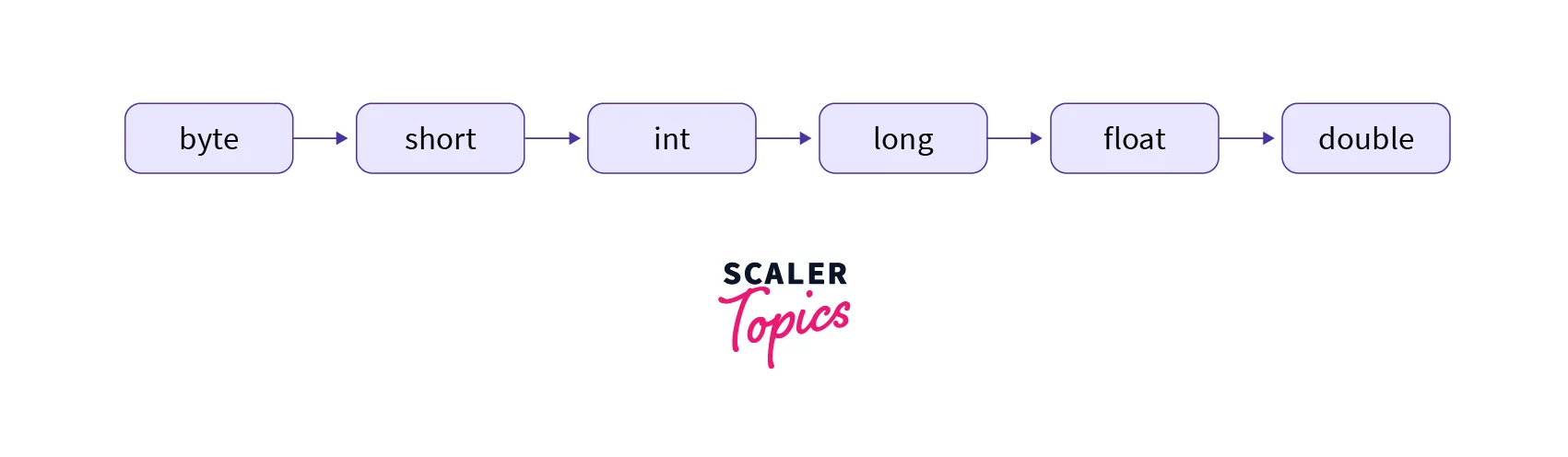
The above-shown data types are arranged in an ascending order on which widening casting can be applied in the given order only, like byte can be converted into short , short can be converted into an int , an int can be converted into long , and so on.
In Java, byte variable takes the least bytes (1 byte), while a double variable takes the most bytes (8 bytes) in the memory.
- Narrowing Casting: This type of casting necessarily requires the manual conversion of larger data types to smaller data types.
- This conversion is also called explicit casting as it is explicitly required to perform this conversion.
- Narrowing Casting can lead to loss of data and it must be done consciously.
- It can be performed by the user using the explicit typecasting methods only.
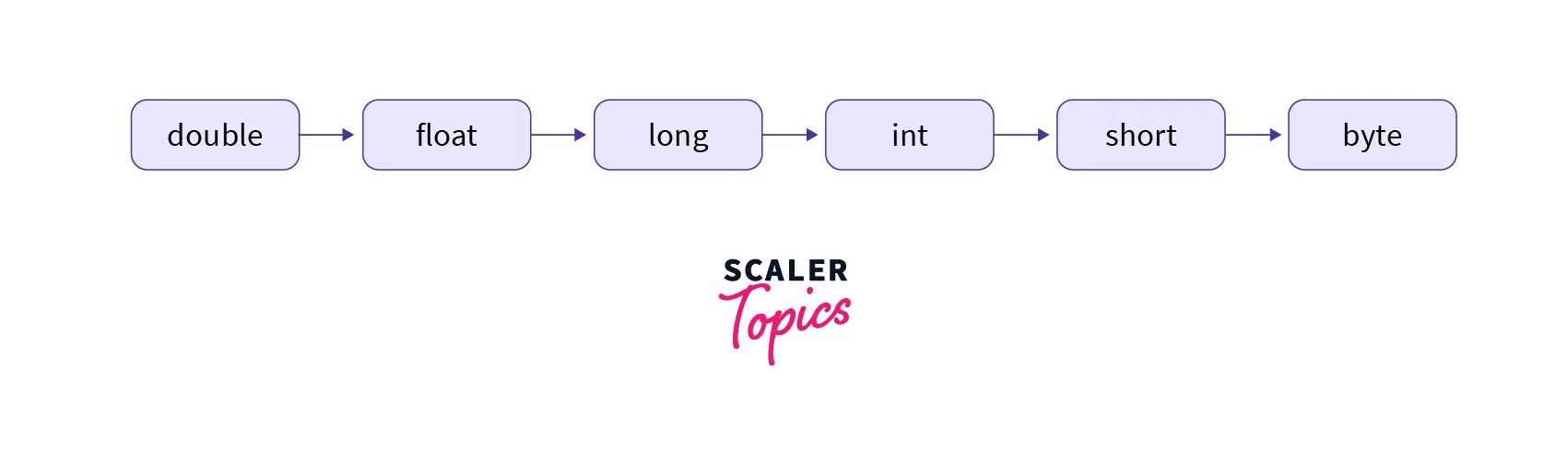
The above-shown data types are arranged in a descending order on which narrowing casting can be applied by the user.
Note: From the above explanation, we can conclude that a variable/expression of type int can be converted into the type long without the loss of data using the widening casting technique and we can also convert an int to a long using explicit typecasting methods. Let’s see these methods below.
Method 1: Convert int to Long in Java using Implicit Conversion (Simple Assignment Operation)
In Java, an int variable ( 4 bytes ) is a smaller data type as compared to a long variable ( 8 bytes ). So, we can convert an int to a long variable using a simple assignment operation, i.e., implicit/automatic conversion by the compiler. It is also known as automatic type promotion by the compiler.
Example Java Program:
Explanation:
- Simple assignment of the variable i , j and k to the variables l , m and n respectively converts these int values to long implicitly.
- We can see the class type Long in the output using the getClass() method.
Method 2: Convert int to Long in Java Using Explicit Typecasting
The process of sending information by the user to the compiler that the program is attempting a data type conversion is known as explicit conversion or explicit typecasting. We can also convert an int variable to a long variable using explicit typecasting. We have to put the data type we want and the other variable/expression in the parentheses like the given syntax below:
It creates a long data type value var that contains the same value as the int_var_name variable of type int .
Example Java Program:
Explanation:
- The (long) expression before the int variables (i) , (j) , and (k) in the above Java program converts the value of i = 10 , j = 15 , and k = 20 to long type, which is the explicit type casting method.
- We can see from the output that the getClass() method prints Long in the output after casting of the variables.
Method 3: Convert int to Long Object in Java Using valueOf() Method
We can also convert an int variable to an object of the Long wrapper class using the in-built valueOf() method of the Long wrapper class in Java. Let’s see the syntax and parameters for the valueOf() function.
The integer value that we’re converting into Long is the only parameter passed to the function valueOf() method.
Return value: It returns an object of type Long wrapper class with the same value as of the int_var_name variable of type int .
Let’s see the Java program to understand this method:
Example Java Program:
Explanation:
In the above program, the valueOf() method of the Long wrapper class in Java converts the int variable i = 15 to an object of the Long wrapper class, i.e., L = 15 .
Conclusion
- In programming, it is often required to change the data type of a variable to execute a some mathematical operation or avoid loss of data. This phenomenon is called typecasting.
- The int data type is a smaller data type than long , so it can be converted using a simple assignment operation (implicit type casting) of an int variable to a long variable.
- It can be converted using explicit type casting, (long)(int_var_name) .
- It can also be converted using the valueOf() method of the Long wrapper class in Java, Long.valueOf(int_var_name) .
Java Convert int to long with examples
In this tutorial, we will see how to convert int to long with examples.
Since int is smaller data type than long, it can be converted to long with a simple assignment. This is known as implicit type casting or type promotion, compiler automatically converts smaller data type to larger data type. We can also convert int to long using valueOf() method of Long wrapper class.
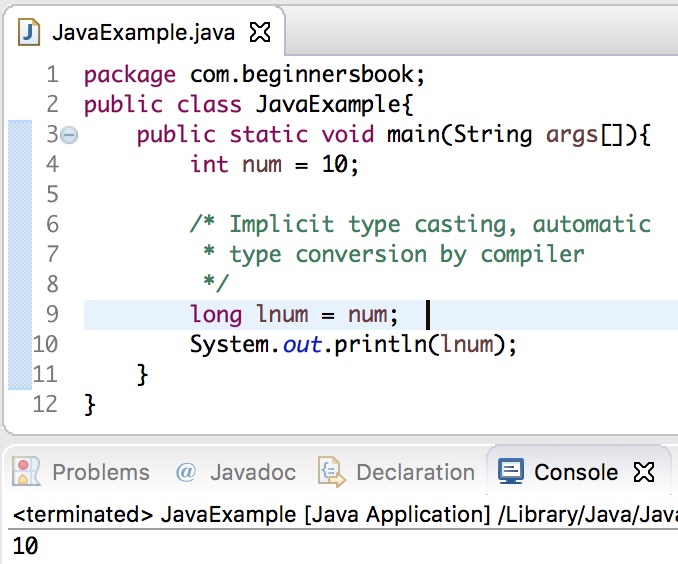
Java int to long using implicit type casting
In the following example, we are simply assigning integer data type to a long data type. Since integer is a smaller data type compared to long, the compiler automatically converts int to long, this is known as type promotion.
Output:
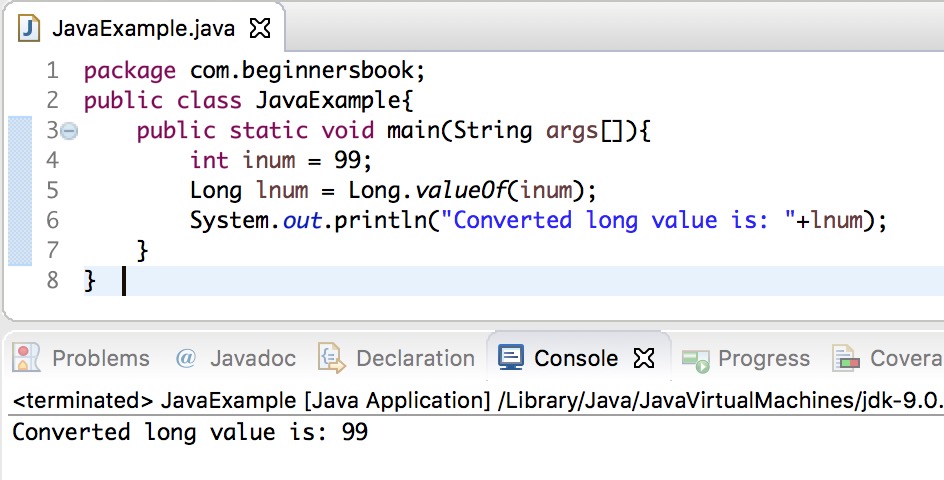
Java int to long Example using Long.valueOf() method
In the following example, we are converting int to long using valueOf() method of Long Wrapper class. The valueOf() method accepts integer as an argument and returns a long value after the conversion.
Output:
Top Related Articles:
About the Author
I have 15 years of experience in the IT industry, working with renowned multinational corporations. Additionally, I have dedicated over a decade to teaching, allowing me to refine my skills in delivering information in a simple and easily understandable manner.