- Java String to int Conversion – 10 Examples
- Java String to int Conversion Methods
- Important Points for String to int Parsing
- Java String to integer Examples
- 1. parseInt(String s)
- 2. parseInt(String s, int radix)
- 3. parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix)
- 4. valueOf(String s)
- 5. valueOf(String s, int radix)
- 6. NumberFormatException Example
- 7. NullPointerException when parsing substring
- 8. IndexOutOfBoundsException when parsing substring
- 9. NumberFormatException when radix is out of range
- 10. Java String to int Removing Leading Zeroes
- Conclusion
- References:
- Java String to Int – How to Convert a String to an Integer
- 1. Use Integer.parseInt() to Convert a String to an Integer
- 2. Use Integer.valueOf() to Convert a String to an Integer
- How to Handle the NumberFormat Exception in Java
- What Causes NumberFormatException
- Null input string
- Empty input string
- Input string with leading/trailing whitespaces
- Input string with inappropriate symbols
- Input string with non-numeric data
- Alphanumeric input string
- Input string exceeding the range of the target data type
- Mismatch of data type between input string and the target data type
- NumberFormatException Example
- How to Handle NumberFormatException
- Track, Analyze and Manage Errors with Rollbar
Java String to int Conversion – 10 Examples
Java String to int conversion can be done using the Integer wrapper class. There are two static methods for this purpose – parseInt() and valueOf().
Java String to int Conversion Methods
The Integer class provides 5 overloaded methods for the string to int conversion.
- parseInt(String s): parses the string as a signed decimal value. The string should have only decimal digits. The first character can be ASCII minus sign (-) or plus sign (+).
- parseInt(String s, int radix): parses the given string as the signed integer in the radix.
- parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix): The method is useful in parsing a substring to an integer. If the index values are invalid, IndexOutOfBoundsException is thrown. If the CharSequence is null, NullPointerException is thrown.
- valueOf(String s): This method returns an Integer object. The string is parsed as a signed decimal value. It calls parseInt (s, 10) internally.
- valueOf(String s, int radix): internally calls the parseInt(s, radix) method and returns the Integer object.
Important Points for String to int Parsing
- All the parseInt() and valueOf() methods throw NumberFormatException if the string is not parsable.
- The radix value should be in the supported range i.e. from Character.MIN_RADIX (2) to Character.MAX_RADIX(36), otherwise NumberFormatException is thrown.
- The parseInt() methods return int primitive data type.
- The valueOf() methods return an Integer object.
- The valueOf() methods internally calls parseInt() methods.
- Since Java supports autoboxing, we can use int and Integer in our program interchangeably. So we can use either parseInt() or valueOf() method to convert a string to integer.
- The parseInt() method to parse substring was added to String class in Java 9 release.
- The string should not contain the prefix used to denote an integer in the different radix. For example, “FF” is valid but “0xFF” is not a valid string for the conversion.
- The valueOf() methods are present because it’s present in every wrapper class and String to convert other data types to this object. Recommended Read: Java String valueOf() method.
Java String to integer Examples
Let’s look at some examples for parsing a string to an integer using the parseInt() and valueOf() methods.
1. parseInt(String s)
jshell> Integer.parseInt("123"); $69 ==> 123 jshell> Integer.parseInt("-123"); $70 ==> -123 jshell> Integer.parseInt("+123"); $71 ==> 123 jshell> Integer.parseInt("-0"); $72 ==> 0 jshell> Integer.parseInt("+0"); $73 ==> 0 2. parseInt(String s, int radix)
jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 16); $74 ==> 255 jshell> Integer.parseInt("1111", 2); $75 ==> 15 3. parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix)
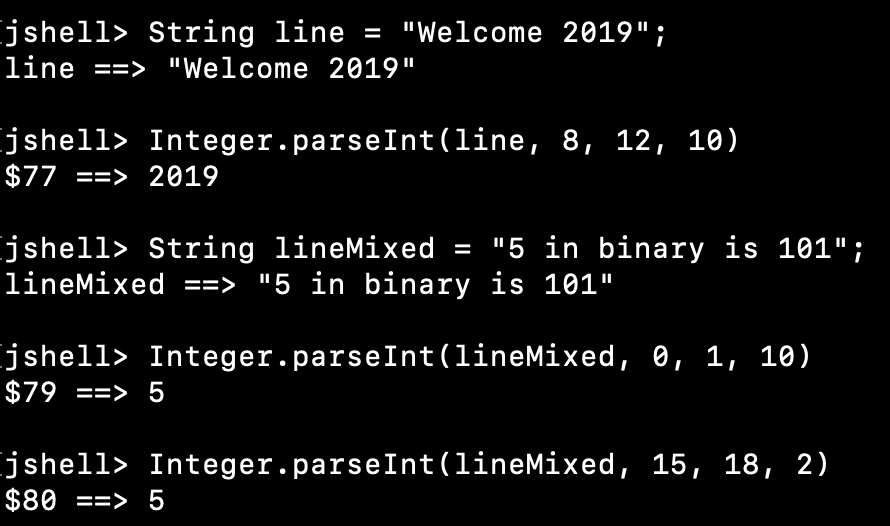
jshell> String line = "Welcome 2019"; line ==> "Welcome 2019" jshell> Integer.parseInt(line, 8, 12, 10) $77 ==> 2019 jshell> String lineMixed = "5 in binary is 101"; lineMixed ==> "5 in binary is 101" jshell> Integer.parseInt(lineMixed, 0, 1, 10) $79 ==> 5 jshell> Integer.parseInt(lineMixed, 15, 18, 2) $80 ==> 5
4. valueOf(String s)
jshell> Integer io = Integer.valueOf(123); io ==> 123 jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf(123); i ==> 123
The valueOf() method returns Integer object. But, we can assign it to int also because Java supports autoboxing.
5. valueOf(String s, int radix)
jshell> Integer.valueOf("F12", 16) $84 ==> 3858 jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf("F12", 16) i ==> 3858 jshell> int i = Integer.valueOf("077", 8) i ==> 63 6. NumberFormatException Example
jshell> Integer.parseInt("abc"); | Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "abc" | at NumberFormatException.forInputString (NumberFormatException.java:68) | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:658) | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:776) | at (#87:1) jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 8); | Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "FF" under radix 8 | at NumberFormatException.forInputString (NumberFormatException.java:68) | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:658) | at (#88:1) jshell> 7. NullPointerException when parsing substring
jshell> Integer.parseInt(null, 1, 2, 10); | Exception java.lang.NullPointerException | at Objects.requireNonNull (Objects.java:221) | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:701) | at (#89:1) jshell>
8. IndexOutOfBoundsException when parsing substring
jshell> Integer.parseInt("Hello 2019", 1, 100, 10); | Exception java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:704) | at (#90:1) jshell> 9. NumberFormatException when radix is out of range
jshell> Integer.parseInt("FF", 50); | Exception java.lang.NumberFormatException: radix 50 greater than Character.MAX_RADIX | at Integer.parseInt (Integer.java:629) | at (#91:1) jshell> 10. Java String to int Removing Leading Zeroes
If the string is prefixed with zeroes, they are removed when converted to int.
jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077"); $95 ==> 77 jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 16); $96 ==> 119 jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 12); $97 ==> 91 jshell> Integer.parseInt("00077", 8); $98 ==> 63 Conclusion
Java String to int conversion is very easy. We can use either parseInt() or valueOf() method. Java 9 added another utility method to parse substring to an integer.
References:
Java String to Int – How to Convert a String to an Integer
Thanoshan MV
String objects are represented as a string of characters.
If you have worked in Java Swing, it has components such as JTextField and JTextArea which we use to get our input from the GUI. It takes our input as a string.
If we want to make a simple calculator using Swing, we need to figure out how to convert a string to an integer. This leads us to the question – how can we convert a string to an integer?
In Java, we can use Integer.valueOf() and Integer.parseInt() to convert a string to an integer.
1. Use Integer.parseInt() to Convert a String to an Integer
This method returns the string as a primitive type int. If the string does not contain a valid integer then it will throw a NumberFormatException.
So, every time we convert a string to an int, we need to take care of this exception by placing the code inside the try-catch block.
Let’s consider an example of converting a string to an int using Integer.parseInt() :
String str = "25"; try < int number = Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println(number); // output = 25 >catch (NumberFormatException ex)
Let’s try to break this code by inputting an invalid integer:
String str = "25T"; try < int number = Integer.parseInt(str); System.out.println(number); >catch (NumberFormatException ex)
As you can see in the above code, we have tried to convert 25T to an integer. This is not a valid input. Therefore, it must throw a NumberFormatException.
Here’s the output of the above code:
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "25T" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:615) at OOP.StringTest.main(StringTest.java:51)Next, we will consider how to convert a string to an integer using the Integer.valueOf() method.
2. Use Integer.valueOf() to Convert a String to an Integer
This method returns the string as an integer object. If you look at the Java documentation, Integer.valueOf() returns an integer object which is equivalent to a new Integer(Integer.parseInt(s)) .
We will place our code inside the try-catch block when using this method. Let us consider an example using the Integer.valueOf() method:
String str = "25"; try < Integer number = Integer.valueOf(str); System.out.println(number); // output = 25 >catch (NumberFormatException ex)
Now, let’s try to break the above code by inputting an invalid integer number:
String str = "25TA"; try < Integer number = Integer.valueOf(str); System.out.println(number); >catch (NumberFormatException ex)
Similar to the previous example, the above code will throw an exception.
Here’s the output of the above code:
java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "25TA" at java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:65) at java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:580) at java.lang.Integer.valueOf(Integer.java:766) at OOP.StringTest.main(StringTest.java:42)We can also create a method to check if the passed-in string is numeric or not before using the above mentioned methods.
I have created a simple method for checking whether the passed-in string is numeric or not.
public class StringTest < public static void main(String[] args) < String str = "25"; String str1 = "25.06"; System.out.println(isNumeric(str)); System.out.println(isNumeric(str1)); >private static boolean isNumeric(String str) < return str != null && str.matches("[0-9.]+"); >>The isNumeric() method takes a string as an argument. First it checks if it is null or not. After that we use the matches() method to check if it contains digits 0 to 9 and a period character.
This is a simple way to check numeric values. You can write or search Google for more advanced regular expressions to capture numerics depending on your use case.
It is a best practice to check if the passed-in string is numeric or not before trying to convert it to integer.
You can connect with me on Medium.
Happy Coding!
How to Handle the NumberFormat Exception in Java
The NumberFormatException is an unchecked exception in Java that occurs when an attempt is made to convert a string with an incorrect format to a numeric value. Therefore, this exception is thrown when it is not possible to convert a string to a numeric type (e.g. int, float). For example, this exception occurs if a string is attempted to be parsed to an integer but the string contains a boolean value.
Since the NumberFormatException is an unchecked exception, it does not need to be declared in the throws clause of a method or constructor. It can be handled in code using a try-catch block.
What Causes NumberFormatException
There can be various cases related to improper string format for conversion to numeric values. Some of them are:
Null input string
Empty input string
Input string with leading/trailing whitespaces
Integer myInt = new Integer(" 123 ");Input string with inappropriate symbols
Input string with non-numeric data
Integer.parseInt("Twenty Two");Alphanumeric input string
Input string exceeding the range of the target data type
Integer.parseInt("12345678901");Mismatch of data type between input string and the target data type
NumberFormatException Example
Here is an example of a NumberFormatException thrown when attempting to convert an alphanumeric string to an integer:
public class NumberFormatExceptionExample < public static void main(String args[]) < int a = Integer.parseInt("1a"); System.out.println(a); > >In this example, a string containing both numbers and characters is attempted to be parsed to an integer, leading to a NumberFormatException:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "1a" at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:68) at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:652) at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:770) at NumberFormatExceptionExample.main(NumberFormatExceptionExample.java:3)Such operations should be avoided where possible by paying attention to detail and making sure strings attempted to be parsed to numeric values are appropriate and legal.
How to Handle NumberFormatException
The NumberFormatException is an exception in Java, and therefore can be handled using try-catch blocks using the following steps:
- Surround the statements that can throw an NumberFormatException in try-catch blocks
- Catch the NumberFormatException
- Depending on the requirements of the application, take necessary action. For example, log the exception with an appropriate message.
The code in the earlier example can be updated with the above steps:
public class NumberFormatExceptionExample < public static void main(String args[]) < try < int a = Integer.parseInt("1a"); System.out.println(a); > catch (NumberFormatException nfe) < System.out.println("NumberFormat Exception: invalid input string"); > System.out.println("Continuing execution. "); > >Surrounding the code in try-catch blocks like the above allows the program to continue execution after the exception is encountered:
NumberFormat Exception: invalid input string Continuing execution. Track, Analyze and Manage Errors with Rollbar
Finding exceptions in your Java code is challenging. It can make deploying production code an unnerving experience. Being able to track, analyze, and manage errors in real-time can help you to proceed with more confidence. Rollbar automates error monitoring, tracking and triaging, making fixing Java errors and exceptions easier than ever. Sign Up Today!