PATH and CLASSPATH
This section explains how to use the PATH and CLASSPATH environment variables on Microsoft Windows, Solaris, and Linux. Consult the installation instructions included with your installation of the Java Development Kit (JDK) software bundle for current information.
After installing the software, the JDK directory will have the structure shown below.
The bin directory contains both the compiler and the launcher.
Update the PATH Environment Variable (Microsoft Windows)
You can run Java applications just fine without setting the PATH environment variable. Or, you can optionally set it as a convenience.
Set the PATH environment variable if you want to be able to conveniently run the executables ( javac.exe , java.exe , javadoc.exe , and so on) from any directory without having to type the full path of the command. If you do not set the PATH variable, you need to specify the full path to the executable every time you run it, such as:
C:\Java\jdk1.7.0\bin\javac MyClass.java
The PATH environment variable is a series of directories separated by semicolons ( ; ). Microsoft Windows looks for programs in the PATH directories in order, from left to right. You should have only one bin directory for the JDK in the path at a time (those following the first are ignored), so if one is already present, you can update that particular entry.
The following is an example of a PATH environment variable:
C:\Java\jdk1.7.0\bin;C:\Windows\System32\;C:\Windows\;C:\Windows\System32\Wbem
It is useful to set the PATH environment variable permanently so it will persist after rebooting. To make a permanent change to the PATH variable, use the System icon in the Control Panel. The precise procedure varies depending on the version of Windows:
- Select Start, select Control Panel. double click System, and select the Advanced tab.
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New .
- In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.
- From the desktop, right click the My Computer icon.
- Choose Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Advanced tab (Advanced system settings link in Vista).
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New .
- In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.
- From the desktop, right click the Computer icon.
- Choose Properties from the context menu.
- Click the Advanced system settings link.
- Click Environment Variables. In the section System Variables, find the PATH environment variable and select it. Click Edit. If the PATH environment variable does not exist, click New .
- In the Edit System Variable (or New System Variable) window, specify the value of the PATH environment variable. Click OK. Close all remaining windows by clicking OK.
Note: You may see a PATH environment variable similar to the following when editing it from the Control Panel:
%JAVA_HOME%\bin;%SystemRoot%\system32;%SystemRoot%;%SystemRoot%\System32\Wbem
Variables enclosed in percentage signs ( % ) are existing environment variables. If one of these variables is listed in the Environment Variables window from the Control Panel (such as JAVA_HOME ), then you can edit its value. If it does not appear, then it is a special environment variable that the operating system has defined. For example, SystemRoot is the location of the Microsoft Windows system folder. To obtain the value of a environment variable, enter the following at a command prompt. (This example obtains the value of the SystemRoot environment variable):
Update the PATH Variable (Solaris and Linux)
You can run the JDK just fine without setting the PATH variable, or you can optionally set it as a convenience. However, you should set the path variable if you want to be able to run the executables ( javac , java , javadoc , and so on) from any directory without having to type the full path of the command. If you do not set the PATH variable, you need to specify the full path to the executable every time you run it, such as:
% /usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin/javac MyClass.java
To find out if the path is properly set, execute:
This will print the version of the java tool, if it can find it. If the version is old or you get the error java: Command not found, then the path is not properly set.
To set the path permanently, set the path in your startup file.
For C shell ( csh ), edit the startup file (~/.cshrc ):
set path=(/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin $path)
For bash , edit the startup file ( ~/.bashrc ):
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH export PATH
For ksh , the startup file is named by the environment variable, ENV . To set the path:
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH export PATH
For sh , edit the profile file ( ~/.profile ):
PATH=/usr/local/jdk1.7.0/bin:$PATH export PATH
Then load the startup file and verify that the path is set by repeating the java command:
% source ~/.cshrc % java -version
Checking the CLASSPATH variable (All platforms)
The CLASSPATH variable is one way to tell applications, including the JDK tools, where to look for user classes. (Classes that are part of the JRE, JDK platform, and extensions should be defined through other means, such as the bootstrap class path or the extensions directory.)
The preferred way to specify the class path is by using the -cp command line switch. This allows the CLASSPATH to be set individually for each application without affecting other applications. Setting the CLASSPATH can be tricky and should be performed with care.
The default value of the class path is «.», meaning that only the current directory is searched. Specifying either the CLASSPATH variable or the -cp command line switch overrides this value.
To check whether CLASSPATH is set on Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP, execute the following:
On Solaris or Linux, execute the following:
If CLASSPATH is not set you will get a CLASSPATH: Undefined variable error (Solaris or Linux) or simply %CLASSPATH% (Microsoft Windows NT/2000/XP).
To modify the CLASSPATH , use the same procedure you used for the PATH variable.
Class path wildcards allow you to include an entire directory of .jar files in the class path without explicitly naming them individually. For more information, including an explanation of class path wildcards, and a detailed description on how to clean up the CLASSPATH environment variable, see the Setting the Class Path technical note.
Previous page: Miscellaneous Methods in System
Next page: Questions and Exercises: The Platform Environment
How to Add JAR file to Classpath in Java?
JAR is an abbreviation of JAVA Archive. It is used for aggregating multiple files into a single one, and it is present in a ZIP format. It can also be used as an archiving tool but the main intention to use this file for development is that the Java applets and their components(.class files) can be easily downloaded to a client browser in just one single HTTP request, rather than establishing a new connection for just one thing. This will improve the speed with which applets can be loaded onto a web page and starts their work. It also supports compression, which reduces the file size and the download time will be improved.
Methods: JAR file can be added in a classpath in two different ways
Method 1 – Using Eclipse IDE
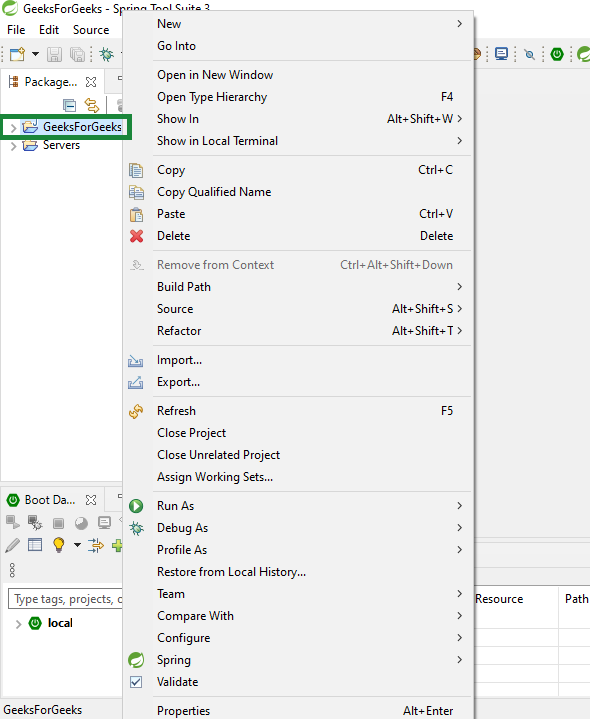
Step 1: Right-Click on your project name
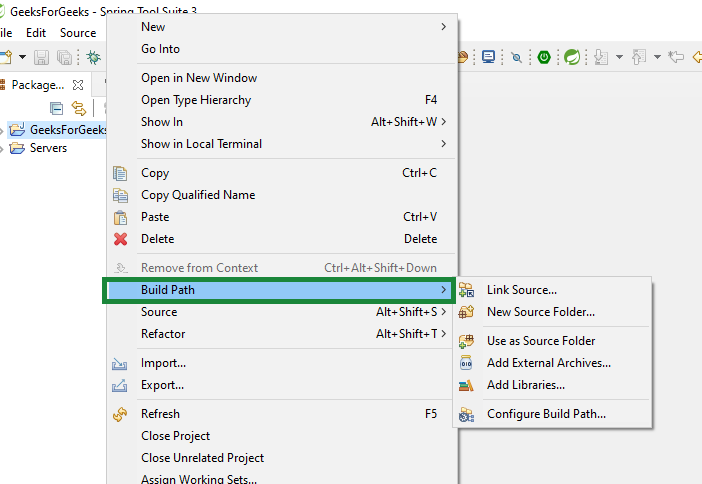
Step 2: Click on Build Path
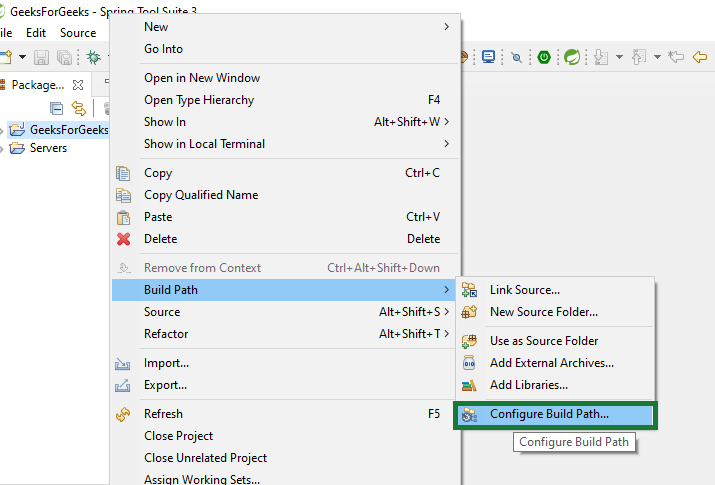
Step 3: Click on configure build path
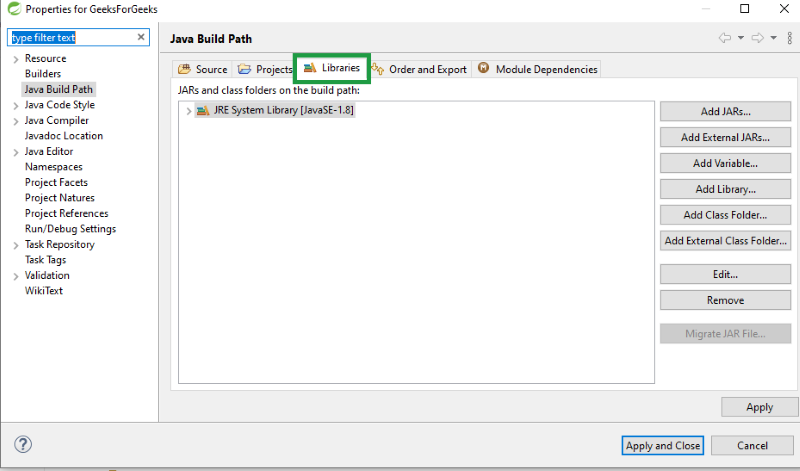
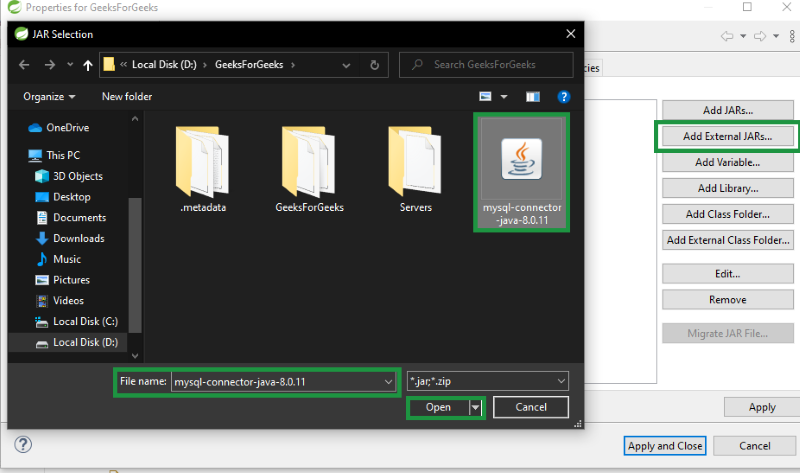
Step 4: Click on libraries and click on “Add External JARs”
Step 5: Select the jar file from the folder where you have saved your jar file
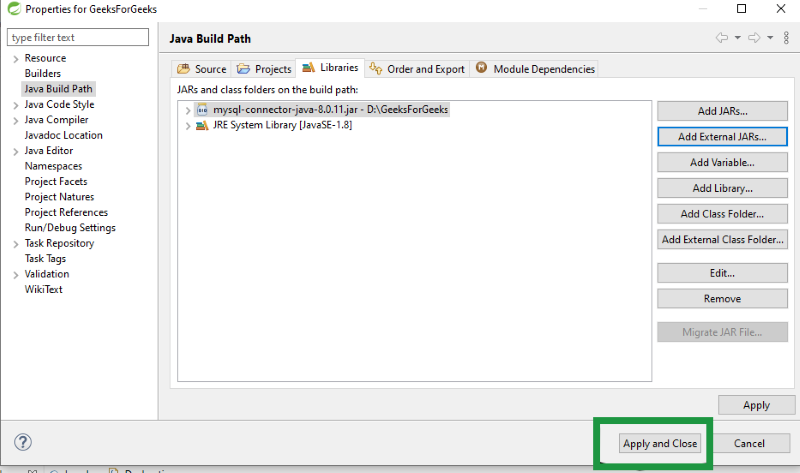
Step 6: Click on Apply and Ok.
Method 2 – Using the command line
Command 1: By including JAR name in CLASSPATH environment variable
CLASSPATH environment variable is not case-sensitive. It can be either Classpath or classpath which is similar to PATH environment variable which we can use to locate Java binaries like javaw and java command.
Command 2: By including name of JAR file in -a classpath command-line option
This option is viable when we are passing –classpath option while running our java program like java –classpath $(CLASSPATH) Main. In this case, CLASSPATH shell variable contains the list of Jar file which is required by the application. One of the best advantages of using classpath command-line option is that it allows us to use every application to have its own set of JAR classpath. In other cases, it’s not available to all Java program which runs on the same host.
Command 3: By including the jar name in the Class-Path option in the manifest
When we are running an executable JAR file we always notice that the Class-Path attribute in the file inside the META-INF folder. Therefore, we can say that Class-Path is given the highest priority and it overrides the CLASSPATH environment variable as well as –classpath command-line option. Henceforth, we can deduce that its a good place to include all JAR files required by Java Application.
Command 4: By using Java 6 wildcard option to include multiple JAR
From Java 1.6+ onwards we can use a wildcard for including all jars in a directory to set classpath or else to provide Java program using classpath command-line option. We can illustrate the Java command example to add multiple JAR into classpath using Java 6 wildcard method as follows,
java.exe -classpath D:\lib\*Main
In this method, we include all JAR files inside ‘D:\lib’ directory into the classpath. We must ensure that syntax is correct. Some more important points about using Java 6 wildcard to include multiple JAR in classpath are as follows:
Whenever JAR and classfile are present in the same directory then we need to include both of them separately
Java -classpath /classes: /lib/*
In Java 6 wildcard which includes all JAR, it will not search for JARs in a subdirectory.
Wildcard is included in all JAR is not honored in the case when we are running Java program with JAR file and having Class-Path attribute in the manifest file. JAR wildcard is honored when we use –cp or –classpath option
Command 5: Adding JAR in ext directory example be it ‘C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0\jre\lib\ext’
By using the above method we can add multiple JAR in our classpath. JAR from ext directory can be loaded by extension Classloader. It has been given higher priority than application class loader which loads JAR from either CLASSPATH environment variable or else directories specified in –classpath or –cp