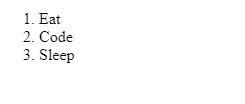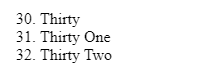- How to Set a Custom Starting Point in HTML Ordered Lists
- Setting a Custom Starting Point for a List in HTML
- Setting a Custom Starting Point for a List in HTML with a Different Type
- Overwriting the start Attribute
- Html start list at number
- Definition and Usage
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Attribute Values
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- Html start list at number
- Try it
- Attributes
- Usage notes
- HTML List – How to Use Bullet Points, Ordered, and Unordered Lists
- How to Make Lists in HTML
- How to Make an Ordered List with HTML
- Before We End.
- HTML Ordered List
- Ordered Lists Type
- start Attribute
- reversed Attribute
- Nesting Lists
- Table of Contents
How to Set a Custom Starting Point in HTML Ordered Lists
Ordered lists in HTML provide a powerful mechanism for displaying data and information in a structured numerical or alphabetical manner. In this post, we’ll learn about the start attribute that will allow us to customize the starting point of our lists.
HTML ordered lists can automatically keep track of how many items we have in a list and will apply the correct value to the list item and subsequent items in a sequential order. But sometimes, we want to take control over how the numbers are represented and in this case, we’ll look at how we can set a custom starting number or letter for our ordered lists in HTML.
Setting a Custom Starting Point for a List in HTML
- and apply the start attribute to it with the value we’d like our list to start at. For example:
The above ordered list will have the first list item start at 10, instead of 1, and the subsequent items will be 11 and 12. The content rendered would look like this:
Setting a Custom Starting Point for a List in HTML with a Different Type
- element called type and here we’ll specify the type of marker to use for our ordered list of items.
By default, and if we don’t specify the type, it’ll default to type=»1″ , which means our list items will be numbered with numbers. type=»A» will have our list items numbered with uppercase letters, and subsequently type=»a» will list our items numbered with lowercase letters. Finally, we can have our list items numbered with uppercase roman numerals or lowercase roman numerals by setting the type to either type=»I» for uppercase or type=»i» for lowercase.
To set a custom starting point in addition to a custom type, we can combine the type and start attributes in our ol element like so:
In the above example, our first list item will start at X, followed by Y and Z for the subsequent list items, instead of the default A, B, C. It’s important to note that even when changing the type of list items, the start attribute always takes a number as the starting point, and passing anything else, will result in the starting item starting at 1.
Overwriting the start Attribute
- and subsequent numbering will be based of the that value. Let’s see an example:
This list will start at 10, then the next list item will be numbered 25, and the last item in the list will be numbered 26. Let’s see another example:
In this instance, the first list item will be 7 instead of 5, the second list item will be 8, and the last list item, since it does have its own value attribute, 3.
Html start list at number
An ordered list starting at «50»:
Definition and Usage
The start attribute specifies the start value of the first list item in an ordered list.
This value is always an integer, even when the numbering type is letters or romans. E.g., to start counting list items from the letter «c» or the roman number «iii», use start=»3″.
Browser Support
Syntax
Attribute Values
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
Html start list at number
The HTML element represents an ordered list of items — typically rendered as a numbered list.
Try it
Attributes
This element also accepts the global attributes.
This Boolean attribute specifies that the list’s items are in reverse order. Items will be numbered from high to low.
An integer to start counting from for the list items. Always an Arabic numeral (1, 2, 3, etc.), even when the numbering type is letters or Roman numerals. For example, to start numbering elements from the letter «d» or the Roman numeral «iv,» use start=»4″ .
- a for lowercase letters
- A for uppercase letters
- i for lowercase Roman numerals
- I for uppercase Roman numerals
- 1 for numbers (default)
The specified type is used for the entire list unless a different type attribute is used on an enclosed element.
Note: Unless the type of the list number matters (like legal or technical documents where items are referenced by their number/letter), use the CSS list-style-type property instead.
Usage notes
Typically, ordered list items display with a preceding marker, such as a number or letter.
- Steps in a recipe
- Turn-by-turn directions
- The list of ingredients in decreasing proportion on nutrition information labels
- element — otherwise you can use .
HTML List – How to Use Bullet Points, Ordered, and Unordered Lists
TAPAS ADHIKARY
Listing items on a web page is a common task you’ll have to do as a web developer. You may have to list shopping cart items, the order of students based on their grades, dogs with the loudest bark – and so on.
So you need to know the different ways you can list items using HTML. While you might think it’s a trivial thing to learn, it’s important. And it’s one of the most commonly used features of HTML in web development.
In this article, you’ll learn all about HTML listing elements, their properties, styling, and how to actually use them to create neat lists. I hope you find it helpful.
How to Make Lists in HTML
In HTML, we can list items either in an ordered or unordered fashion.
An ordered list uses numbers or some sort of notation that indicates a series of items.
For example, an ordered list can start with number 1, and continue through 2, 3, 4, and so on. Your ordered list can also start with the letter A and go through B, C, D, and so on.
Here is an example of an ordered list with students’ names and marks.
On the other hand, we have unordered lists, like a TODO list for example. Here I am so passionate about coding that I skipped my breakfast 🤓.
There is one more type of list called a description list that we will learn as well below.
Now let’s get into a bit more detail and see how to create each type of list in HTML.
How to Make an Ordered List with HTML
- tag. The ol in the tag stands for an ordered list. Inside each of the ordered list elements
- Prepare the ingredients.
- Eggs
- Salt
- Butter
- Mix the ingredients and cook on a low flame.
- Serve hot with garnish. You can use
- Chives
- Bacon
- Coriander
- and
tag.
Here is the complete HTML structure for an ordered list:
The output of the above ordered list is:
So, we have the list of elements ordered with a number starting with 1 and incremented to 2 and 3. Try this CodePen and see if you can change and play around with using ol-li .
Similarly, you can use lower case letters like a as the type value to list the elements with a, b, c, and so on.
If you want to use Roman numerals, use the value I for an ordered list with Roman numerals:
The output looks like this:
Check out the CodePen below to try other types:
Feel free to play around with the start attribute using this CodePen:
You can see the bullet points for each of the list items above, but you can customize them. We’ll learn that too.
But before that, feel free to use this CodePen to change and run the code.
You can use the CodePen below to try out the same. Feel free to modify it as you wish:
Try out this CodePen to experiment further with description lists:
Well, this is not what we want. So next we will write a few CSS rules and properties to make it look like a page header (at least close to it).
Now it is much better and looks closer to a realistic page header.
Again, you can use this CodePen to change and try out things with the header.
Before We End.
That’s all for now. I hope you’ve found this article insightful, and that it helps you understand HTML lists more clearly. You can find all the examples together in this CodePen Collection.
Let’s connect. You will find me active on Twitter (@tapasadhikary). Feel free to give a follow. I’ve also started sharing knowledge using my YouTube channel, so you can check it out, too.
You may also like these articles:
HTML Ordered List
We use the HTML ordered list to define a list where the sequence or order of the list items is important. We can use the HTML ordered list for recipes, algorithms, top ten lists, and so on.
- tag to create an unordered list. For example,
Browser Output
By default, ordered lists are ordered by numbers, however, we can change them as per our choice.
Ordered Lists Type
We use the type attribute to change the marker for the list. There are five types of numbering in the ordered list. They are
| Type | Description |
| «1»(Default) | The list is numbered with numbers. |
| «a» | The list is numbered with lower-case alphabets. |
| «A» | The list is numbered with upper-case alphabets. |
| «i» | The list is numbered with lower-case roman numerals. |
| «I» | The list is numbered with upper-case roman numerals. |
Below, we can see examples for all the number types.
start Attribute
We use the start attribute to change the starting point for the numbering of the list. For example,
Browser Output
Here, we change the starting value of the list to 5.
This attribute also works with other types. For example,
Browser Output
Similarly, we can use the start attribute along with all other types.
reversed Attribute
We can use the reversed attribute on the ordered list to reverse the numbering on the list. For example,
Browser Output
Here, we can see the order of the list is reversed, the first list item is numbered 4 and the last is numbered 1.
Similarly, the reversed attribute can also be used with other types and in conjunction with the start attribute. For example,
Browser Output
In the above example, we use the upper-case roman numeral type and start at 10 and reverse the order of the numbers.
Nesting Lists
In HTML, we can create a nested list by adding one list inside another. For example,
Browser Output
In the above example, you can see we have added an ordered list inside another ordered list.
In this case, the list item of the outer ordered list also includes an ordered list.
Similarly, we can also mix list types while nesting and add an unordered list inside the ordered list. For example,
Browser Output
Note: In our examples, we are nesting the list up to a single level, however, we can also nest lists up to multiple levels.