- How to Force a Button or Link to be 100% Width CSS Tutorial
- 12 Comments on “How to Force a Button or Link to be 100% Width CSS Tutorial”
- Увеличить зону кликабельности ссылки — HTML/CSS
- Плохой
- Злой
- Хороший
- HTML sizes Attribute
- Browser Support
- Syntax
- Attribute Values
- COLOR PICKER
- Report Error
- Thank You For Helping Us!
- HTML Tag
- Syntax
- Example of the HTML tag:
- Result
- Attributes
How to Force a Button or Link to be 100% Width CSS Tutorial
These are instructions on how to make an HTML link or button expand to be as wide as its parent element. Maybe you have been confused in the past and that darn link just never wants to grow.
Here is the CSS you are going to want to apply to that link.
text-align : center ; /*This will result in centering the link text, which is probably what you want -brianjohnsondesign.com*/
And the corresponding HTML:
The secret here is that you need to use display:block; to actually force the button to grow to the full width. You also can’t really use left or right margins or padding, as they will just mess up the width and cause it to be off-center or larger than its container. Top or bottom margins or padding won’t cause any problems, however.
Keep in mind, as well, you need to make sure that the parent div or element of the link must be the width you are trying to force this button to be. Check and make sure it has a width!
Brian Johnson is a website developer and designer living in Minneapolis, Minnesota with a passion for code and WordPress. He spends his days building WordPress websites for small businesses, developing new code with the online community, and living life.
12 Comments on “How to Force a Button or Link to be 100% Width CSS Tutorial”
This doesn’t work if you want a margin on the side of your button. I found that you can work around this by using: width: calc(100% – 6em); where you set your subtraction distance (as in 6em above) along with your margins to give the appropriate appearance that you want.
Увеличить зону кликабельности ссылки — HTML/CSS
Необходимо сделать ссылкой не только подзаголовок, но и саму картинку. Есть три способа три: назовем их хороший, плохой и злой.
Плохой
Просто обернуть и заголовок, и картинку в ссылку следующим образом:
Злой
Обернуть все в одну ссылку:
Хороший
Разместить ссылку в заголовке, а затем расширить область ссылки на всю карточку с помощь псевдоэлемента :before:
div position: relative; > a:before content: ''; position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; > Можно использовать любой из этих трех способов, но лично я предпочитаю последний.
HTML sizes Attribute
The sizes attribute specifies the sizes of icons for visual media.
This attribute is only used if rel=»icon» .
Browser Support
Syntax
Attribute Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| HeightxWidth | Specifies one or more sizes for the linked icon. The height and width values are separated by an «x» or «X». |
COLOR PICKER
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, do not hesitate to send us an e-mail:
Thank You For Helping Us!
Your message has been sent to W3Schools.
Top Tutorials
Top References
Top Examples
Get Certified
W3Schools is optimized for learning and training. Examples might be simplified to improve reading and learning. Tutorials, references, and examples are constantly reviewed to avoid errors, but we cannot warrant full correctness of all content. While using W3Schools, you agree to have read and accepted our terms of use, cookie and privacy policy.
HTML Tag
The tag sets the relationship between the current document and the external resource. It is generally used to link to the external CSS stylesheet.
The tag can be used to link different versions of a page. This is useful if there are several translations of content.
An HTML document can have several elements for loading different types of script or page. All these elements should be placed in the section of the document (commonly before the closing tag), and they can be used many times.
Syntax
The tag is empty, which means that the closing tag isn’t required. It contains only attributes. But in XHTML, the () tag must be closed ().
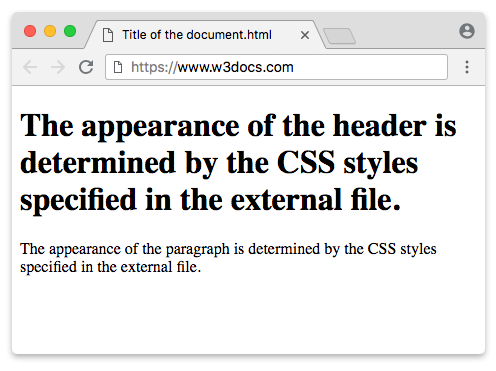
Example of the HTML tag:
html> html> head> link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css"> head> body> h1>The appearance of the header is determined by the CSS styles specified in the external file. h1> p>The appearance of the paragraph is determined by the CSS styles specified in the external file. p> body> html>Result
Attributes
| Attribute | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| charset | char_encoding | Defines the coding of the linked document. Not supported in HTML5. |
| href | URL | Defines the URL of the external file. |
| hreflang | language_code | Defines the text language of the linked document. |
| media | media_query | Defines the device, for which the styles will be applied. |
| rel | alternate archives author bookmark external first help icon last license next nofollow noreferrer pingback prefetch prev search sidebar stylesheet tag up | Defines the relationship between the current document and the linked file. |
| rev | reversed relationship | Defines the relationship between the current and linked documents. Not supported in HTML5. |
| sizes | HeightxWeight | Sets the size of associated icons. Used only with rel = «icon». |
| target | Defines how the link should be opened: | |
| _blank | In a new window. | |
| _self | In the current window. | |
| _top | To the full width of the window. | |
| _parent | In the parent frame. | |
| frame_name | In the frame. Not supported in HTML5. | |
| type | media_type | Defines the MIME-type (specification for network transfer of various types of files) of the linked document. |