- XOR in Python
- Bitwise Operator
- Python XOR Operator
- XOR using Operator Module
- XOR in Python: How to Use Bitwise XOR Operator
- What is the XOR operator?
- How to find XOR value in python?
- Use cases of XOR
- 01) Encryption
- 02) Swapping Two Numbers
- 03) Checking equality
- Conclusion
- What is XOR in Python?
- How to perform the bitwise XOR in Python?
- XOR ^ Operator between 2 integers
- Performing XOR on two booleans
- Swapping two integers using XOR without a temporary variable
- XOR in Python using Operator Module
- Learn more about bitwise operators
- Conclusion
XOR in Python
XOR Operator in Python is also known as “exclusive or” that compares two binary numbers bitwise if two bits are identical XOR outputs as 0 and when two bits are different then XOR outputs as 1. XOR can even be used on booleans.
XOR is mainly used in situations where we don’t want two conditions to be true simultaneously. In this tutorial, we will look explore multiple ways to perform XOR (exclusive OR) operations in Python with examples.
Bitwise Operator
Bitwise operators in Python are also called binary operators, and it is mainly used to perform Bitwise calculations on integers, the integers are first converted into binary, and later the operations are performed bit by bit.
Python XOR Operator
Let’s take a look at using the XOR ^ Operator between 2 integers. When we perform XOR between 2 integers, the operator returns the integer as output.
a= 5 #0101 b = 3 #0011 result = (a ^ b) #0110 print(result) # Output # 6 (0110)Let’s take a look at using XOR on two booleans. In the case of boolean, the true is treated as 1, and the false is treated as 0. Thus the output returned will be either true or false.
print(True ^ True) print(True ^ False) print(False ^ True) print(False ^ False)XOR using Operator Module
We can even achieve XOR using the built-in operator module in Python. The operator module has a xor() function, which can perform an XOR operation on integers and booleans, as shown below.
import operator print(operator.xor(5,3)) print(operator.xor(True,True)) print(operator.xor(True,False)) print(operator.xor(False,True)) print(operator.xor(False,False)) XOR in Python: How to Use Bitwise XOR Operator
Operators are the building block of any expression that we see. Be it mathematical or logical, without operators it would become very difficult to explain what operations we want to perform.
Imagine having to drive a car that does not have a steering wheel, it would be impossible to tell where the car is going to go. Similarly, without operators, we would not be able to make the compiler or interpreter of our code understand what operations we are performing. One such operator we shall see today is the XOR operator.
What is the XOR operator?
Also known as the exclusive OR, the XOR operator is a bitwise operator. What are bitwise operators? Any operator that operates on binary numbers is called a bitwise operator. They are used to perform some special operation on a binary string, that is a sequence of 0s and 1s.
Binary operators are used to performing operations on the bit level, which affects every bit in the number individually.
So, What is an exclusive OR operator? The XOR operation returns a 1 if the two operand bits are different and it returns 0 if the two operand bits are the same.
Let us simplify the technical jargon a bit! Take two binary numbers, 1100 and 0010. ‘⊕’ is the symbol for the exclusive OR operation and the XOR operation between the two binary numbers can be written as:
the result of this will be 1110.
How did we get that result? Let us see the results bit by bit, literally speaking, have a look at the following table to understand how the results came.
What do we notice? When the two bits are different, the resulting bit is always 1 and when the two bits are the same, the resulting bit is always 0. That is the rule for Exclusive OR. Here is an image for easy reference:
Now that we know how it works mathematically, let’s see its implementation in python.
How to find XOR value in python?
The XOR operator in python can be applied using the “^” symbol. The XOR operator is used in various situations that we shall see in the section below, for now, let us have a look at how the code is implemented:
A = 0b1100 B = 0b0010 print(bin(A^B))
Use cases of XOR
01) Encryption
Exclusive OR is one of the first methods that was used in encryption. It is a very naive method but it is very easy to implement. Though using exclusive OR alone is a very weak method of implementing encryption, combined with other methods, it can create powerful encryption.
Let us have a look at an example of how encryption using XOR or exclusive OR would look. We have a data item ’10’ that we want to send across to our friend. First, we decide on a key, which is a number that only we and our friends will know. Let us say this key is 5. The next step is using this key for encrypting the number.
We perform the XOR operation on 10 and 5. The interpreter will first convert the decimal numbers to binary numbers and then perform the operation. Once the resulting binary number is found, it converts it back to a decimal number again. So,
10 ⊕ 5 = 1010 ⊕ 0101 = 1111 = 15
After getting the result 15 we send the encrypted message to our friend. Our friend receives the encrypted message 15 and needs to extract the actual message. They use the common key we had decided first, they perform the XOR operation on 15 and 5.
15 ⊕ 5 = 1111 ⊕ 0101 = 1010 = 10
Now our friend has the original message.
02) Swapping Two Numbers
We just saw how the XOR operation is used for encryption, let us now see how it can be used to perform the swap between two numbers. Let us say we have two numbers 10 and 15 that we wish to swap. 10 is stored in variable A and 15 is stored in variable B. We perform the swaps using the XOR operation in the following manner:
A ⊕ B = 10 ⊕ 15 = 1010 ⊕ 1111 = 0101 = 5
We store the result in A, so A becomes 0101. Now, we do A ⊕ B again,
A ⊕ B = 5 ⊕ 15 = 0101 ⊕ 1111 = 1010 = 10
We store this result in B, so B becomes 1010. Then we perform A ⊕ B again,
A ⊕ B = 0101 ⊕ 1010 = 1111 = 15
We store this result in A. Therefore now the values of A and B are 15 and 10. The swap has taken place. What actions did we perform?
Here is the source code for implementation:
A = 10 B = 15 print("Before:",A,B) A = A^B B = A^B A = A^B print("After",A,B)
03) Checking equality
How do we use XOR for checking equality? Do we know the fundamental rule about XOR? It returns 1 if the two operands are different and 0 if the two operands are the same.
Let us say we had to compare two boolean values. We can XOR the two boolean values and if it returns 1 we can say they are not equal and if it returns 0 we can say they are equal.
Conclusion
We saw one of the bitwise operators, the XOR or Exclusive OR operator. Bitwise operators work on the given operands one bit by one bit. The XOR operation is also used for various tasks like encryption, swapping, and equality checks.
What is XOR in Python?
In Python, XOR is a bitwise operator that is also known as Exclusive OR.
It is a logical operator which outputs 1 1 1 when either of the operands is 1 1 1 (one is 1 1 1 and the other one is 0 0 0 ), but both are not 1 1 1 , and both are not 0 0 0 .
The symbol for XOR in Python is ‘^’ and in mathematics, its symbol is ‘⊕’.
The XOR operator is placed between two numbers or boolean values.
How to perform the bitwise XOR in Python?
In Python, we can perform the bitwise XOR operation using the «^» symbol. The XOR operation can be used for different purposes; XOR of two integers, XOR of two booleans, Swapping two numbers using XOR, etc.
We can also use the xor() function using the operator module in Python.
XOR ^ Operator between 2 integers
As XOR is a bitwise operator, it will compare bits of both the integers bit by bit after converting them into binary numbers.
Truth table for XOR (binary)
In the above example, we are finding the XOR of 1 5 15 1 5 and 3 2 32 3 2 , the result of which is 4 7 47 4 7 . The XOR operator first converted both the numbers in their binary form and then compared their bits bitwise.
To understand the working of XOR operation better, let us find the XOR of 15 and 32 by comparing their bits:
1 5 = 0 b 0 0 1 1 1 1 15 = 0b001111 1 5 = 0 b 0 0 1 1 1 1
3 2 = 0 b 1 0 0 0 0 0 32 = 0b100000 3 2 = 0 b 1 0 0 0 0 0
⟹ 1 5 ⊕ 3 2 = 0 b 0 0 1 1 1 1 ⊕ 0 b 1 0 0 0 0 0 \implies15 ⊕ 32 = 0b001111 ⊕ 0b100000 ⟹ 1 5 ⊕ 3 2 = 0 b 0 0 1 1 1 1 ⊕ 0 b 1 0 0 0 0 0
⟹ 1 5 ⊕ 3 2 = 0 b 1 0 1 1 1 1 \implies15 ⊕ 32 = 0b101111 ⟹ 1 5 ⊕ 3 2 = 0 b 1 0 1 1 1 1
The XOR of 1 5 15 1 5 and 3 2 32 3 2 is 0 b 1 0 1 1 1 1 0b101111 0 b 1 0 1 1 1 1 , i.e., 4 7 47 4 7 .
Performing XOR on two booleans
XOR results T r u e True T r u e when either of the operands are T r u e True T r u e (one is T r u e True T r u e and the other one is F a l s e False F a l s e ) but both are not T r u e True T r u e and both are not F a l s e False F a l s e .
Truth table for XOR (boolean)
In the above example, we are finding the XOR of the boolean values ( T r u e True T r u e and F a l s e False F a l s e ).
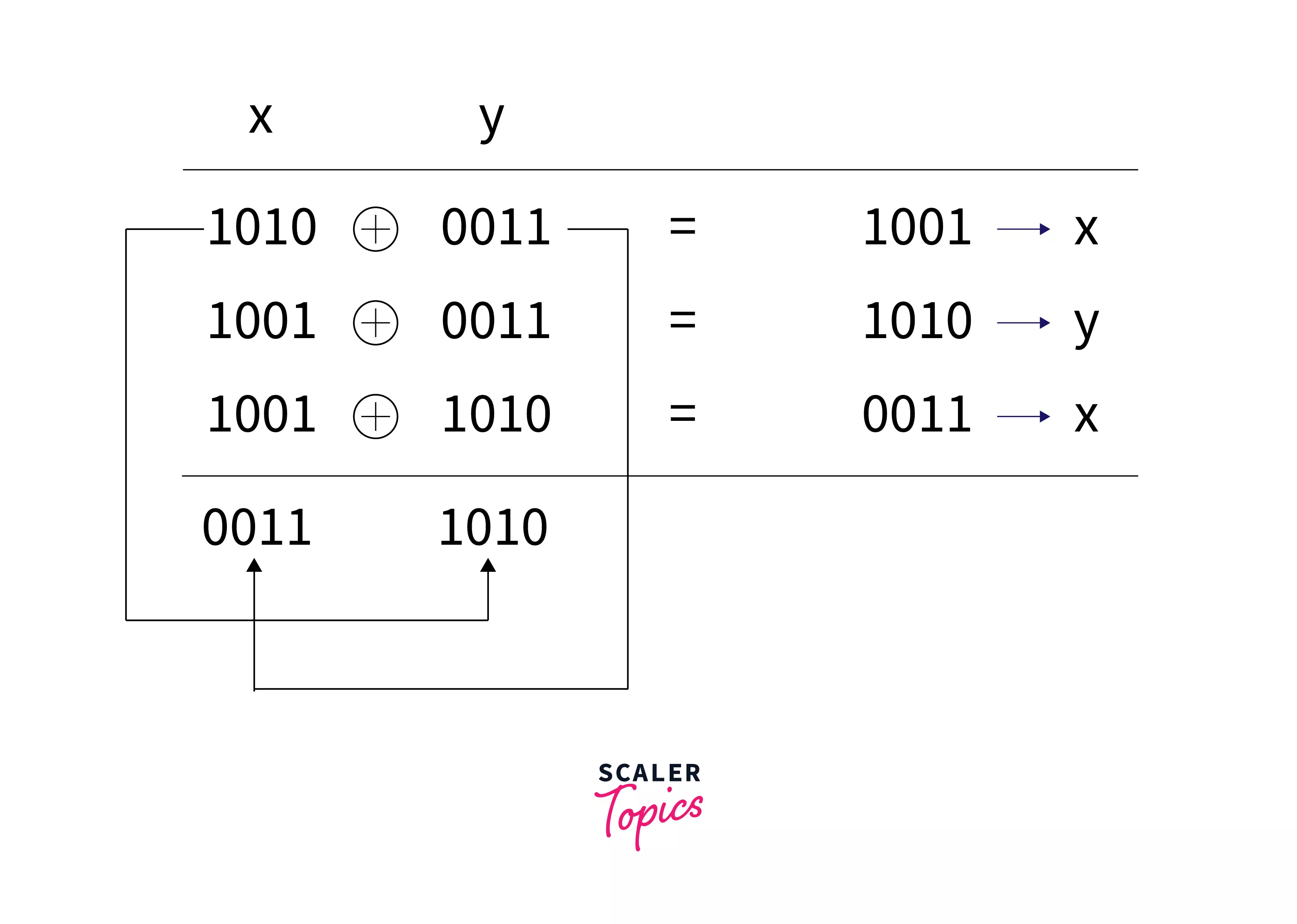
Swapping two integers using XOR without a temporary variable
The XOR swap algorithm can swap the values of two integers without the use of a temporary variable, which is normally required in other swapping algorithms.
In the above program, we are swapping two integers without using a temporary variable with the help of the XOR operator .
XOR in Python using Operator Module
We can also use the XOR operation using the xor() function in the operator module. The xor() function can perform XOR operations on integers and booleans.
The above example uses the operator.xor() function with booleans and integers.
Learn more about bitwise operators
The bitwise operators are used to perform bitwise calculations on integers. The integers are first converted into binary numbers, and then the operations are performed bit by bit. The result is always in decimal format.
They can also be used with boolean values.
To learn more about bitwise operators, click here.
Conclusion
- XOR is a bitwise operator that is short for Exclusive OR.
- It returns 1 1 1 when one and only one of the operands are 1 1 1 or T r u e True T r u e .
- XOR in Python is denoted using the «^» symbol.
- We can swap two integers without using a temporary variable with the help of the XOR operation.
- XOR operation can also be used with the help of the xor() function by importing the operator module.