- How To Save a Dictionary to File in Python
- Save Dictionary to File Using Strings in Python
- Save Dictionary to File in Binary Format in Python
- Conclusion
- save dictionary python
- save dictionary as csv file
- save dictionary to json file
- save dictionary to text file (raw, .txt)
- save dictionary to a pickle file (.pkl)
- How To Save a Dictionary to File in Python
- Save Dictionary to File Using Strings in Python
- Save Dictionary to File in Binary Format in Python
- Conclusion
How To Save a Dictionary to File in Python
A python dictionary is used to store key-value mappings in a program. Sometimes, we might need to store the dictionary directly in a file. In this article, we will discuss how we can save a dictionary directly to a file in Python.
Save Dictionary to File Using Strings in Python
To save a dictionary into a file, we can first convert the dictionary into a string. After that, we can save the string in a text file. For this, we will follow the following steps.
- First, we will convert the dictionary into a string using the str() function. The str() function takes an object as input and returns its string representation.
- After obtaining the string representation of the dictionary, we will open a text file in write mode using the open() function. The open() function takes the file name and the mode as input arguments and returns a file stream object say myFile.
- After obtaining the file stream object myFile, we will write the string to the text file using the write() method. The write() method, when invoked on a file object, takes a string as an input argument and writes it to the file.
- After execution of the write() method, we will close the file stream using the close() method.
By following the above steps, you can save a dictionary to a file in string form. After saving the dictionary to the file, you can verify the file content by opening the file. In the following code, we have first saved a python dictionary to a file.
myFile = open('sample.txt', 'w') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) myFile.write(str(myDict)) myFile.close() myFile = open('sample.txt', 'r') print("The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:") print(myFile.read())The dictionary is: The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:
Save Dictionary to File in Binary Format in Python
Instead of storing the dictionary in the text format, we can directly store the dictionary in the binary format. For this, we will use the pickle module in Python. To save the dictionary to file using the pickle module, we will follow the following steps.
- First, we will open a file in write binary (wb) mode using the open() function. The open() function takes the file name and the mode as input arguments and returns a file stream object say myFile.
- The pickle module provides us with the dump() method with the help of which, we can save a dictionary in binary format to the file. The dump() method takes an object as its first input argument and a file stream as the second input argument. After execution, it saves the object to the file in binary format. We will pass the dictionary as the first argument and myFile as the second input argument to the dump() method.
- After execution of the dump() method, we will close the file using the close() method.
Following is the python code to save a dictionary to a file in python.
import pickle myFile = open('sample_file', 'wb') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) pickle.dump(myDict,myFile) myFile.close()After saving the dictionary in the binary format, we can retrieve it using the load() method in the pickle module. The load() method takes the file stream containing the python object in binary form as its input argument and returns the Python object. After saving the dictionary to file using the dump() method, we can recreate the dictionary from the file as shown below.
import pickle myFile = open('sample_file', 'wb') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) pickle.dump(myDict,myFile) myFile.close() myFile = open('sample_file', 'rb') print("The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:") print(pickle.load(myFile))The dictionary is: The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed two ways to save a dictionary to a file in python. To know more about dictionaries, you can read this article on dictionary comprehension in python.
save dictionary python
How to make python save a dictionary to a file. These are small programs that allows you to create a dictionary and then, when running the program, it will create a file that contains the data in the original dictionary.
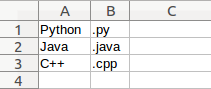
Given a dictionary such as:
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
- Comma seperated value file (.csv)
- Json file (.json)
- Text file (.txt)
- Pickle file (.pkl)
save dictionary as csv file
The csv module allows Python programs to write to and read from CSV (comma-separated value) files.
CSV is a common format used for exchanging data between applications. The module provides classes to represent CSV records and fields, and allows outputs to be formatted as CSV files.
In this format every value is separated between a comma, for instance like this:
Python,py,programming,
Bitmap,bmp,picture,
Sound,mp3,audio,
You can write it to a file with the csv module.
# load csv module
import csv
# define a dictionary with key value pairs
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# open file for writing, «w» is writing
w = csv.writer(open(«output.csv», «w»))
# loop over dictionary keys and values
for key, val in dict.items():
# write every key and value to file
w.writerow(How to save python dict)
The dictionary file (csv) can be opened in Google Docs or Excel
save dictionary to json file
Today, a JSON file has become more and more common to transfer data in the world. JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format.
JSON is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate.
JSON is a text format that is completely language independent but uses conventions that are familiar to programmers of the C-family of languages, including C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl, Python, and many others.
JSON was originally derived from the JavaScript scripting language, but it is not limited to any one programming language.
If you want to save a dictionary to a json file
# load json module
import json
# python dictionary with key value pairs
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# create json object from dictionary
json = json.dumps(dict)
# open file for writing, «w»
f = open(«dict.json»,«w»)
# write json object to file
f.write(json)
# close file
f.close()
save dictionary to text file (raw, .txt)
The program below writes a dictionary to an text string. It uses the str() call to convert the dictionary to a text string. While it is easy to write as a text string, this format makes it harder to read the file.
You can save your dictionary to a text file using the code below:
# define dict
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# open file for writing
f = open(«dict.txt»,«w»)
# write file
f.write( str(dict) )
# close file
f.close()
save dictionary to a pickle file (.pkl)
The pickle module may be used to save dictionaries (or other objects) to a file. The module can serialize and deserialize Python objects.
In Python, pickle is a built-in module that implements object serialization. It is both cross-platform and cross language, meaning that it can save and load objects between Python programs running on different operating systems, as well as between Python running on different platforms.
The pickle module is written entirely in Python, and is available in CPython implementations, such as Jython or IronPython. To enable the loading of pickles in other Python modules, pickle supports being executed from the command line.
The program below writes it to a pickle file.
# load pickle module
import pickle
# define dictionary
dict = {‘Python’ : ‘.py’, ‘C++’ : ‘.cpp’, ‘Java’ : ‘.java’}
# create a binary pickle file
f = open(«file.pkl»,«wb»)
# write the python object (dict) to pickle file
pickle.dump(dict,f)
# close file
f.close()
How To Save a Dictionary to File in Python
A python dictionary is used to store key-value mappings in a program. Sometimes, we might need to store the dictionary directly in a file. In this article, we will discuss how we can save a dictionary directly to a file in Python.
Save Dictionary to File Using Strings in Python
To save a dictionary into a file, we can first convert the dictionary into a string. After that, we can save the string in a text file. For this, we will follow the following steps.
- First, we will convert the dictionary into a string using the str() function. The str() function takes an object as input and returns its string representation.
- After obtaining the string representation of the dictionary, we will open a text file in write mode using the open() function. The open() function takes the file name and the mode as input arguments and returns a file stream object say myFile.
- After obtaining the file stream object myFile, we will write the string to the text file using the write() method. The write() method, when invoked on a file object, takes a string as an input argument and writes it to the file.
- After execution of the write() method, we will close the file stream using the close() method.
By following the above steps, you can save a dictionary to a file in string form. After saving the dictionary to the file, you can verify the file content by opening the file. In the following code, we have first saved a python dictionary to a file.
myFile = open('sample.txt', 'w') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) myFile.write(str(myDict)) myFile.close() myFile = open('sample.txt', 'r') print("The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:") print(myFile.read())The dictionary is: The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:
Save Dictionary to File in Binary Format in Python
Instead of storing the dictionary in the text format, we can directly store the dictionary in the binary format. For this, we will use the pickle module in Python. To save the dictionary to file using the pickle module, we will follow the following steps.
- First, we will open a file in write binary (wb) mode using the open() function. The open() function takes the file name and the mode as input arguments and returns a file stream object say myFile.
- The pickle module provides us with the dump() method with the help of which, we can save a dictionary in binary format to the file. The dump() method takes an object as its first input argument and a file stream as the second input argument. After execution, it saves the object to the file in binary format. We will pass the dictionary as the first argument and myFile as the second input argument to the dump() method.
- After execution of the dump() method, we will close the file using the close() method.
Following is the python code to save a dictionary to a file in python.
import pickle myFile = open('sample_file', 'wb') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) pickle.dump(myDict,myFile) myFile.close()After saving the dictionary in the binary format, we can retrieve it using the load() method in the pickle module. The load() method takes the file stream containing the python object in binary form as its input argument and returns the Python object. After saving the dictionary to file using the dump() method, we can recreate the dictionary from the file as shown below.
import pickle myFile = open('sample_file', 'wb') myDict = print("The dictionary is:") print(myDict) pickle.dump(myDict,myFile) myFile.close() myFile = open('sample_file', 'rb') print("The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:") print(pickle.load(myFile))The dictionary is: The content of the file after saving the dictionary is:
Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed two ways to save a dictionary to a file in python. To know more about dictionaries, you can read this article on dictionary comprehension in python.