- How to move text in HTML
- A code example
- Output
- How To Move Text In Css
- Using Margin and Padding
- Using Position Property
- Relative Positioning
- Absolute Positioning
- Fixed Positioning
- Sticky Positioning
- Using Transform Property
- Disclaimer
- How to Move Text Up and Down in HTML — All You Need to Know
- How to move text up and down in HTML
- The simplest way to move the text down in HTML
- How to make text move up and down with marquee in HTML and CSS
- Explainer
- How to use the marquee attribute in CSS
- Move the Text Up Using CSS
- Use the position and bottom CSS Properties to Move the Text Up
How to move text in HTML
To move your text in HTML, you will need to use the text-align property. Text-align is a CSS property that will align the HTML text to the left, right or center of the web page.
A code example
Here are the examples of how to use text-align to move text in HTML:
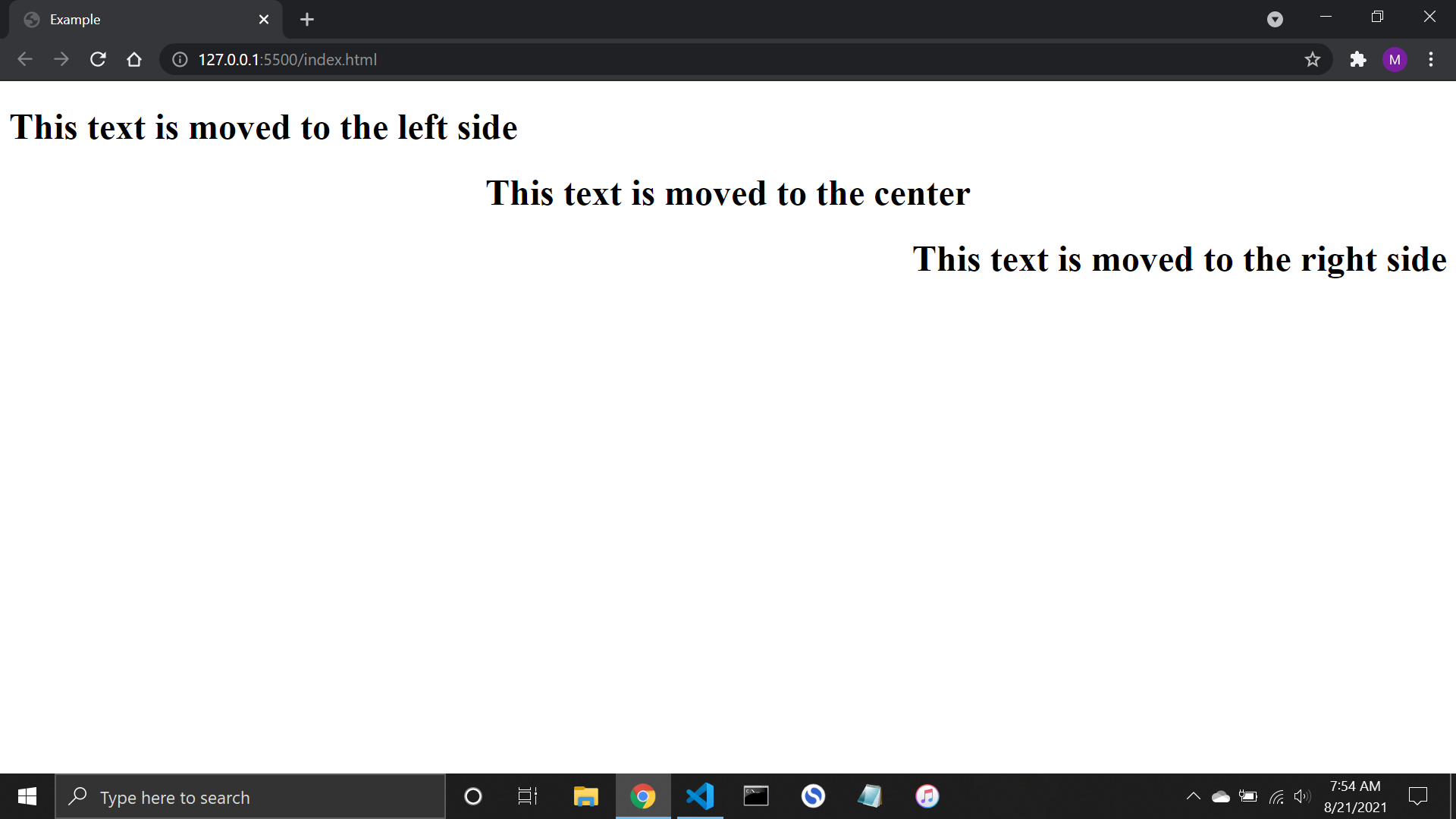
html lang="en"> head> meta charset="UTF-8" /> meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /> meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /> title>Exampletitle> head> style> .text-1 < text-align: left; > .text-2 < text-align: center; > .text-3 < text-align: right; > style> body> h1 class="text-1">This text is moved to the left sideh1> h1 class="text-2">This text is moved to the centerh1> h1 class="text-3">This text is moved to the right sideh1> body> html> Output
And this is how it will turn out:
Get my free e-book to prepare for the technical interview or start to Learn Full-Stack JavaScript
How To Move Text In Css
When it comes to designing a website, moving and positioning text is an essential skill to master. CSS provides us with several options to move text on a webpage. In this blog post, we will explore various techniques to move text using CSS, making your web design journey smoother and more efficient.
Using Margin and Padding
The most common method to move text in CSS is by using margin and padding properties. Margin is the space outside an element, while padding is the space inside an element.
For example, let’s say you want to move a paragraph of text 40 pixels from the top and 20 pixels from the left:
If you want to move the text inside a container, you can use padding:
Using Position Property
The position property in CSS allows you to position an element relative to its parent or the viewport. The most common values for the position property are relative, absolute, fixed, and sticky.
Relative Positioning
When an element is positioned relatively, it is positioned relative to its normal position. For example, if you want to move an element 10 pixels to the right and 5 pixels down, you can use the following code:
Absolute Positioning
Absolute positioning positions an element relative to its nearest positioned ancestor. If there’s no positioned ancestor, it positions the element relative to the viewport. For example, to position an element 20 pixels from the top and 30 pixels from the left:
Fixed Positioning
Fixed positioning positions an element relative to the viewport, which means it stays in the same position even if the page is scrolled. For example, to position a fixed header 10 pixels from the top of the viewport:
Sticky Positioning
Sticky positioning is a combination of relative and fixed positioning. An element with a sticky position acts as a relatively positioned element until it reaches a specified point, after which it behaves as a fixed element. For example, a sticky header that sticks to the top of the viewport when scrolled:
Using Transform Property
The transform property allows you to move, scale, rotate, and skew an element. To move an element using the transform property, you can use the translate() function. For example, to move a paragraph 10 pixels to the right and 20 pixels down:
These are just a few of the many ways to move and position text using CSS. By mastering these techniques, you can easily create stunning and responsive web designs that cater to your desired layout and style.
Disclaimer
This site earns money from ads and affiliate links. If you click on a link to a product we may make a small commission on your purchase. Thanks for supporting us.
How to Move Text Up and Down in HTML — All You Need to Know
When creating content in HTML, the ability to move the text up and down is paramount to able to create white space between sentences, paragraphs, and images.
With little space between blocks of content, the text is difficult to read.
Fortunately, separating text is easy to do and there are several different methods you can use to move text up and down in HTML.
In pure HTML, there are limited options as some methods are no longer supported by all browsers.
Depending on what you are trying to achieve, it may be necessary to use HTML and CSS. Both methods are covered in this tutorial, including templates you can copy and paste.
How to move text up and down in HTML
A line break moves the text down a line. In CSS, the padding-bottom or padding-top values will move text up or down. The HTML marquee tag creates moving text, however, the CSS animate property replaced it. Subscript and superscript are for moving text up and down within a word or sentence.
The simplest way to move the text down in HTML
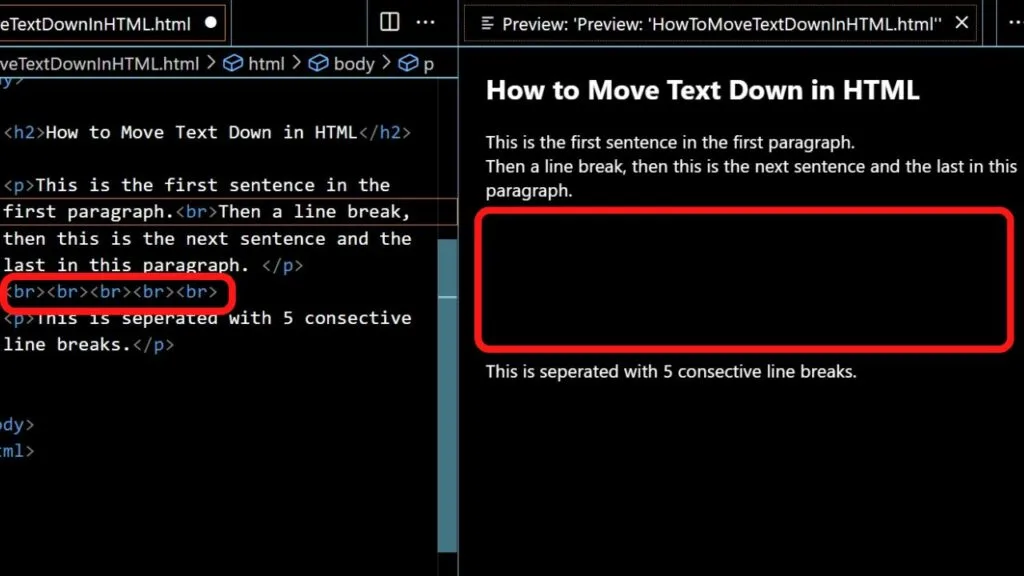
To move your text down a single line, add a line break in HTML.
The height of a line break in HTML cannot be changed unless you apply a line-height in the CSS stylesheet, however, you can increase the spacing by using multiple line breaks consecutively.
Five line breaks in a row will create five blank lines.
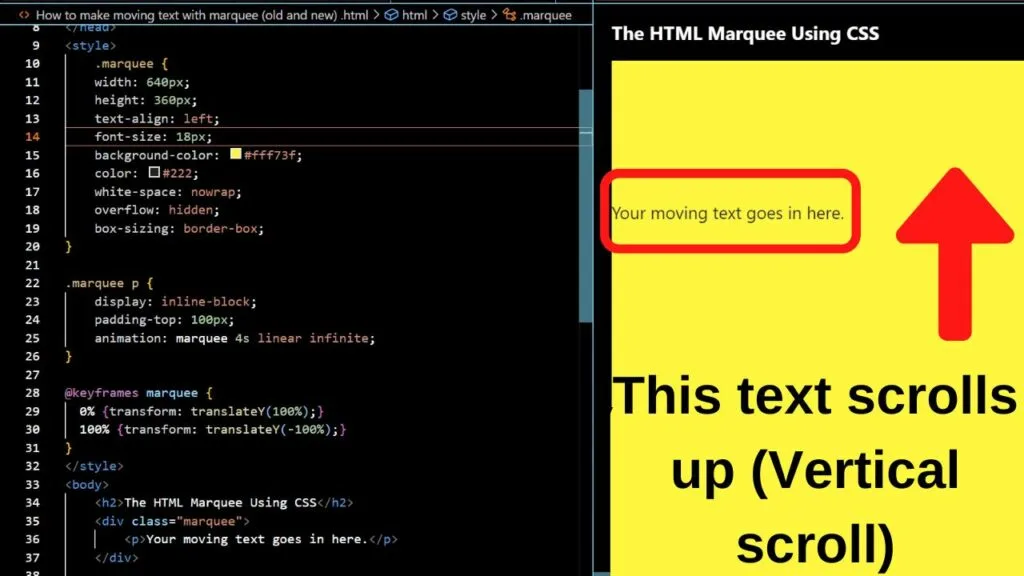
How to make text move up and down with marquee in HTML and CSS
The marquee tag can be used to create text that moves up and down. It is a deprecated HTML tag, therefore it is not recommended.
If you want to take the chance while some browsers still support it, it can be done, but be warned, any browser updates can render the HTML markup useless.
To use the marquee tag in pure HTML, use the following code:
Explainer
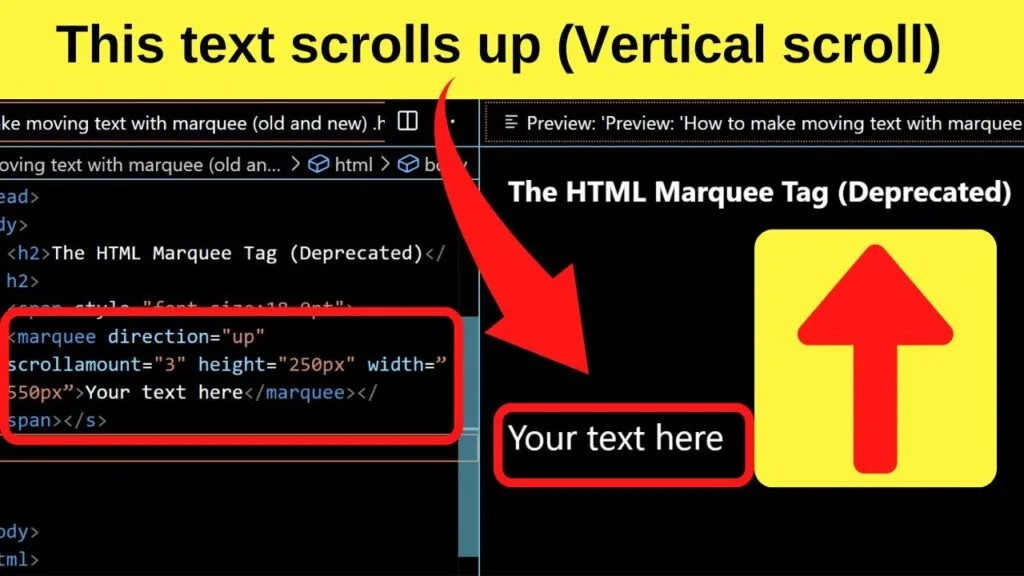
The default direction for the marquee tag in HTML is to move the text from right to left. To change the direction, add the direction attribute directly after the marquee tag. This can be set to up, down, left or right.
The scrollamount attribute controls the speed the text moves at.
The default value is 6. It is fast. To slow it down, add the scrollamount attribute and set the value to below six unless you want super fast scrolling (not advised).
The height value dictates the size of the HTML block.
Setting it higher will increase the white space. It is as though the text within the marquee tag is within an invisible container. You can separate it further by adding a border if you like.
The modern alternative for creating the same effect is to markup your CSS stylesheet with the animate attribute along with a keyframes-at-rule.
The @keyframes rule must be defined for the marquee property to work.
How to use the marquee attribute in CSS
An adaptable template you can use to move text up or down with CSS animation and a keyframes rule is
Move the Text Up Using CSS
- Use the position and bottom CSS Properties to Move the Text Up
- Use the margin-top CSS Property to Move the Text Up
Sometimes, while developing web pages, we put the texts at the bottom or in the footer, so we might need to leave a space below the text and move the text up. We will learn how to move up the text from the webpage’s bottom.
Use the position and bottom CSS Properties to Move the Text Up
In the example below, we have created the element, which we can identify using the bottom-text class name. Inside the element, we have added the element with some text and assigned a text class to it.
In CSS code, we have given position: absolute to the element to move it relative to its parent element, which is the document itself. Also, we have given margin-top: 90vh that will put the element with the class name bottom-text at the bottom of the webpage.
We have added some CSS to the text class to move the text upside from its current position. Here, we have chosen relative as a value of the position property, which allows us to move the text relative to its position.
To move the text up, we have used the bottom property, which will move the text up by 60px, as we have assigned that value. Users can also change the value of the bottom property and move text up by different amounts.
Assigning negative values to the bottom property will move the text down.
div class="bottom-text"> h3 class="text">This is the text at bottom.h3> div> .bottom-text position: absolute; margin-top: 90vh; > .text position: relative; bottom: 60px; >