- How to install python module fiona on Windows OS ?
- What is “fiona” ?
- Python Requirements
- Download a binary distribution of GDAL
- URL
- Choose “win32” or “x64”?
- What should we download?
- Update environment variables
- Fiona’s binary wheel
- FQA
- Conclusion
- References
- Saved searches
- Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
- License
- Toblerity/Fiona
- Name already in use
- Sign In Required
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching GitHub Desktop
- Launching Xcode
- Launching Visual Studio Code
- Latest commit
- Git stats
- Files
- README.rst
How to install python module fiona on Windows OS ?
In this blog, I talk about the requirements and the steps for installing module fiona on Windows OS.
Recently, I learn how to visualise geographical data with python. However, I met difficulties when I installed the module fiona (on my professional PC which is Windows OS). So in this blog, I’ll introduce how to install fiona module on Windows OS with following points:
- What is fiona ?
- Python Requirements
- Download a binary distribution of GDAL
- Fiona’s binary wheel
- Frequently Questioned Answers (FQA)
What is “fiona” ?
Fiona is designed to be simple and dependable. It focuses on reading and writing data in standard Python IO style and relies upon familiar Python types and protocols such as files, dictionaries, mappings, and iterators instead of classes specific to OGR. Fiona can read and write real-world data using multi-layered GIS formats and zipped virtual file systems and integrates readily with other Python GIS packages such as pyproj , Rtree , and Shapely .
Python Requirements
- Python versions 2.7 or 3.4+.
- GDAL version 1.11-2.4. ❗ GDAL version 3 is not yet supported.
- Fiona depends on the modules enum34 , six , cligj , munch , argparse , and ordereddict . Pip will fetch these requirements for you, but users installing Fiona from a Windows installer must get them separately.
Download a binary distribution of GDAL
URL
Choose “win32” or “x64”?
It depends on your python:
import struct print(struct.calcsize("P") * 8)You will get 64 or 32 to indicate which python version do you have installed.
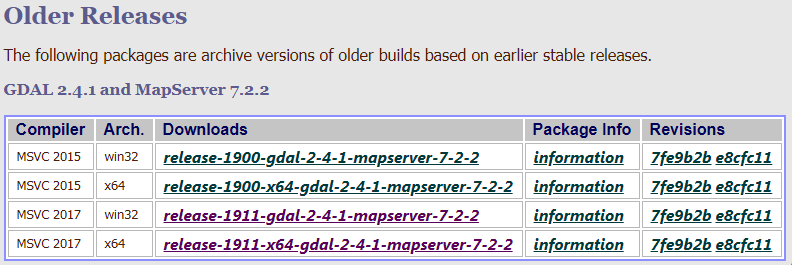
What should we download?
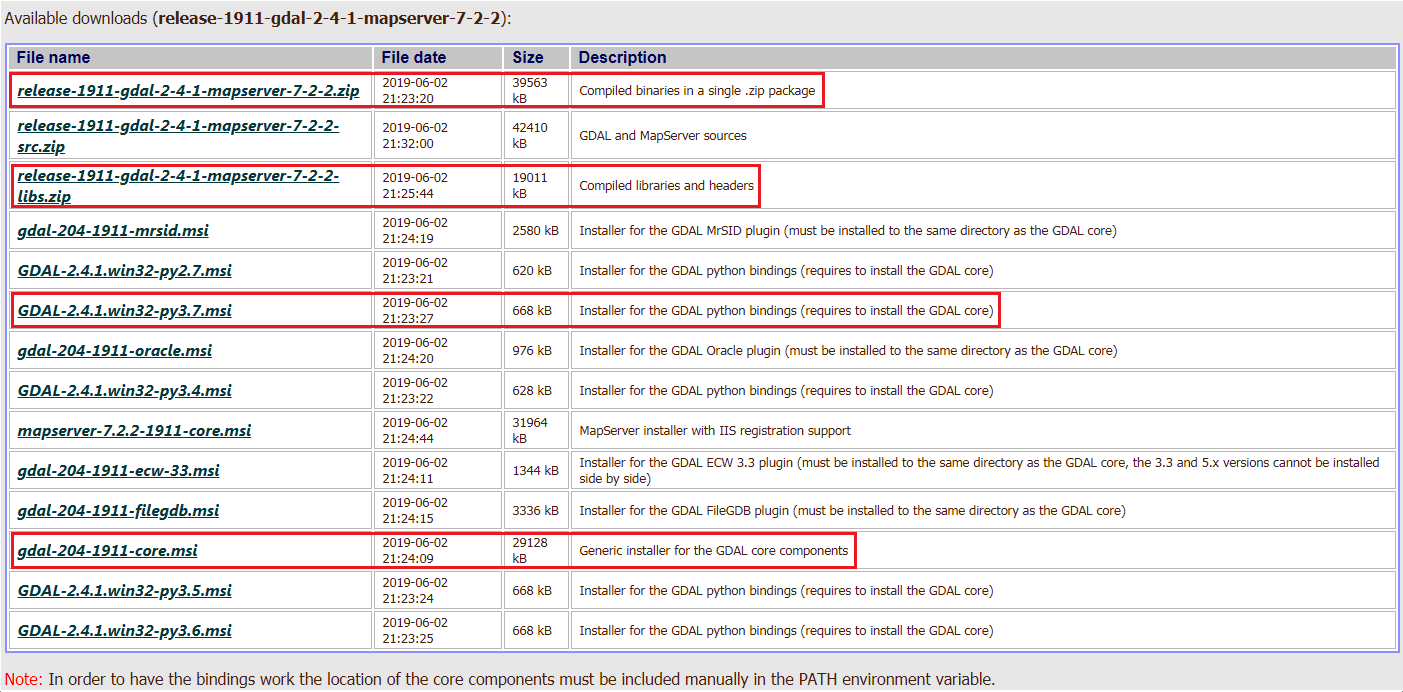
Since python that I have installed is version Python 3.7 (32 bit), I choose “release-1911-gdal-2-4-1-mapserver-7-2-2”.
- Compiled binaries in a single .zip package.
- Compiled libraries and headers.
- Generic installer for the GDAL core components.
- Installer for the GDAL python bindings (requires to install the GDAL core).
Update environment variables
- PATH : C:\Program Files (x86)\GDAL
- GDAL_DATA : C:\Program Files (x86)\GDAL\gdal-data
- GDAL_DRIVER_PATH : C:\Program Files (x86)\GDAL\gdalplugins
- GDAL_VERSION : 2.4.1
Fiona’s binary wheel
FQA
- Q1: ImportError: DLL load failed: %1 is not a valid Win32 application (ImportError: DLL load failed: %1 n est pas une application Win32 valide)
This might because your python is 32 bit version. Thus, all python modules should be 32 bit as well. Similarly, if your python is 64 bit version, you should install 64 bit python modules. - Q2: … is not a supported wheel on this platform
Item. - Q3: ImportError: DLL load failed: The specified module could not be found.
Maybe you forgot installing one/some of dependencies of module fiona : GDAL , enum34 , six , cligj , munch , argparse , and ordereddict . More detail in section “Python Requirements”.
Conclusion
In this blog, I talk about the requirements and the steps for installing module fiona on Windows OS. Hope it’s useful for you!
References
- Toblerity, “Fiona”, github.com. [Online]. Available: https://github.com/Toblerity/Fiona
- Mohamed Ali Jamaoui, “Check if python version is 64 or 32 bit”, Intelligea. [Online]. Available: https://intelligea.wordpress.com/2015/08/05/check-if-python-version-is-64-or-32-bit/
- Albert Kochaphum, “Installing GDAL for Windows”, UCLA Sandbox. [Online]. Available: https://sandbox.idre.ucla.edu/sandbox/tutorials/installing-gdal-for-windows
This work is licensed under a Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International license.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session. You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.
Fiona reads and writes geographic data files
License
Toblerity/Fiona
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
Name already in use
A tag already exists with the provided branch name. Many Git commands accept both tag and branch names, so creating this branch may cause unexpected behavior. Are you sure you want to create this branch?
Sign In Required
Please sign in to use Codespaces.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching GitHub Desktop
If nothing happens, download GitHub Desktop and try again.
Launching Xcode
If nothing happens, download Xcode and try again.
Launching Visual Studio Code
Your codespace will open once ready.
There was a problem preparing your codespace, please try again.
Latest commit
Git stats
Files
Failed to load latest commit information.
README.rst
Fiona streams simple feature data to and from GIS formats like GeoPackage and Shapefile.
Fiona can read and write real-world data using multi-layered GIS formats, zipped and in-memory virtual file systems, from files on your hard drive or in cloud storage. This project includes Python modules and a command line interface (CLI).
Fiona depends on GDAL but is different from GDAL’s own bindings. Fiona is designed to be highly productive and to make it easy to write code which is easy to read.
Fiona has several extension modules which link against libgdal. This complicates installation. Binary distributions (wheels) containing libgdal and its own dependencies are available from the Python Package Index and can be installed using pip.
These wheels are mainly intended to make installation easy for simple applications, not so much for production. They are not tested for compatibility with all other binary wheels, conda packages, or QGIS, and omit many of GDAL’s optional format drivers. If you need, for example, GML support you will need to build and install Fiona from a source distribution. It is possible to install Fiona from source using pip (version >= 22.3) and the —no-binary option. A specific GDAL installation can be selected by setting the GDAL_CONFIG environment variable.
pip install -U pip pip install --no-binary fiona fiona
Many users find Anaconda and conda-forge a good way to install Fiona and get access to more optional format drivers (like GML).
Fiona 2.0 requires Python 3.7 or higher and GDAL 3.2 or higher.
Features are read from and written to file-like Collection objects returned from the fiona.open() function. Features are data classes modeled on the GeoJSON format. They don’t have any spatial methods of their own, so if you want to transform them you will need Shapely or something like it. Here is an example of using Fiona to read some features from one data file, change their geometry attributes using Shapely, and write them to a new data file.
import fiona from fiona import Feature, Geometry from shapely.geometry import mapping, shape # Open a file for reading. We'll call this the source. with fiona.open( "zip+https://github.com/Toblerity/Fiona/files/11151652/coutwildrnp.zip" ) as src: # The file we'll write to must be initialized with a coordinate # system, a format driver name, and a record schema. We can get # initial values from the open source's profile property and then # modify them as we need. profile = src.profile profile["schema"]["geometry"] = "Point" profile["driver"] = "GPKG" # Open an output file, using the same format driver and coordinate # reference system as the source. The profile mapping fills in the # keyword parameters of fiona.open. with fiona.open("centroids.gpkg", "w", **profile) as dst: # Process only the feature records intersecting a box. for feat in src.filter(bbox=(-107.0, 37.0, -105.0, 39.0)): # Get the feature's centroid. centroid_shp = shape(feat.geometry).centroid new_geom = Geometry.from_dict(centroid_shp) # Write the feature out. dst.write( Feature(geometry=new_geom, properties=f.properties) ) # The destination's contents are flushed to disk and the file is # closed when its with block ends. This effectively # executes ``dst.flush(); dst.close()``.
Fiona’s command line interface, named «fio», is documented at docs/cli.rst. The CLI has a number of different commands. Its fio cat command streams GeoJSON features from any dataset.
$ fio cat --compact tests/data/coutwildrnp.shp | jq -c '.' <"geometry":<"coordinates":[[[-111.73527526855469,41.995094299316406]. ]]>> .
For more details about this project, please see: