- Java User Input (Scanner)
- Example
- Input Types
- Example
- Работа со сканером в Java (ввод и вывод данных)
- Пример №1 — с методом nextInt ()
- How to import scanner in java
- How to import scanner in java?
- What is a scanner class in Java?
- How do we import scanner class in Java?
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Muhammad Huzaifa
- Everything You Need to Know About Java Scanner
- What is Scanner class in Java?
- How to use Scanner in Java?
- How to import scanner in Java?
Java User Input (Scanner)
The Scanner class is used to get user input, and it is found in the java.util package.
To use the Scanner class, create an object of the class and use any of the available methods found in the Scanner class documentation. In our example, we will use the nextLine() method, which is used to read Strings:
Example
import java.util.Scanner; // Import the Scanner class class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); // Create a Scanner object System.out.println("Enter username"); String userName = myObj.nextLine(); // Read user input System.out.println("Username is: " + userName); // Output user input >> If you don’t know what a package is, read our Java Packages Tutorial.
Input Types
In the example above, we used the nextLine() method, which is used to read Strings. To read other types, look at the table below:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| nextBoolean() | Reads a boolean value from the user |
| nextByte() | Reads a byte value from the user |
| nextDouble() | Reads a double value from the user |
| nextFloat() | Reads a float value from the user |
| nextInt() | Reads a int value from the user |
| nextLine() | Reads a String value from the user |
| nextLong() | Reads a long value from the user |
| nextShort() | Reads a short value from the user |
In the example below, we use different methods to read data of various types:
Example
import java.util.Scanner; class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Scanner myObj = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("Enter name, age and salary:"); // String input String name = myObj.nextLine(); // Numerical input int age = myObj.nextInt(); double salary = myObj.nextDouble(); // Output input by user System.out.println("Name: " + name); System.out.println("Age: " + age); System.out.println("Salary: " + salary); >> Note: If you enter wrong input (e.g. text in a numerical input), you will get an exception/error message (like «InputMismatchException»).
You can read more about exceptions and how to handle errors in the Exceptions chapter.
Работа со сканером в Java (ввод и вывод данных)
Предлагаем вспомнить 2 примера из жизни, которые как нельзя кстати будут для изучения данной темы.
- Когда мы путешествуем, в аэропорту наш багаж пропускают через ленту со сканером. Вот она была наша сумка на входе. Просканировал сканер сумку и работник аэропорта четко знает что ж мы там такое везём в ней.
- Точно также работает сканнер в магазинах. Вот был штрих-код на входе, отсканировал штрих-код продавец и теперь всё-всё знает о продукте, который числится под этим штрих-кодом.
Чем то схожие задачи есть и в мире программирования на Java. Например, часто необходимо выполнить такие задачи:
- Пользователь ввёл в консоли какое-то число. А программа должна считать с консоли, какое же число ввёл пользователь.
- Пользователь ввёл в консоли какое-то слово. А программа должна считать с консоли, какое же слово ввёл пользователь.
Для решения таких задач в Java используется сканер (от англ. Scanner). Запомните: если что-то ввели в консоли, а нам надо считать что же именно ввели — используем сканер.
Итак, рассмотрим несколько примеров кода, после которых Вы:
- Поймёте на практике как работает сканер. Всего в статье будет 6 примеров кода. Рекомендуем все примеры кода запускать на своём компьютере и на практике изучать как это работает.
- Освоите 4 метода сканера:
Методы — это, грубо говоря, действия , которые может выполнять Scanner. На самом деле методов у сканера намного больше. Но на данном этапе Вам будет достаточно этих 4 методов. Ну что, поехали.
Пример №1 — с методом nextInt ()
Допустим, мы хотим, чтоб пользователь ввёл в консоль любое целое число от 1 до 10 , а программа вывела ему ответ, какое именно число он ввёл.
Поскольку нам необходимо как бы «сосканировать», какое число ввёл пользователь, всё логично — нам понадобится сканер. Ниже приводим решение и комментарии к решению.
Если Вы попробуете запустить этот код на своём компьютере, то в консоли Вы увидите следующее:
Введите любое целое число от 1 до 10:
Затем, если Вы, например, введёте число 5, то в консоли будет следующее:
Введите любое целое число от 1 до 10: 5
Вы ввели число 5
Комментарии:
В статье «Что такое библиотека Java?» мы с Вами разобрались, что в Java есть огромная библиотека протестированного кода — это уже готовые решения ко многим задачам, которые стоят перед программистами в их ежедневной работе . Также мы говорили о различных пакетах, классах и методах. Так вот, сейчас мы будем с Вами работать с пакетом java.util. В этом пакете есть класс Scanner. И у него есть методы (действия), которые позволяют работать с вводом и выводом информации в консоль.
Но чтобы мы смогли использовать в нашем коде класс Scanner, нам необходимо сделать 3 шага.
Шаг №1 — обязательно прописать вот такую строчку в коде
How to import scanner in java
- Haskell vs. PureScript: The difference is complexity Haskell and PureScript each provide their own unique development advantages, so how should developers choose between these two .
- A quick intro to the MACH architecture strategy While not particularly prescriptive, alignment with a MACH architecture strategy can help software teams ensure application .
- How to maintain polyglot persistence for microservices Managing microservice data may be difficult without polyglot persistence in place. Examine how the strategy works, its challenges.
- The basics of implementing an API testing framework With an increasing need for API testing, having an efficient test strategy is a big concern for testers. How can teams evaluate .
- The potential of ChatGPT for software testing ChatGPT can help software testers write tests and plan coverage. How can teams anticipate both AI’s future testing capabilities .
- Retail companies gain DORA metrics ROI from specialist tools DORA metrics and other measures of engineering efficiency are popping up in add-ons to existing DevOps tools. But third-party .
- How to create and manage Amazon EBS snapshots via AWS CLI EBS snapshots are an essential part of any data backup and recovery strategy in EC2-based deployments. Become familiar with how .
- Prices for cloud infrastructure soar 30% Tough macroeconomic conditions as well as high average selling prices for cloud computing and storage servers have forced .
- Deploy a low-latency app with AWS Local Zones in 5 steps Once you decide AWS Local Zones are right for your application, it’s time for deployment. Follow along in this step-by-step video.
- Microsoft to expand free cloud logging following recent hacks Microsoft faced criticism over a lack of free cloud log data after a China-based threat actor compromised email accounts of .
- Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway flaw exploited in the wild Critical remote code execution flaw CVE-2023-3519 was one of three vulnerabilities in Citrix’s NetScaler ADC and Gateway. .
- Using defense in depth to secure cloud-stored data To better secure cloud-resident data, organizations are deploying cloud-native tools from CSPs and third-party tools from MSPs to.
- AWS Control Tower aims to simplify multi-account management Many organizations struggle to manage their vast collection of AWS accounts, but Control Tower can help. The service automates .
- Break down the Amazon EKS pricing model There are several important variables within the Amazon EKS pricing model. Dig into the numbers to ensure you deploy the service .
- Compare EKS vs. self-managed Kubernetes on AWS AWS users face a choice when deploying Kubernetes: run it themselves on EC2 or let Amazon do the heavy lifting with EKS. See .
How to import scanner in java?
Java is a well-known popular language that is used all over the world. Despite its unique features, the reason why most programmers like this language is because this language provides easy and flexible user interaction which is a remarkable thing for a programming language. Now there is a chance that you most likely think, how a user can interact with the program and provide input. For this purpose, Java provides us with a built-in class called the Scanner class.
In this write-up, we acknowledged regarding following outcomes
What is a scanner class in Java?
In Java, the scanner class is present in the java.util package. This class contains many methods that are used to get input from the user at runtime and uses different methods to get an integer, primitive type input from the user. Following are some popular and important methods used by this class to get user input
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| next() | This method is used to get string type input. |
| nextInt() | This method is used to get integer type input. |
| nextFloat() | This method is used to get floating-point number input. |
| nextBoolean() | This method is used to get Boolean type input. |
| nextShort() | This method is used to get short integer value input. |
| nextLong() | This method is used to get Long integer value input. |
| close() | This method is used to close or terminate the scanner. |
How do we import scanner class in Java?
As we mentioned above, the scanner class is a part of java.util package. So to import the scanner class in java we need to import the java.util.Scanner package first according to the following syntax.
Before using the methods of the scanner class you must import this class along with its package by using the above syntax in order to inherit its properties.
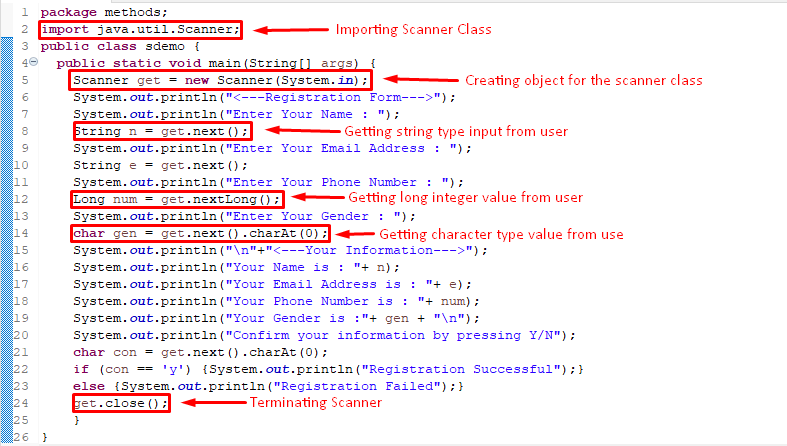
package methods ;
import java. util . Scanner ;
public class sdemo {
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
Scanner get = new Scanner ( System. in ) ;
System. out . println ( «» ) ;
System. out . println ( «Enter Your Name : » ) ;
String n = get . next ( ) ;
System. out . println ( «Enter Your Email Address : » ) ;
String e = get . next ( ) ;
System. out . println ( «Enter Your Phone Number : » ) ;
Long num = get . nextLong ( ) ;
System. out . println ( «Enter Your Gender : » ) ;
char gen = get . next ( ) . charAt ( 0 ) ;
System. out . println ( » \n » + «» ) ;
System. out . println ( «Your Name is : » + n ) ;
System. out . println ( «Your Email Address is : » + e ) ;
System. out . println ( «Your Phone Number is : » + num ) ;
System. out . println ( «Your Gender is :» + gen + » \n » ) ;
System. out . println ( «Confirm your information by pressing Y/N» ) ;
char con = get . next ( ) . charAt ( 0 ) ;
if ( con == ‘y’ ) { System. out . println ( «Registration Successful» ) ; }
else { System. out . println ( «Registration Failed» ) ; }
get . close ( ) ;
}
}
In this code, first we import the scanner class to inherit its properties. Then the object is created for the Scanner class to inherit its properties and use its methods. Then we get user information by using next(), nextLong(), next().CharAt(0) methods of this class.
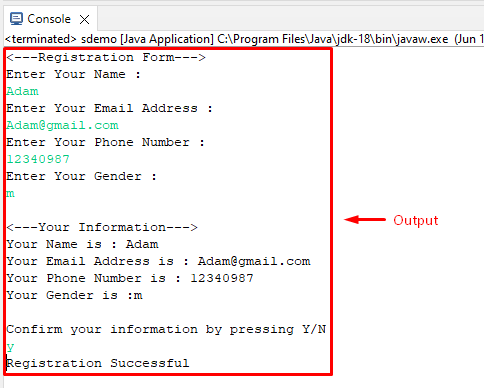
Output:
Output:
In the output, it is clearly seen that we get input from the user with the help of scanner class methods.
You have learned the purpose of scanner class and also how to use/import in Java.
Conclusion
In Java, the scanner class is imported by using the import keyword with java.util.Scanner which is the part of java.util and to use the methods of this class we need to create the object for this class first. In this article, we learned about the scanner class and its purpose. Also, we have gone through the process of importing the scanner class in Java with a detailed example for your better understanding.
About the author
Muhammad Huzaifa
I am a computer science graduate with a passion to learn technical knowledge and share it
with the world. I love to work on top state-of-the-art computing languages. My aim is to best
serve the community with my work.
Everything You Need to Know About Java Scanner
Even though Java Scanner was introduced long time ago in the Java SE 5 version in 2004, developers still ask questions about its use and particular use cases. In this article, we answer the most common questions related to this class and we hope our answers will be helpful to you — now, let’s get started!
What is Scanner class in Java?
Scanner is a class in java.util package that is used for parsing primitive types and strings by using regular expressions. Basically it is used for reading input from the command line, although this approach is not very effective for situations where time is limited. For time-sensitive cases it’s preferable to use reading values from a file.
How to use Scanner in Java?
To use this class, you’ll need to create a class object and select one of the methods described in the documentation.
To get the instance of Java Scanner that reads user input, you’ll have to pass the input stream (System.in) in the constructor of Scanner.
To get the instance of Java Scanner that is responsible for strings parsing, you’ll have to pass the strings in the constructor of Scanner.
Scanner has a lot of constructors for different types of input. You can find all of them in Scanner.java class.
How to import scanner in Java?
Since Scanner belongs to the java.util package, you can import it without downloading any external libraries. There are two ways of how you can do this:
If you plan to work with the java.util. Scanner class only, you can import it directly.
If you work with other modules in the java.util library, it may be a good idea to import the full library.
The first line of code imports the Scanner class. The second line of code imports all the packages within the java.util library, including Scanner.