- How to check null in java
- Learn Latest Tutorials
- Preparation
- Trending Technologies
- B.Tech / MCA
- Javatpoint Services
- Training For College Campus
- How to Check Null in Java
- Using an If Statement
- Using a Null Check
- Expert Q&A
- You Might Also Like
- Check if an Object Is Null in Java
- Java Check if Object Is Null Using the == Operator
- Java Check if Object Is Null Using java.utils.Objects
- Related Article — Java Object
- How to Check if an Object is Null in Java
- How to Check if an Object is null in Java?
- Method 1: Check if an Object is null in Java Using Comparison Operator
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 2: Check if an Object is null in Java Using isNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 3: Check if an Object is null in Java Using nonNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Method 4: Check if an Object is null in Java Using requireNonNull() Method
- Syntax
- Example
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Farah Batool
How to check null in java
Learn Latest Tutorials
Preparation
Trending Technologies
B.Tech / MCA
Javatpoint Services
JavaTpoint offers too many high quality services. Mail us on h[email protected], to get more information about given services.
- Website Designing
- Website Development
- Java Development
- PHP Development
- WordPress
- Graphic Designing
- Logo
- Digital Marketing
- On Page and Off Page SEO
- PPC
- Content Development
- Corporate Training
- Classroom and Online Training
- Data Entry
Training For College Campus
JavaTpoint offers college campus training on Core Java, Advance Java, .Net, Android, Hadoop, PHP, Web Technology and Python. Please mail your requirement at [email protected].
Duration: 1 week to 2 week
Like/Subscribe us for latest updates or newsletter 




How to Check Null in Java
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow’s Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 327,854 times.
A null indicates that a variable doesn’t point to any object and holds no value. You can use a basic ‘if’ statement to check a null in a piece of code. Null is commonly used to denote or verify the non-existence of something. Within that context, it can be used as a condition to start or stop other processes within the code. [1] X Research source
Using an If Statement
- A value of “0” and null are not the same and will behave differently.
- variableName = null;
- For example, if the value is null, then print text “object is null”. If “==” does not find the variable to be null, then it will skip the condition or can take a different path.
Object object = null ; if ( object == null ) System.out.print ( "object is null "); >
Using a Null Check
Use null as a condition for ending a process. Returning a null value can be used to trigger the end of a loop or break a process. This is more commonly used to throw an error or exception when something has gone wrong or an undesired condition has been hit.
synchronized method() while (method()==null); method().nowCanDoStuff(); >
Expert Q&A
Some consider heavy use of nulls a poor practice in object oriented programming, where values should always be pointed to objects. [2] X Research source [3] X Research source
You Might Also Like
How to Set JAVA_HOME for JDK & JRE: A Step-by-Step Guide
Use Easy Windows CMD Commands to Check Your Java Version
How to Do Division in Java (Integer and Floating Point)
How to Compile and Run Java Programs Using Notepad++
Simple Steps to Type a Bunny with Your Keyboard
Check if an Object Is Null in Java
- Java Check if Object Is Null Using the == Operator
- Java Check if Object Is Null Using java.utils.Objects
This tutorial will go through the methods to check if an object is null in Java with some briefly explained examples.
Java Check if Object Is Null Using the == Operator
As an example, we have created two classes — User1 and User2 . The class User1 has one instance variable name and the Getter and Setter methods to update and retrieve the instance variable name . The User2 class has one method, getUser1Object , which returns the instance of class User1 .
In the main method, we create an object of the User2 class named user and call the getUser1Object() on it, which returns the instance of the class User1 . Now we check if the instance of the User1 class returned by the method is null or not by using the == operator in the if-else condition.
If the object returned is not null , we can set the name in the User1 class by calling the setter method of the class and passing a custom string as a parameter to it.
public class JavaCheckNullObject public static void main(String[] args) User2 user; user = new User2(); User1 getUserObject = user.getUser1Object(); if (getUserObject == null) System.out.println("Object is Null"); > else System.out.println("Not Null"); getUserObject.setName("Sam"); System.out.println(getUserObject.getName()); > > > class User2 User1 user; public User1 getUser1Object() return user; > > class User1 String name; public String getName() return name; > public void setName(String name) this.name = name; > > Java Check if Object Is Null Using java.utils.Objects
The java.utils.Objects class has static utility methods for operating an object. One of the methods is isNull() , which returns a boolean value if the provided reference is null, otherwise it returns false.
We have created two classes — User1 and User2 as shown in the code below. In the main method, we created an object of the User2 class using the new keyword and called the getUser1Object() method. It returns an object of class User1 , which we later store in getUser1Object .
To check if it is null, we call the isNull() method and pass the object getUserObject as a parameter. It returns true as the passed object is null.
import java.util.Objects; public class JavaCheckNullObject public static void main(String[] args) User2 user; user = new User2(); User1 getUserObject = user.getUser1Object(); if (Objects.isNull(getUserObject) ) System.out.println("Object is Null"); > else System.out.println("Not Null"); getUserObject.setName("Sam"); System.out.println(getUserObject.getName()); > > > class User2 User1 user; public User1 getUser1Object() return user; > > class User1 String name; public String getName() return name; > public void setName(String name) this.name = name; > > Rupam Saini is an android developer, who also works sometimes as a web developer., He likes to read books and write about various things.
Related Article — Java Object
Copyright © 2023. All right reserved
How to Check if an Object is Null in Java
Java is a dynamic object-oriented programming language that implements classes and objects. A unique instance of a class defines an object of the class. It is a self-contained entity with a state and behavior that facilitates mapping real-world entities while coding. The class defines the data and methods, and its object can utilize them to represent a specific entity.
This article will demonstrate the methods to check if the object is null in Java.
How to Check if an Object is null in Java?
For checking whether the object is null or not, you can use:
We will now implement each of the mentioned methods, one by one!
Method 1: Check if an Object is null in Java Using Comparison Operator
In Java, the comparison operator “==” is mostly used to compare two entities. It returns true or false after performing the comparison. This operator can also be utilized to determine whether an object is null or not.
Syntax
The syntax for verifying an object is null using the Comparison Operator is given below:
Example
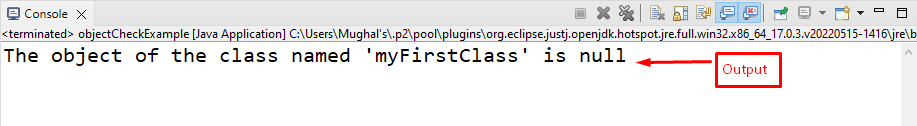
In this example, we have two classes named “myFirstClass” and “objectCheckExample”. The “myFirstClass” contains an empty constructor, that is called when the object or instance of the class is instantiated:
Here, we will create an instance of the “myFirstClass” in the main() method of “objectCheckExample” class and then we will check either the object is null or not by adding the comparison operator “==” in the “if” statement:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
if ( myClass1 == null )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
The output shows the object “myClass1” is null because we have only declared it. Without instantiation, the object is considered null:
Now, let’s confirm whether the object is null or not when it is instantiated.
Method 2: Check if an Object is null in Java Using isNull() Method
Another method to check whether an object is null or not is the “isNull()” method. It is a static method of the Objects class. It receives an object as an argument and outputs the boolean value true or false.
Syntax
Follow the below given syntax for “isNull()” method:
Here, “myClass1” object will be validated using the “isNull()” method.
Example
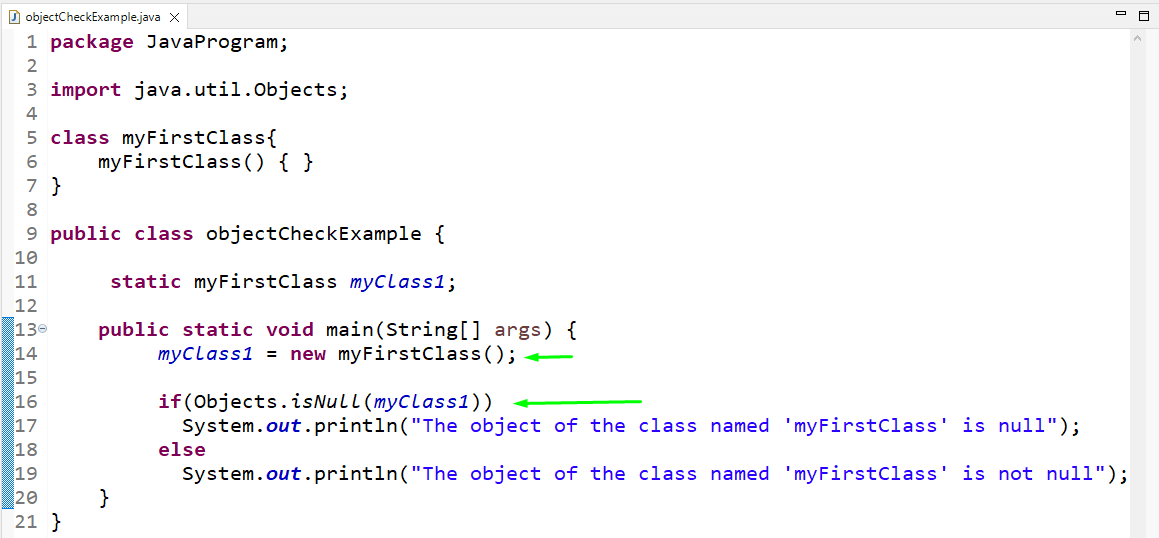
We will create an instance of “myFirstClass” in the main() method of the class named “objectCheckExample”. Using the “new” keyword, the object will be declared and instantiated simultaneously. After that, check whether the object is null or not with the help of the “isNull()” method. As this is a static method so, it will be called by using the class name “Objects”:
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( ) ;
if ( Objects. isNull ( myClass1 ) )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
— else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
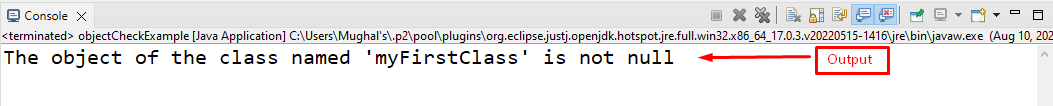
The output indicates that the object of class “myFirstClass” is not null because the object is instantiated:
Let’s check the other ways to verify the object is null or not.
Method 3: Check if an Object is null in Java Using nonNull() Method
We can also verify whether the object is null or not with the help of the “nonNull()” method. It is also a static method belonging to the Objects class. It also takes an object as a parameter and returns a boolean value where true means the object is not null.
Syntax
Here, the syntax for the method is given:
The negation (!) operator is used to convert the result of the “nonNull()” method so that it returns false if the object is not null.
Example
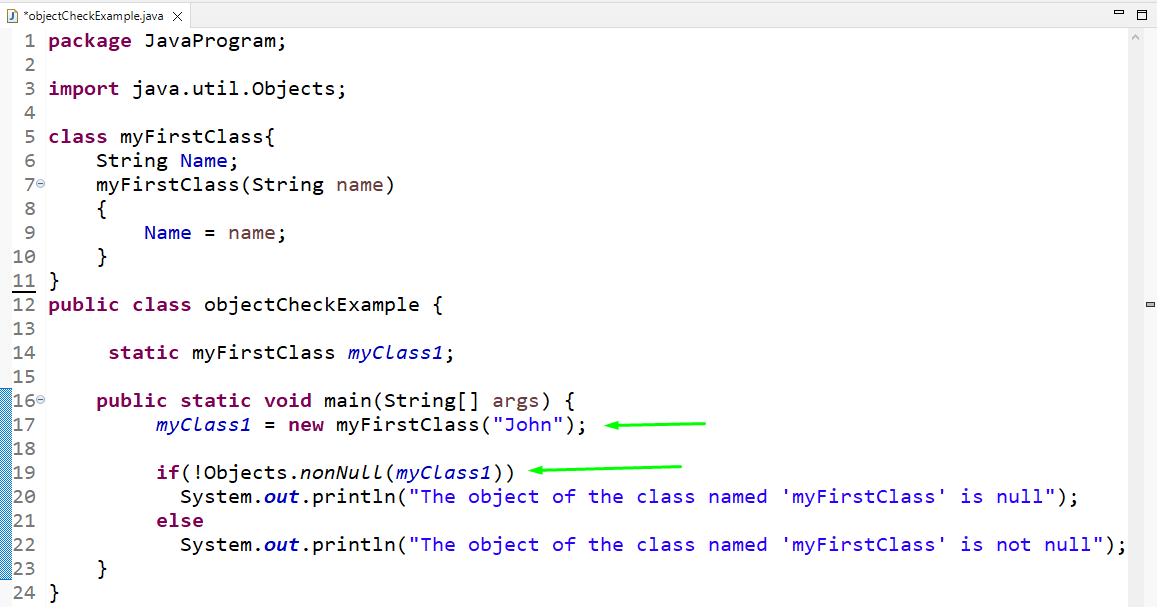
In our “myFirstClass”, we will now create a String type variable “Name” and a parameterized constructor that takes “name” as a parameter:
In the main() method of the “objectCheckExample” class, pass the name “John” as an argument to the created object. After that we will verify the object by using the “nonNull()” method:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( «John» ) ;
if ( ! Objects. nonNull ( myClass1 ) )
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
else
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
}
As you can see, the object is not null because we have assigned value to its “Name” property:
Let’s check one more method to verify the object is null or not.
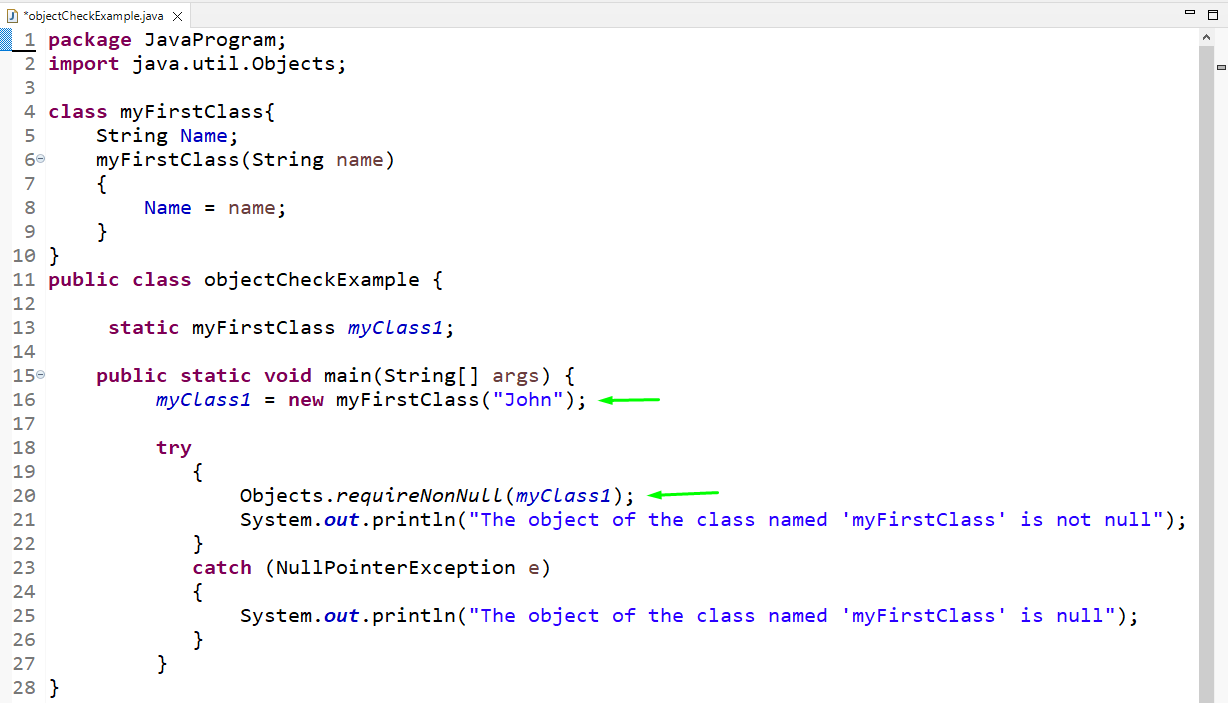
Method 4: Check if an Object is null in Java Using requireNonNull() Method
The “requireNonNull()” method is a static method and belongs to the Objects class. It takes the class object as an input in the method. If the object is null, an exception is thrown.
Syntax
Following described syntax is used for the “requireNonNull()” method:
Example
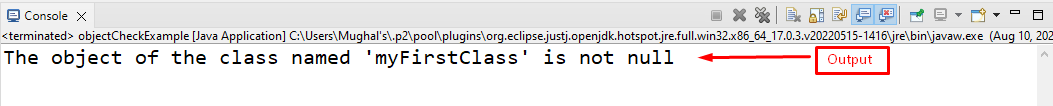
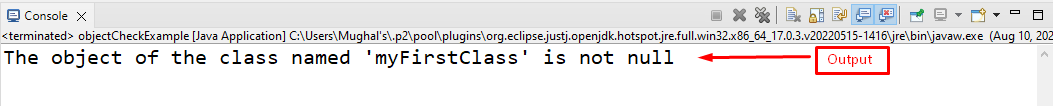
We will verify whether the created object “myClass1” is null or not by using the “requireNonNull()” method. Here, we will add a try-catch block to handle the exception.
In the try block, we call the “requireNonNull()” method and pass the “myClass1” object to it. It will print the specified line if the object is not null. Otherwise, it goes to the catch block and throw a null exception by printing the given statement:
public class objectCheckExample {
static myFirstClass myClass1 ;
public static void main ( String [ ] args ) {
myClass1 = new myFirstClass ( «John» ) ;
try
{
Objects. requireNonNull ( myClass1 ) ;
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is not null» ) ;
}
catch ( NullPointerException e )
{
System . out . println ( «The object of the class named ‘myFirstClass’ is null» ) ;
}
}
}
The resultant output shows that the object is not null because it contains a value:
We have provided all the essential information about how to check an Object is null in Java.
Conclusion
To verify if the object in Java is null or not, you can use different methods: Comparison Operator, isNull() method, nonNull() method, and requireNonNull() method. It is a good practice to verify whether the object is null or not while coding; otherwise, you can face failures and unexpected outputs. This article demonstrated the methods to determine if an object is null in Java.
About the author
Farah Batool
I completed my master’s degree in computer science. I am an academic researcher and love to learn and write about new technologies. I am passionate about writing and sharing my experience with the world.