- container-name
- Syntax
- Values
- Formal definition
- Formal syntax
- Examples
- Using a container name
- Using multiple container names
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
- container-name¶
- Синтаксис¶
- Спецификация¶
- Примеры¶
- Пример 1¶
- Пример 2¶
- container
- Syntax
- Values
- Formal definition
- Formal syntax
- Example
- Specifications
- Browser compatibility
- See also
- Found a content problem with this page?
- MDN
- Support
- Our communities
- Developers
- HTML container
- What is a «container» in HTML?
- your container title here
- How do I make a «container» box in HTML?
- your container title here
- How do «containers» work in HTML?
- your container title here
container-name
The container-name CSS property specifies a list of query container names used by the @container at-rule in a container query. A container query will apply styles to elements based on the size of the nearest ancestor with a containment context. When a containment context is given a name, it can be specifically targeted using the @container at-rule instead of the nearest ancestor with containment.
Syntax
/* A single name */ container-name: myLayout; /* Multiple names */ container-name: myPageLayout myComponentLibrary; /* Global Values */ container-name: inherit; container-name: initial; container-name: revert; container-name: revert-layer; container-name: unset;
Values
A case-sensitive string that is used to identify the container.
The following conditions apply:
Formal definition
Formal syntax
Examples
Using a container name
Given the following HTML example which is a card component with a title and some text:
div class="card"> div class="post-meta"> h2>Card titleh2> p>My post details.p> div> div class="post-excerpt"> p> A preview of my a href="https://example.com">blog posta> about cats. p> div> div>
To create a containment context, add the container-type property to an element in CSS. The following example creates two containment contexts, one for the card meta information and one for the post excerpt:
Note: A shorthand syntax for these declarations are described in the container page.
.post-meta container-type: inline-size; > .post-excerpt container-type: inline-size; container-name: excerpt; > Writing a container query via the @container at-rule will apply styles to the elements of the container when the query evaluates to true. The following example has two container queries, one that will apply only to the contents of the .post-excerpt element and one that will apply to both the .post-meta and .post-excerpt contents:
@container excerpt (min-width: 400px) p visibility: hidden; > > @container (min-width: 400px) p font-size: 2rem; > >
For more information on writing container queries, see the CSS Container Queries page.
Using multiple container names
You can also provide multiple names to a container context separated by a space:
.post-meta container-type: inline-size; container-name: meta card; > This will allow you to target the container using either name in the @container at-rule. This is useful if you want to target the same container with multiple container queries where either condition could be true:
@container meta (max-width: 500px) p visibility: hidden; > > @container card (max-height: 200px) h2 font-size: 1.5em; > >
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
- CSS container queries
- @container at-rule
- CSS container shorthand property
- CSS container-type property
- CSS content-visibility property
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Jul 17, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.
container-name¶
Свойство container-name указывает список имен контейнеров запроса, используемых правилом @container в запросе контейнера.
Запрос контейнера будет применять стили к элементам на основе размера ближайшего предка с контекстом включения. Когда вмещающему контексту дается имя, он может быть специально нацелен с помощью правила @container вместо ближайшего предка с вмещающим элементом.
Изображения, фильтры, композиция
- contain
- contain-intrinsic-block-size
- contain-intrinsic-height
- contain-intrinsic-inline-size
- contain-intrinsic-size
- contain-intrinsic-width
- container
- container-name
- container-type
- @container
- content-visibility
Синтаксис¶
container-name: container-name>; Спецификация¶
Примеры¶
Пример 1¶
Учитывая следующий пример HTML, который представляет собой компонент карты с заголовком и некоторым текстом:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
div class="card"> div class="post-meta"> h2>Card titleh2> p>My post details.p> div> div class="post-excerpt"> p> A preview of my a href="https://example.com">blog posta> about cats. p> div> div> Чтобы создать контекст включения, добавьте свойство container-type к элементу в CSS. В следующем примере создаются два контекста включения: один для метаинформации карты и один для выдержки из поста:
.post-meta container-type: inline-size; > .post-excerpt container-type: inline-size; container-name: excerpt; > При написании запроса контейнера с помощью at-правила @container стили будут применяться к элементам контейнера, когда запрос будет оценен как true . В следующем примере есть два контейнерных запроса, один из которых будет применяться только к содержимому элемента .post-excerpt , а другой — к содержимому как .post-meta , так и .post-excerpt :
@container excerpt (min-width: 400px) p visibility: hidden; > > @container (min-width: 400px) p font-size: 2rem; > > Пример 2¶
Вы также можете указать несколько имен для контекста контейнера, разделенных пробелом:
.post-meta container-type: inline-size; container-name: meta card; > Это позволит вам нацеливаться на контейнер, используя любое имя в правиле @container . Это полезно, если вы хотите настроить таргетинг на один и тот же контейнер с несколькими запросами контейнера, где любое условие может быть истинным:
@container meta (max-width: 500px) p visibility: hidden; > > @container nav (max-height: 200px) h2 font-size: 1.5em; > > container
The container shorthand CSS property establishes the element as a query container and specifies the name or name for the containment context used in a container query.
Syntax
/* */ container: my-layout; /* / */ container: my-layout / size; /* Global Values */ container: inherit; container: initial; container: revert; container: revert-layer; container: unset;
Values
A case-sensitive name for the containment context. More details on the syntax are covered in the container-name property page.
The type of containment context. More details on the syntax are covered in the container-type property page.
Formal definition
- container-name : none
- container-type : normal
- container-name : no
- container-type : no
- container-name : none or an ordered list of identifiers
- container-type : as specified
- container-name : Not animatable
- container-type : a color
Formal syntax
Example
Given the following HTML example which is a card component with an image, a title, and some text:
div class="post"> div class="card"> h2>Card titleh2> p>Card contentp> div> div>
The explicit way to create a container context is to declare a container-type with an optional container-name :
.post container-type: inline-size; container-name: sidebar; > The container shorthand is intended to make this simpler to define in a single declaration:
.post container: sidebar / inline-size; > You can then target that container by name using the @container at-rule:
@container sidebar (min-width: 400px) /* */ >
For more information on container queries, see the CSS Container Queries page.
Specifications
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser
See also
- CSS container queries
- @container at-rule
- CSS contain property
- CSS container-type property
- CSS container-name property
- CSS content-visibility property
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on Jul 17, 2023 by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
MDN
Support
Our communities
Developers
Visit Mozilla Corporation’s not-for-profit parent, the Mozilla Foundation.
Portions of this content are ©1998– 2023 by individual mozilla.org contributors. Content available under a Creative Commons license.
HTML container
div is a tag.
class is an attribute of div tag
container is a class name.
Also, we have container tags what it is:
What is a «container» in HTML?
«container» is a class name in this HTML code:
div is a tag.
class is an attribute of div tag
container is a class name.
your container title here
Your text here
Another text : - Grape silver beet collard
greens avocado quandong fennel gumbo black-eyed
pea watercress potato tigernut corn groundnut.
Chickweed okra pea winter purslane
coriander yarrow sweet pepper radish garlic
brussels sprout groundnut summer purslane
earthnut pea tomato spring onion azuki bean gourd.
Gumbo kakadu plum komatsuna
black-eyed pea green bean zucchini gourd
winter purslane silver beet rock melon
radish asparagus spinach. -
Note: you can change name class «content» with another name as «main_box» how you like.
How do I make a «container» box in HTML?
How do I make a «container» box in HTML?
To make a «container» HTML element you mast declare as a class name like:
your container title here
This is a paragraph
under the containe box
Your text here
Another text : - Grape silver beet
collard greens avocado quandong fennel gumbo black-eyed
pea watercress potato tigernut corn groundnut.
Chickweed okra pea winter purslane
coriander yarrow sweet pepper radish garlic
brussels sprout groundnut summer purslane
earthnut pea tomato spring onion azuki bean gourd.
Gumbo kakadu plum komatsuna
black-eyed pea green bean zucchini gourd
winter purslane silver beet rock melon
radish asparagus spinach. -
Note: you can change name class «content» with another name how you like.
Tags: container class, fluid, tags, elements, box, border, template, row padding, responsive, size, width, center, table, background color
How do «containers» work in HTML?
As shown in the paragraphs above. A container is a
Also, we have container tags what it is:
Example — How do «containers» work in HTML?
This is an editor and you can change parameters in the box below
your container title here
This is a paragraph
under the containe box
Your text here
Another text : - Grape silver beet collard
greens avocado quandong fennel gumbo black-eyed
pea watercress potato tigernut corn groundnut.
Chickweed okra pea winter purslane
coriander yarrow sweet pepper radish garlic
brussels sprout groundnut summer purslane
earthnut pea tomato spring onion azuki bean gourd.
Gumbo kakadu plum komatsuna
black-eyed pea green bean zucchini gourd winter
purslane silver beet rock melon
radish asparagus spinach. -
container class, fluid, tags, elements, box, border, template, row padding, responsive, size, width, center, table, background color
HTML container — html tutorial

This tool makes it easy to create, adjust, and experiment with custom colors for the web.
Magnews2 is a modern and creative free magazine and news website template that will help you kick off your online project in style.
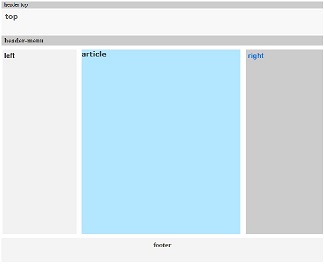
Find here examples of creative and unique website layouts.
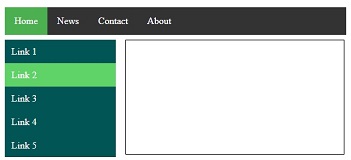
Find here examples of creative and unique website CSS HTML menu.


This tool makes it easy to create, adjust, and experiment with custom colors for the web.
Magnews2 is a modern and creative free magazine and news website template that will help you kick off your online project in style.
Find here examples of creative and unique website layouts.
Find here examples of creative and unique website CSS HTML menu.