- PHP glob
- Introduction to the PHP glob() function
- PHP glob() function examples
- 1) Using the PHP glob() function to list all files in a directory
- 2) Using the PHP glob() function to calculate get the total size of files
- 3) Using the PHP glob() function to include the dotfiles
- Summary
- Поиск файлов в PHP
- Поиск в директории
- Список всех файлов и директорий
- Результат:
- Только файлы
- Результат:
- Только директории
- Результат:
- Поиск по расширению
- Результат:
- Поиск по нескольким расширениям
- Результат:
- Поиск по имени файла
- Результат:
- Результат:
- Поиск в дереве
- Список всех файлов
- Результат:
- Список всех директорий
- Результат:
- Поиск по имени/расширению
- Результат:
- glob
- Список параметров
- Возвращаемые значения
- Список изменений
- Примеры
- Примечания
- Смотрите также
PHP glob
Summary: in this tutorial, you’ll learn how to use the PHP glob() function to get the list of files and directories that match a pattern.
Introduction to the PHP glob() function
The glob() function finds pathnames that match a pattern.
Here’s the syntax of the glob() function:
glob ( string $pattern , int $flags = 0 ) : array|falseCode language: PHP (php)The glob() function takes two parameters:
The $pattern is the pattern to match. To construct a pattern, you use the following special characters:
- Use * to match zero or more characters
- Use — to match exactly one character
- Use [] to match one character from a group of characters listed in the [] . To negate the matching, you use the ! character as the first character in the group.
- Use \ to escape the following characters, except when the GLOB_NOESCAPE flag is set.
The $flag is one or more options that determine the behavior of the glob() function.
For example, if the $flag is GLOB_MARK , the glob() function adds a slash ( / ) or backslash ( \ ) to each matching directory. For a complete list of valid flags, check the glob() function documentation.
To combine flags, you use the | character. For example: GLOB_ONLYDIR|GLOB_NOSORT .
The glob() function returns an array that contains the matched files/directories.
If no files or directories match the pattern, the glob() function returns an empty array.
If an error occurs, the glob() function returns an false .
PHP glob() function examples
Let’s take some examples of using the PHP glob() function.
1) Using the PHP glob() function to list all files in a directory
The following example uses the glob() funtion to list all *.php file in the src directory:
$path = 'src/*.php'; $filenames = glob($path); foreach ($filenames as $filename) < echo $filename . '
'; >Code language: PHP (php)In this example, the pattern *.php matches any file whose extension is php .
2) Using the PHP glob() function to calculate get the total size of files
To get the total size of files in a directory which match a pattern, you use these steps:
- First, find the matching files using the glob() function.
- Second, get the size of each file by passing the result of the glob() function to the array_map() function.
- Third, get the total size by passing the result of the array_map() to the array_sum() function.
The following code illustrates how to use the glob() , array_map(), and array_sum() function to find the total size of the *.php files in the src directory:
echo array_sum(array_map('filesize', glob('./src/*.php')));Code language: PHP (php)3) Using the PHP glob() function to include the dotfiles
The glob(‘*’) ignores hidden files by default. This means that it doesn’t return the file whose name starts with a dot e.g., ( .gitignore ), which are known as dotfiles.
If you want to match the dotfiles, you can use the * as the pattern with the GLOB_BRACE flag. This pattern excludes the directories . and .. :
$filenames = glob('*', GLOB_BRACE); foreach ($filenames as $filename) < echo $filename . '
'; >Code language: PHP (php)Summary
Поиск файлов в PHP
Для поиска файлов на сервере хорошо подходит функция glob(), которая возвращает список файлов по заданной маске, например:
В маске можно использовать следующие специальные символы:
| * | Соответствует нулю или большему количеству любых символов. |
| ? | Один любой символ. |
| [. ] | Один символ входящий в группу. |
| [. ] | Один символ не входящий в группу. |
| Вхождение подстрок, работает с флагом GLOB_BRACE . | |
| \ | Экранирует следующий символ, кроме случаев, когда используется флаг GLOB_NOESCAPE . |
| GLOB_MARK | Добавляет слеш к каждой возвращаемой директории. |
| GLOB_NOSORT | Возвращает файлы в том виде, в котором они содержатся в директории (без сортировки). Если этот флаг не указан, то имена сортируются по алфавиту. |
| GLOB_NOCHECK | Возвращает шаблон поиска, если с его помощью не был найден ни один файл. |
| GLOB_NOESCAPE | Обратные слеши не экранируют метасимволы. |
| GLOB_BRACE | Раскрывает для совпадения с « a », « b » или « c ». |
| GLOB_ONLYDIR | Возвращает только директории, совпадающие с шаблоном. |
| GLOB_ERR | Останавливается при ошибках чтения (например, директории без права чтения), по умолчанию ошибки игнорируются. |
Возможно использовать несколько флагов:
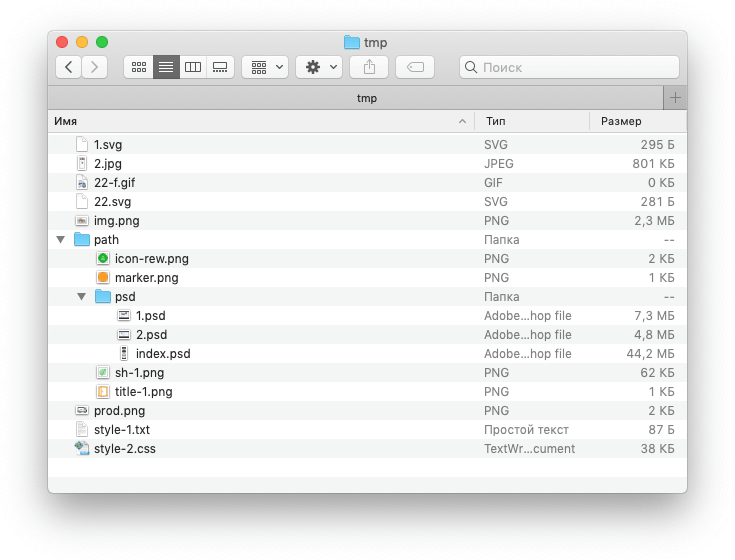
$files = glob('/tmp/*.jpg', GLOB_NOSORT|GLOB_ERR);Далее во всех примерах используется папка tmp со следующим содержимым:
Поиск в директории
Список всех файлов и директорий
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/*') as $file) < $files[] = basename($file); >print_r($files); Результат:
Array ( [0] => 1.svg [1] => 2.jpg [2] => 22-f.gif [3] => 22.svg [4] => img.png [5] => path [6] => prod.png [7] => style-1.txt [8] => style-2.css )Только файлы
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/*') as $file) < if (is_file($file)) < $files[] = basename($file); >> print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => 1.svg [1] => 2.jpg [2] => 22-f.gif [3] => 22.svg [4] => img.png [5] => prod.png [6] => style-1.txt [7] => style-2.css )Только директории
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/*') as $file) < if (is_dir($file)) < $files[] = basename($file); >> print_r($files);Результат:
Поиск по расширению
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/*.svg') as $file) < $files[] = basename($file); >print_r($files);Результат:
Поиск по нескольким расширениям
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/*.', GLOB_BRACE) as $file) < $files[] = basename($file); >print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => 2.jpg [1] => img.png [2] => prod.png )Поиск по имени файла
$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/style*.*') as $file) < $files[] = basename($file); >print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => style-1.txt [1] => style-2.css )$dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = array(); foreach(glob($dir . '/5*.*', GLOB_BRACE) as $obj) < $files[] = basename($obj); >print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => 1.svg [1] => 2.jpg [2] => 22-f.gif [3] => 22.svg )Поиск в дереве
Список всех файлов
function glob_tree_files($path, $_base_path = null) < if (is_null($_base_path)) < $_base_path = ''; >else < $_base_path .= basename($path) . '/'; >$out = array(); foreach(glob($path . '/*') as $file) < if (is_dir($file)) < $out = array_merge($out, glob_tree_files($file, $_base_path)); >else < $out[] = $_base_path . basename($file); >> return $out; > $dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = glob_tree_files($dir); print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => 1.svg [1] => 2.jpg [2] => 22-f.gif [3] => 22.svg [4] => img.png [5] => path/icon-rew.png [6] => path/marker.png [7] => path/psd/1.psd [8] => path/psd/2.psd [9] => path/psd/index.psd [10] => path/sh-1.png [11] => path/title-1.png [12] => prod.png [13] => style-1.txt [14] => style-2.css )Список всех директорий
function glob_tree_dirs($path, $_base_path = null) < if (is_null($_base_path)) < $_base_path = ''; >else < $_base_path .= basename($path) . '/'; >$out = array(); foreach(glob($path . '/*', GLOB_ONLYDIR) as $file) < if (is_dir($file)) < $out[] = $_base_path . basename($file); $out = array_merge($out, glob_tree_dirs($file, $_base_path)); >> return $out; > $dir = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = glob_tree_dirs($dir); print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => path [1] => path/psd )Поиск по имени/расширению
function glob_tree_search($path, $pattern, $_base_path = null) < if (is_null($_base_path)) < $_base_path = ''; >else < $_base_path .= basename($path) . '/'; >$out = array(); foreach(glob($path . '/' . $pattern, GLOB_BRACE) as $file) < $out[] = $_base_path . basename($file); >foreach(glob($path . '/*', GLOB_ONLYDIR) as $file) < $out = array_merge($out, glob_tree_search($file, $pattern, $_base_path)); >return $out; > $path = __DIR__ . '/tmp'; $files = glob_tree_search($path, '*.'); print_r($files);Результат:
Array ( [0] => 2.jpg [1] => img.png [2] => prod.png [3] => path/icon-rew.png [4] => path/marker.png [5] => path/sh-1.png [6] => path/title-1.png )Чтобы в результирующих списках выводились полные пути к файлам, достаточно удалить функцию basename() .
glob
Функция glob() ищет все пути, совпадающие с шаблоном pattern согласно правилам, используемым в функции glob() библиотеки libc, которые похожи на правила, используемые большинством распространённых оболочек.
Список параметров
Шаблон. Не происходит раскрытие тильды и подстановка параметров.
- GLOB_MARK — Добавляет слеш к каждой возвращаемой директории.
- GLOB_NOSORT — Возвращает файлы в том виде, в котором они содержатся в директории (без сортировки). Если этот флаг не указан, то имена сортируются по алфавиту.
- GLOB_NOCHECK — Возвращает шаблон поиска, если с его помощью не был найден ни один файл.
- GLOB_NOESCAPE — Обратные слеши не экранируют метасимволы.
- GLOB_BRACE — Раскрывает для совпадения с ‘a’, ‘b’ или ‘c’.
- GLOB_ONLYDIR — Возвращает только директории, совпадающие с шаблоном.
- GLOB_ERR — Останавливается при ошибках чтения (например, директории без права чтения), по умолчанию ошибки игнорируются.
Возвращаемые значения
Возвращает массив, который содержит совпадающие файлы/директории, пустой массив в случае отсутствия совпадения или FALSE в случае ошибки.
Замечание:
На некоторых системах невозможно отличить отсутствие совпадения и ошибку.
Список изменений
| Версия | Описание |
|---|---|
| 5.1.0 | Добавлена константа GLOB_ERR |
Примеры
Пример #1 Удобный способ, как при помощи glob() можно заменить opendir() и её друзей.
foreach ( glob ( «*.txt» ) as $filename ) echo » $filename размер » . filesize ( $filename ) . «\n» ;
>
?>
Результатом выполнения данного примера будет что-то подобное:
funclist.txt размер 44686 funcsummary.txt размер 267625 quickref.txt размер 137820
Примечания
Замечание: Эта функция неприменима для работы с удаленными файлами, поскольку файл должен быть доступен через файловую систему сервера.
Замечание: Эта функция недоступна на некоторых системах (например, старой Sun OS).
Замечание: Флаг GLOB_BRACE недоступен на некоторых не GNU-системах, например, Solaris.
Смотрите также
- opendir() — Открывает дескриптор каталога
- readdir() — Получает элемент каталога по его дескриптору
- closedir() — Освобождает дескриптор каталога
- fnmatch() — Проверяет совпадение имени файла с шаблоном