- Python Getting Started
- Python Quickstart
- The Python Command Line
- Get Started With Python
- Table of contents
- What is Python?
- Applications of Python
- Install Python
- Create and Run Your First Python Program
- Run Python Using IDLE
- Run Python on Command Line
- Execute Python File
- Syntax and Indentation in Python
- Using Blank Lines in code
- End-of-Line to Terminate a Statement
- Semicolumn to Separate Multiple Statements
- Indentation
- Next Steps
- About Vishal
- Related Tutorial Topics:
- Python Exercises and Quizzes
Python Getting Started
Many PCs and Macs will have python already installed.
To check if you have python installed on a Windows PC, search in the start bar for Python or run the following on the Command Line (cmd.exe):
To check if you have python installed on a Linux or Mac, then on linux open the command line or on Mac open the Terminal and type:
If you find that you do not have Python installed on your computer, then you can download it for free from the following website: https://www.python.org/
Python Quickstart
Python is an interpreted programming language, this means that as a developer you write Python (.py) files in a text editor and then put those files into the python interpreter to be executed.
The way to run a python file is like this on the command line:
Where «helloworld.py» is the name of your python file.
Let’s write our first Python file, called helloworld.py, which can be done in any text editor.
Simple as that. Save your file. Open your command line, navigate to the directory where you saved your file, and run:
Congratulations, you have written and executed your first Python program.
The Python Command Line
To test a short amount of code in python sometimes it is quickest and easiest not to write the code in a file. This is made possible because Python can be run as a command line itself.
Type the following on the Windows, Mac or Linux command line:
From there you can write any python, including our hello world example from earlier in the tutorial:
C:\Users\Your Name>python
Python 3.6.4 (v3.6.4:d48eceb, Dec 19 2017, 06:04:45) [MSC v.1900 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
>>> print(«Hello, World!»)
Which will write «Hello, World!» in the command line:
C:\Users\Your Name>python
Python 3.6.4 (v3.6.4:d48eceb, Dec 19 2017, 06:04:45) [MSC v.1900 32 bit (Intel)] on win32
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
>>> print(«Hello, World!»)
Hello, World!
Whenever you are done in the python command line, you can simply type the following to quit the python command line interface:
Get Started With Python
Python is one of the most popular programming languages, often used for data analytics and machine learning applications. This article will help you get started with Python Programming language by installing it and running your first program. Also, it will walk you through the basic concepts.
Table of contents
- What is Python?
- Applications of Python
- Install Python
- Create and Run Your First Python Program
- Run Python Using IDLE
- Run Python on Command Line
- Execute Python File
- Using Blank Lines in code
- End-of-Line to Terminate a Statement
- Semicolumn to Separate Multiple Statements
- Indentation
What is Python?
Python is a general-purpose, high-level, interpreted, object-oriented programming language used for various applications.
Python was developed by Guido Van Rossum in 1989 while working at National Research Institute in the Netherlands. But officially, Python was made available to the public in 1991.
Python code syntax uses English keywords, making it easy to understand. Therefore, Python is recommended as the first programming language for beginners.
In addition, it includes high-level data structures, dynamic typing, dynamic binding, and many more features that make it very attractive for rapid application development.
Python is simple and easy to learn. Syntax emphasizes readability and therefore reduces the cost of program maintenance. In addition, it supports modules and packages, which encourages program modularity and code reuse.
The Python interpreter and the extensive standard library are available in source or binary form for all major platforms. In addition, it has a wide range of standard and third-party libraries that helps in rapid application development.
Applications of Python
We can use Python everywhere because Python is known for its general-purpose nature, which makes it applicable in almost every domain of software development. The most common application areas are:
- Desktop Applications
- Web Applications
- Database Applications
- Network Programming
- Games
- Data Analysis Applications
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence Applications
- IoT
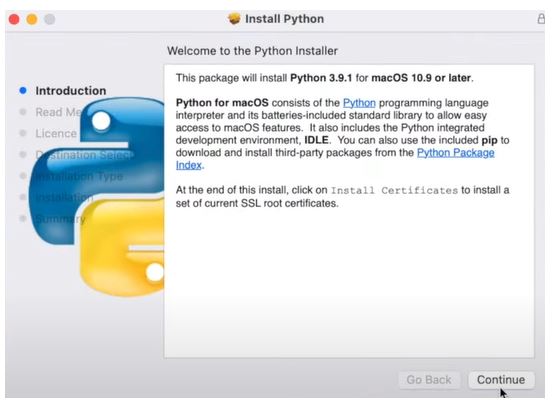
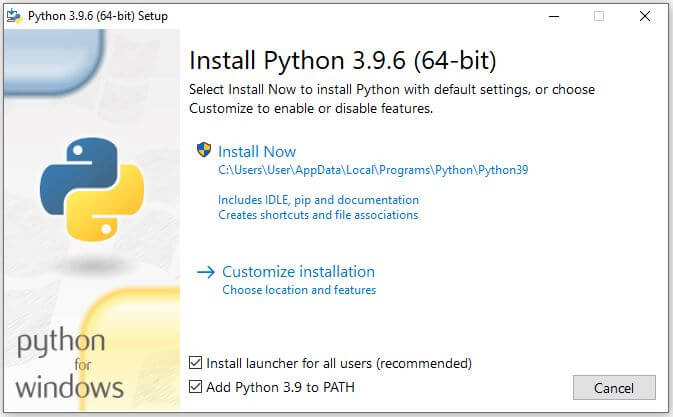
Install Python
It may be possible that some PCs and Macs will have Python already installed. You can check which version of Python is installed before proceeding to the installation.
Open the command line or terminal and type the below command.
If you find Python is not installed, install it using the following instructions.
Installing or updating Python on your computer is the first step to programming in Python. There are multiple installation methods, such as installing Python using an installer or a source code (.zip file)
Download the latest version of Python from python.org. Once you’ve downloaded the installer as per the operating system, Next run an installer by double-clicking on the downloaded file and following the steps.
After installation is completed, we will get a setup successfully install message.
Let’s open the command line or terminal and type the below command to check the version of Python.
Now it’s showing 3.9.6, the currently installed version of Python on our machine, when writing this tutorial.
Create and Run Your First Python Program
Now the installation is completed, let’s see how to write our first Python program.
We can run Python by using the following three ways
- Run Python using IDLE
- Run Python interactively using the command line in immediate mode
- Executing Python File
We will see each one by one but before that, let’s see how to write your first Python program.
Let’s write a simple statement in Python to print the ‘hello world’ on a screen.
- Use the print() function and write a message in its opening and closing brackets shown below.
- A message is a string that is a sequence of characters. In Python, strings are enclosed inside single quotes, double quotes, or triple quotes.
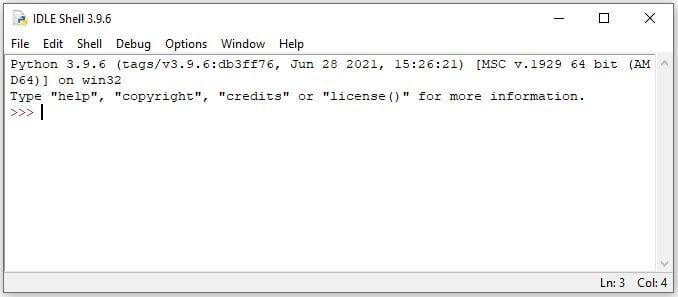
Run Python Using IDLE
IDLE is an integrated development environment (IDE) for Python. The Python installer contains the IDLE module by default. Thus, when you install Python, IDLE gets installed automatically.
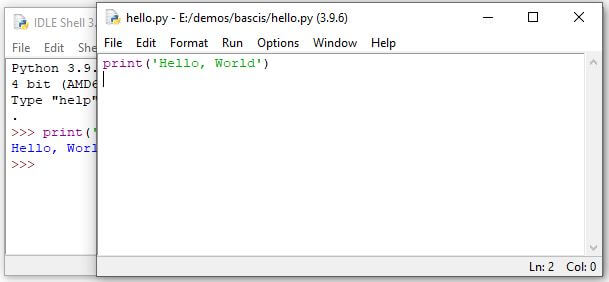
Go to launchpad (for mac) and start icon (for Windows) and type IDLE, to open it. IDLE is an interactive Python Shell where you can write python commands and get the output instantly.
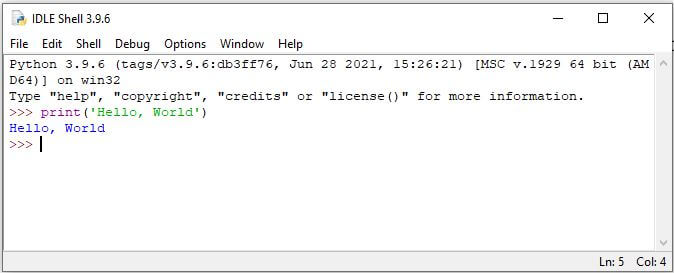
Let’s see how to print ‘hello world’ in Python using IDLE. Type print(‘Hello, World’) and hit enter.
As you can see, we got the output after we executed a print() function with a message.
IDLE has features like coding hinting, syntax highlighting, checking, etc.
Also, we can create a new file, write Python code, and save it with the .py extension. The .py is the python file extension which denotes this is the Python script.
Let’s see how to create a Python script using IDLE.
- Go to the File Menu and select the new file option
- Type the same code (hello world message) in it
- Next, Go to the File menu to save it as hello.py
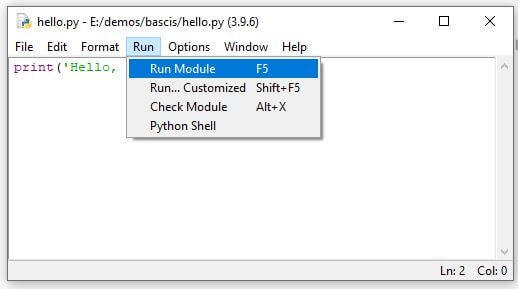
Next, To run the script, go to the Run > Run Module or simply click F5.
Run Python on Command Line
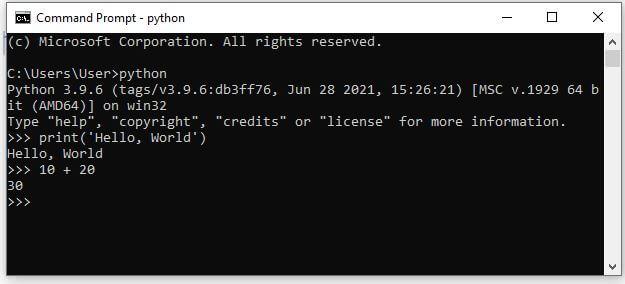
We can also run Python on the command line.
- Type python command on the command line or terminal to run Python interactively. It will invoke the interpreter in immediate mode.
- Next, type Python code and press enter to get the output.
Please find the below image for demonstration.
To exit this mode, type quit() and press enter.
Execute Python File
Python is an interpreted programming language in which we create a code file ( .py with extension) and pass it to the Python interpreter to execute whenever required.
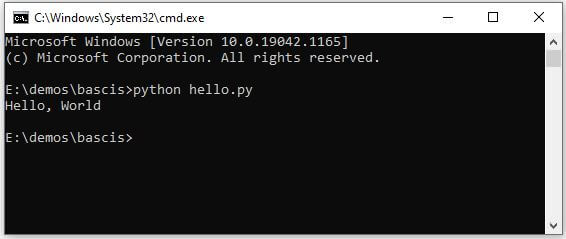
Open any text editor and type the below code in it, and save it as a hello.py
Now, open the terminal or command line and use the below command to execute the message.py. You need to change the directory where this file is present before executing it.
Here python is the command and message.py is the file name you want to execute.
You should get the following output.
Syntax and Indentation in Python
Syntax is the structure of language or a set of rules that defines how a Python program will be written and interpreted.
Using Blank Lines in code
A line containing only white space, possibly with a comment or within a code, is known as a blank line, and Python ignores it.
End-of-Line to Terminate a Statement
In Python end of the line terminate the statement. So you don’t need to write any symbol to mark the end of the line to indicate the statement termination. For example, in other programming languages like Java and C, the statement must end with a semicolon ( ; ).
Python statement ends with the token NEWLINE character ( \n ). But we can extend the statement over multiple lines using line continuation character ( \ ). This is known as an explicit continuation.
addition = 10 + 20 + \ 30 + 40 + \ 50 + 60 + 70 print(addition) # Output: 280Semicolumn to Separate Multiple Statements
In Python, we can add multiple statements on a single line separated by semicolons, as follows:
# two statements in a single l = 2; b = 6 # statement 3 print('Area of rectangle:', l * b) # Output Area of rectangle: 12Most Python style guides don’t recommend adding multiple statements on a single line, though occasionally, it improves readability.
Indentation
Python indentation tells a Python interpreter that the group of statements belongs to a particular block of code. The indentation makes the code look neat, clean, and more readable.
A block is a combination of all multiple statements. Inside a code block, we group multiple statements for a specific purpose.
In other programming languages like C or Java, use curly braces < >to define a block of code. Python uses indentation to denote the code block.
Whitespace is used for indentation in Python to define the indentation level. Ideally, we should use 4 spaces per indentation level. In Python, indented code blocks are always preceded by a colon ( : ) on the previous line.
Take the example of the if-else statement in Python.
num1 = 50 num2 = 100 if num1 > num2: print(num1, 'is greater than', num2) elif num2 > num1: print(num2, 'is greater than', num1) else: print('Both numbers are equal')If one code block is nested in another, the child code block should separate by 4 spaces from the parent code block.
If a block has to be more deeply nested, it is simply indented further to the right. You can understand it better by looking at the following lines of code.
num1 = 500 if num1 > 100: if num1 % 2 == 0: print('Even number is greater than 100')Next Steps
Did you find this page helpful? Let others know about it. Sharing helps me continue to create free Python resources.
About Vishal
I’m Vishal Hule, Founder of PYnative.com. I am a Python developer, and I love to write articles to help students, developers, and learners. Follow me on Twitter
Related Tutorial Topics:
Python Exercises and Quizzes
Free coding exercises and quizzes cover Python basics, data structure, data analytics, and more.
- 15+ Topic-specific Exercises and Quizzes
- Each Exercise contains 10 questions
- Each Quiz contains 12-15 MCQ