- What is the Use of Return Statement in Python?
- Example With Return Statement
- Example Without Return Statement
- Python Return Multiple Values
- Return True, False & String
- Difference between Return and Print Statement in Python
- Python return statement
- Python Function without return statement
- Python Return Statement Example
- Python return statement with expression
- Python return boolean
- Python return string
- Python return tuple
- Python function returning another function
- Python function returning outer function
- Python return multiple values
- Summary
What is the Use of Return Statement in Python?
In Python we use “return” as a keyword, here we can use a function with or without a return statement. If any function is called with return statement it simply returns the value and exit a function.
Return statement simply returns the values as output whereas print() function simply print the value.
Example With Return Statement
# Python 3 Code # working on return statement def addvalue(a, b): return a + b c = addvalue(10, 34) print(c)Explanation
Here we have created a function name addvalue() to add two value a & b and return the value as output by using the return statement. The def keyword is used for creating a method called addvalue(a,b) that takes two parameters and returns their summation. The result of a+b is provided to the user by the return statement.
Then the method addvalue() is called with arguments 10 and 34. The value of the method is stored in the variable c. The next statement prints out the value of c.
The final output of the addvalue() method is 44.
Example Without Return Statement
# Python 3 Code # Function without return statement def addvalue(a, b): # Print the value of a+b print(a + b) addvalue(10, 34)Explanation
In the above-given example, we have used print function to print the output of the function. As you can see in the above example print function returns nothing but print the value directly as output.
The addvalue() method defined by the def keyword takes two parameters. The parameters a and b are added using the print() function. The last line of the code invokes the addvalue() method. Two arguments 10 and 34 are passed to the addvalue() method. The final output is 44.
Python Return Multiple Values
A function can return only one value or object as output, but if you want to return multiple values then you can return the same with the help of list, dictionary and tuple.
All you need to do is convert your multiple outputs into a list (array), dictionary or tuple, and return them as a single object.
# Python 3 Code # Function return multiple value as list def myfunction(a, b): # Print the value of a+b add = a + b sub = a - b return(add, sub) # Take multiple value in list multiv = myfunction(10, 34) # Print values in list print('Addition: ', multiv[0]); print('Subtraction: ' , multiv[1]);Addition: 44 Subtraction: -24Explanation
Here, a method called myfunction() is defined and has two parameters a and b. The two parameters are added/subtracted and stored in a variable called add/sub respectively. The return statement returns the value of add and sub.
Then the myfunction() method is called with the arguments 10 and 34. The result of the function call is stored in the variable multiv. So, now the multiv variable has two values – the result of (a+b) and (a-b). The first print() statement prints out the element at the first index of the variable multiv. Similarly, the next print statement prints out the element at the second index of the multiv variable.
Return True, False & String
# Python 3 Code # Function return Boolean True/False def myfunction(a, b): if(a > b): return True # Return True elif(a == b): return 'A is Equal to B' # Return String else: return False # Return False # Check Boolean print(myfunction(10, 34)) print(myfunction(10, 10)) print(myfunction(22, 11)) False A is Equal to B TrueExplanation
In this program, a function called myfunction() is defined. It takes two parameters a and b. An if statement checks whether the value of a is greater than b. If this is true, the return statement returns True. Else, if the value of a is equal to b, a string ‘A is Equal to B’ is returned by the function. Otherwise, False is returned by the program.
In the end, there are three print statements that display the result of calling the myfunction() method. As the function is passed two values 10 and 34, the first output is False, as 10 is lesser than 34. The next two arguments are 10 and 10. So the output is A is Equal to B.
The last two arguments passed to the myfunction() method are 22 and 11. Thus, as the 22 is greater than 11, the final output is True.
Difference between Return and Print Statement in Python
Returns the value of a function as output.
Print the value of function on terminal.
The output of the function can be pass to other function.
Output can not pass to other function.
# Python 3 Code # working on return statement def addvalue(a, b): return a + b c = addvalue(10, 34) print(c)def addvalue(a, b): # Print the value of a+b print(a + b) addvalue(10, 34)The return and print statements are equally important for programming.
If you just want to execute a simple function that returns a value, the return statement will be enough. In case you want to return a value but also have to print it to the terminal, you need to use the print() method. The print() method can be easily used for displaying the result of a function call to the user.
- Null Object in Python
- TypeError: ‘int’ object is not subscriptable
- Python Comment
- Python lowercase
- Python String find
- Invalid literal for int() with base 10 in Python
- Python Pass Statement
- Python Enumerate
- Python input()
- Python eval
- Python Range
- Python IDE
- Python Print Without Newline
- Python Split()
- Only Size-1 Arrays Can be Converted to Python Scalars
- Attribute Error Python
- Python Combine Lists
- Python list append and extend
- Remove Punctuation Python
- Python KeyError
Python return statement
While we believe that this content benefits our community, we have not yet thoroughly reviewed it. If you have any suggestions for improvements, please let us know by clicking the “report an issue“ button at the bottom of the tutorial.
The python return statement is used to return values from the function. We can use the return statement in a function only. It can’t be used outside of a Python function.
Python Function without return statement
Every function in Python returns something. If the function doesn’t have any return statement, then it returns None .
def print_something(s): print('Printing::', s) output = print_something('Hi') print(f'A function without return statement returns ') Output:
Python Return Statement Example
We can perform some operation in a function and return the result to the caller using the return statement.
def add(x, y): result = x + y return result output = add(5, 4) print(f'Output of add(5, 4) function is ') Output:
Python return statement with expression
We can have expressions also in the return statement. In that case, the expression is evaluated and the result is returned.
def add(x, y): return x + y output = add(5, 4) print(f'Output of add(5, 4) function is ') Output:
Python return boolean
Let’s look at an example where we will return the boolean value of the argument of a function. We will use bool() function to get the boolean value of the object.
def bool_value(x): return bool(x) print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value(False) is ') print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value(True) is ') print(f'Boolean value returned by bool_value("Python") is ') Output:
Python return string
Let’s look at an example where our function will return the string representation of the argument. We can use the str() function to get the string representation of an object.
def str_value(s): return str(s) print(f'String value returned by str_value(False) is ') print(f'String value returned by str_value(True) is ') print(f'String value returned by str_value(10) is ') Output:
Python return tuple
Sometimes we want to convert a number of variables into a tuple. Let’s see how to write a function to return a tuple from a variable number of arguments.
def create_tuple(*args): my_list = [] for arg in args: my_list.append(arg * 10) return tuple(my_list) t = create_tuple(1, 2, 3) print(f'Tuple returned by create_tuple(1,2,3) is ') Output: Further Reading: Python *args and **kwargs
Python function returning another function
We can return a function also from the return statement. This is similar to Currying, which is the technique of translating the evaluation of a function that takes multiple arguments into evaluating a sequence of functions, each with a single argument.
def get_cuboid_volume(h): def volume(l, b): return l * b * h return volume volume_height_10 = get_cuboid_volume(10) cuboid_volume = volume_height_10(5, 4) print(f'Cuboid(5, 4, 10) volume is ') cuboid_volume = volume_height_10(2, 4) print(f'Cuboid(2, 4, 10) volume is ') Output:
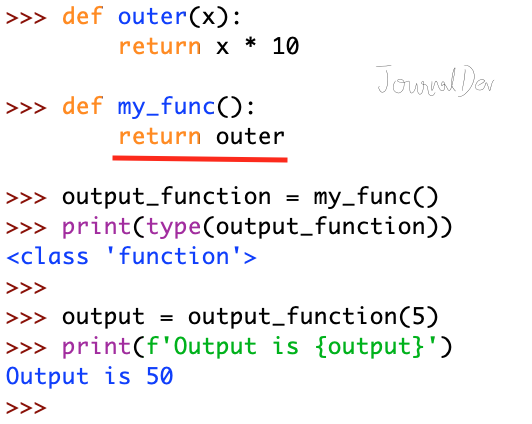
Python function returning outer function
def outer(x): return x * 10 def my_func(): return outer output_function = my_func() print(type(output_function)) output = output_function(5) print(f'Output is ') Output:
Python return multiple values
If you want to return multiple values from a function, you can return tuple, list, or dictionary object as per your requirement. However, if you have to return a huge number of values then using sequence is too much resource hogging operation. We can use yield, in this case, to return multiple values one by one.
def multiply_by_five(*args): for arg in args: yield arg * 5 a = multiply_by_five(4, 5, 6, 8) print(a) # showing the values for i in a: print(i) Output:
Summary
The python return statement is used to return the output from a function. We learned that we can also return a function from another function. Also, expressions are evaluated and then the result is returned from the function. You can checkout complete python script and more Python examples from our GitHub Repository.
Thanks for learning with the DigitalOcean Community. Check out our offerings for compute, storage, networking, and managed databases. Learn more about us