- forEach
- Циклы for, while, do-while, forEach, repeat()
- Интервалы
- Списки и множества
- Map
- Массивы
- Вложенные циклы for
- forEach
- repeat()
- while
- do-while
- Перебрать набор в Kotlin
- 1. Использование forEach() функция
- 2. Использование цикла foreach
- 3. Использование итератора
- 4. Использование неявного toString() функция
- Kotlin ForEach
- What is ForEach Function in Kotlin:
- How to use the forEach function in Kotlin:
- Example # 1: Program of ForEach function to iterate String in Kotlin:
- Example # 2: Program of ForEach function to iterate Integer in Kotlin in Ubuntu 20.04:
- Example # 3: Program of ForEach function to create a custom object in Kotlin:
- Example # 4: Program of ForEachIndex function in Kotlin in Ubuntu 20.04:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Saeed Raza
forEach
Выполняет заданное действие с каждым элементом.
inline fun Map .forEach( action: (EntryK, V>) -> Unit)
Выполняет указанное действие для каждой записи.
inline fun Iterator .forEach(operation: (T) -> Unit)
Выполняет заданную операцию над каждым элементом этого итератора .
import java.util.* fun main(args: ArrayString>) < //sampleStart val iterator = (1..3).iterator() // пропускаем элемент if (iterator.hasNext()) < iterator.next() >// что-то делаем с остальными элементами iterator.forEach < println("The element is $it") > //sampleEnd >
Kotlin 1.8
Накапливает значение начиная с начального и применяя операцию справа налево каждый элемент его индекс исходный массив текущий аккумулятор Возвращает
Группирует элементы из источника Grouping по ключу и последовательно применяет операцию к каждому, передавая ранее накопленное значение текущих аргументов,
Выполняет данное действие для каждого элемента, предоставляя последовательный индекс с функцией действия, которая берет индекс элемента и сама выполняет
Циклы for, while, do-while, forEach, repeat()
Цикл for в Kotlin имеет другой синтаксис. В Java нам нужно инициализировать переменную перед началом цикла, затем указать условие и затем изменять переменную.
Это классический вариант, который применяется и в других языках. Но он довольно неудобный и не понятен для новичков. Например, часто путаются в использовании и .
В Kotlin упростили цикл. Для работы с циклом нужен итератор — массив, Map, интервал чисел и т.д.
Интервалы
Стандартный вариант, когда нужно пробежаться по заданному числу элементов, описывается следующим образом. Если для цикла используется одна команда, можно обойтись без фигурных скобок, но проще всегда использовать блок.
for(i in 1..5) println(i) // Лучше со скобками for(i in 1..5)
Оператор in и его брат !in проверяют вхождение или отсутствие вхождения в диапазон.
В выражении 1..5 мы указываем диапазон от 1 до 5 (пять входит в диапазон). Переменная последовательно примет значение
Диапазон можно заменить переменной.
val range = 1..5 for(i in range)
Списки и множества
fun main() < val list = listOf("C", "A", "T") for (letter in list) < print(letter) >// Можно явно указать тип for (str: String in setOf("C", "A", "T")) < print(str) >> Map
val capitals = mapOf( "USA" to "Washington DC", "England" to "London", "France" to "Paris" ) for ((country, capital) in capitals)
Массивы
val cats = arrayListOf() cats.add("Мурзик") cats.add("Васька") cats.add("Барсик") for(cat in cats) < println("Кот $cat") >// Результат Кот Мурзик Кот Васька Кот Барсик Этот же пример можно переписать, используя индекс:
Проверим, является ли символ не цифрой.
fun isNotDigit(c: Char) = c !in '0'..'9' println(isNotDigit('3')) // false, это всё-таки цифра С помощью index, element и withIndex() можно получить индекс и его значение в массиве.
val cats = arrayListOf("Barsik", "Murzik", "Vaska") for( (index, element) in cats.withIndex()) 0: Мурзик 1: Васька 2: Барсик А как быть с вариантами, когда нужно счётчик не увеличивать на единицу, а уменьшать на 2? Используем ключевые слова downTo и step.
for(i in 10 downTo 1 step 2) < print("$i ") >// выводит: 10 8 6 4 2 Без указания шага значения будут уменьшаться на единицу.
for(i in 10 downTo 1) < print("$i ") >// 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 for (letter in 'Z' downTo 'A') print(letter) // ZYXWVUTSRQPONMLKJIHGFEDCBA Очень часто в циклах встречается выражение size-1, чтобы не выйти за пределы массива. Можно заменить на until.
for(i in 0..cats.size - 1) < println(cats[i]) >for(i in 0 until cats.size)
Хотим выйти из цикла при достижении какого-то значения.
for (i in 1..5) < println(i) // прекращаем перебор, когда достигнем значения 3 if (i == 3) break >// Получим 1 2 3 Ключевое слово continue позволяет продолжить перебор, при этом можно что-то сделать во время перебора, например, мяукнуть. Число 5 при этом не выводится.
println("For loop 1 to 10 continue if number is 5") for (i in 1..10) < if (i == 5) < println("Meow") continue >println(i) > // Результат For loop 1 to 10 continue if number is 5 1 2 3 4 Meow 6 7 8 9 10 Вложенные циклы for
Часто используют два цикла for. Простейший вариант.
// первый цикл for(x in 1..3) < // второй вложенный цикл for(y in 1..3)< print("$x $y \n") >> // результат 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 2 3 3 1 3 2 3 3 Если мы хотим досрочно прервать на каком-то этапе цикл, то можем добавить аннотацию outerLoop@ к первому циклу и внутри второго цикла вызвать [email protected]. Как только значения станут равными (2 2), цикл завершится досрочно.
// первый цикл outerLoop@ for (x in 1..3) < // второй вложенный цикл for (y in 1..3) < print("$x $y \n") if (x == 2 && y == 2) brea[email protected] > > // результат 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 forEach
Пройтись по всем элементам коллекции.
val daysOfWeek = listOf("Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday") daysOfWeek.forEach repeat()
Встроенная функция для повторения команд заданное число раз.
while
Цикл while работает стандартным способом — пока условие остаётся истинным, выполняются команды в блоке цикла. Если код после условия цикла состоит из одной строчки, то фигурные скобки можно опустить.
var i = 1 while (i < 9) < println(i) i = i + 1 >// вышли из цикла и проверяем последнее значение переменной println(i) // 9 Обратите внимание, что внутри цикла мы получим числа от 0 до 8, но если проверить, чему равно значение переменной после цикла, то увидим, что оно больше.
Прервать цикл можно через break.
var i = 1 while (i < 9) < if (i == 5)< break >println(i) i += 1 > // результат 1 2 3 4 do-while
Выполняем какую-то работу, пока выполняется какое-то условие — выводим число, которое увеличивается на единицу, пока число меньше 10.
Можно прервать цикл через break. Когда число станет равным 5, цикл прекратится.
Перебрать набор в Kotlin
В этой статье рассматриваются различные способы перебора набора в Kotlin.
1. Использование forEach() функция
В Kotlin вы можете легко перебрать набор с помощью forEach() функцию, как показано ниже:
2. Использование цикла foreach
Кроме того, вы можете использовать цикл for или цикл foreach для прохода через Set.
3. Использование итератора
Вы также можете позвонить в iterator() который возвращает итератор по набору, как показано ниже:
Или замените цикл while на forEachRemaining() функция.
4. Использование неявного toString() функция
Если вам нужно только отобразить содержимое набора, вы можете просто напечатать строковое представление набора, как показано ниже:
Это все об итерации набора в Kotlin.
Средний рейтинг 4.9 /5. Подсчет голосов: 41
Голосов пока нет! Будьте первым, кто оценит этот пост.
Сожалеем, что этот пост не оказался для вас полезным!
Расскажите, как мы можем улучшить этот пост?
Спасибо за чтение.
Пожалуйста, используйте наш онлайн-компилятор размещать код в комментариях, используя C, C++, Java, Python, JavaScript, C#, PHP и многие другие популярные языки программирования.
Как мы? Порекомендуйте нас своим друзьям и помогите нам расти. Удачного кодирования 🙂
Этот веб-сайт использует файлы cookie. Используя этот сайт, вы соглашаетесь с использованием файлов cookie, нашей политикой, условиями авторского права и другими условиями. Читайте наши Политика конфиденциальности. Понятно
Kotlin ForEach
The Kotlin forEach function can be used to perform any operation of the element in the specified collections. The kotlin is a loop statement that is more conventionally used to make other loops like a while loop. In the article, we will have a clear and simple concept of using the forEach loop function in the kotlin language. The for loop and forEach loop are the same; therefore, it is comparable to the function approach towards the traditional for loop techniques.
What is ForEach Function in Kotlin:
As the forEach function name suggested, it derived its name from the fact that it goes over each collection item one by one. The function always starts with the modifier “forEach.” The for expression is a looping statement that is frequently used in kotlin. It also includes an initialization statement that defines an initial value of an index. The conditional expression then decides whether the loop is continued or not. The last iteration expression permits the index to be adjusted at each pass ends.
Syntax of the ForEach Function in Kotlin:
The general syntax of the forEach loop function we used in Kotlin is given below:
Statements for forEach loop function
ForeEach function takes a condition as a parameter that decides what action should be taken in each collection specified. It allows iterating over each item inside a specified collection of lists and performing some particular function. We could also refer to an item within the forEach loop function code block with the “it” keyword. It is a practical way for performing the conventional task by using a loop path.
How to use the forEach function in Kotlin:
To understand the basics of using the forEach loop function in Kotlin language, we should take a look at the different case examples given below:
Example # 1: Program of ForEach function to iterate String in Kotlin:
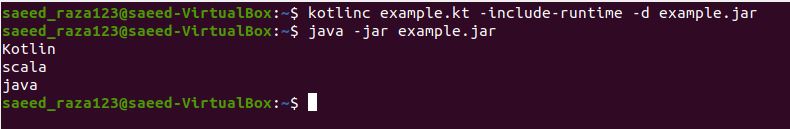
We are using a forEach function that will iterate over each string, and each element of string in the collection will be printed. Let’s execute the simple program of using the forEach function in kotlin.
In the above code example, we have defined the main function we will perform forEach function. We created a variable with the keyword “var” and defined it with “myList.” The variable “myList” is initialized with a collection of lists by using the listOf function. The list is of string type property and contains three string elements. Then we have a called foreach function that will iterate over “myList” each element string. The kotlin println function is used in forEach function that has the “it” modifier passed as a single parameter.
The iteration by using the forEach function gives an output of each element’s list shown on the screen below.
Example # 2: Program of ForEach function to iterate Integer in Kotlin in Ubuntu 20.04:
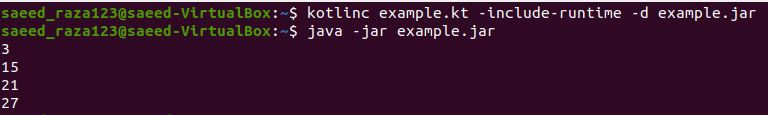
We have a ForEach function for printing the elements in the array. The integers are used in an array that forEach function will iterate over.
In the above example code, we have declared the main function for executing forEach function for Integers. First, we have created a variable as “var” and defined the variable as “Array1” with the int property. The “Array1” is initialized with the array of integers by using the array method. The Array1 has forEach loop function applied. The forEach function will iterate each element in the array and return each integer of an array. We have used the kotlin println function in the forEach block for printing the integers.
Here we can see that the output of every integer element from the array is printed on the terminal screen below.
Example # 3: Program of ForEach function to create a custom object in Kotlin:
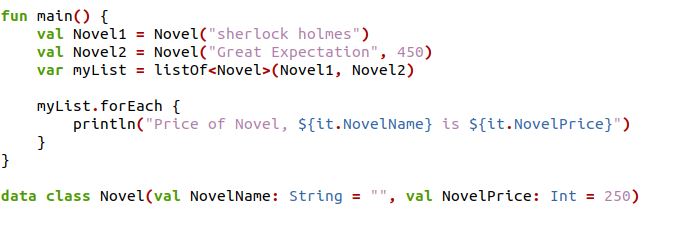
Using the forEach function, we will display a message for each element in a list. We have created a custom object in the below example code.
We have the main function declaration for the code execution in the above code. First, we have defined some variables. The variable is defined with the “val” keyword that tells the score value of the variable. Here we have “Novel1”, the variable stated with the string value. We have another variable, “Novel2,” defined with some string value and an integer value. There is a variable “myList,” which is taking “Novel1” and “Novel2” as a list collection. Then in the forEach function, we have “NovelName” and “NovelPrice,” which we have accessed from the class “Novel.” Through the kotlin println function, we can print the items in the list. We have defined a data class, “Novel,” which holds the variable “NovelName” and “NovelPrice” with the values assigned.
The data of class Novel is printed as output by using the forEach function in the image below.
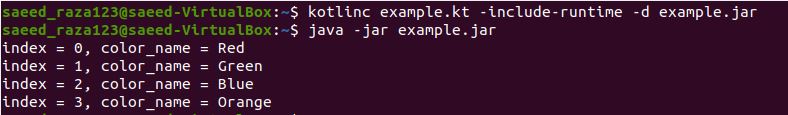
Example # 4: Program of ForEachIndex function in Kotlin in Ubuntu 20.04:
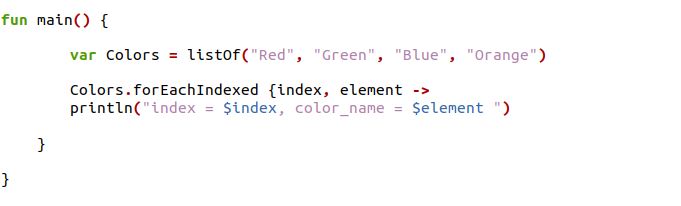
We can also use the forEachIndexed() loop function instead of the forEach() loop function in the kotlin. The forEachIndexed is an inline function that takes an array as input and allows us to access its index and values independently.
We have a variable as “var” in the main function and assign the variable name as “colors.” The variable “colors” is initialized with a listOf function with four different string elements. Then, we have used a forEachIndex function which will traverse a list of colors and print the index value of an element and the element contained in the list.
The output shown in the image has an index value of the elements and the elements.
Conclusion:
The main aim of the article is to give you the easy concept of function and expression in the kotlin language. The forEach function improves the performance of the code. For your better understanding, we have different examples of using the forEach function and demonstrate the use of forEachIndex over a forEach function. It will help you understand the implementation of the forEach function in kotlin.
About the author
Saeed Raza
Hello geeks! I am here to guide you about your tech-related issues. My expertise revolves around Linux, Databases & Programming. Additionally, I am practicing law in Pakistan. Cheers to all of you.