font-size
CSS Свойство font-size определяет размер шрифта. Это свойство также используется для вычисления размера em , ex и других относительных единиц. Подробнее: .
Интерактивный пример
Синтаксис
/* значения в */ font-size: xx-small; font-size: x-small; font-size: small; font-size: medium; font-size: large; font-size: x-large; font-size: xx-large; /* значения в */ font-size: larger; font-size: smaller; /* */ font-size: 12px; font-size: 0.8em; /* */ font-size: 80%; /* Глобальные значения */ font-size: inherit; font-size: initial; font-size: unset;
Свойство font-size устанавливается одним из следующих способов:
- Ключевым словом из перечня абсолютных значений или относительных значений
- Как или , по отношению к размеру родительского элемента.
Значения
Набор ключевых слов абсолютных значений, по отношению к пользовательскому размеру шрифта по умолчанию (им считается medium — среднее).
Больше (larger) или меньше (smaller). Ключевые слова для относительного размера. Шрифт будет больше или меньше по отношению в размеру шрифта родительского элемента.Примерно на такое же соотношение, которое используется в ключевых словах абсолютного размера выше.
Примечание: Для обеспечения максимальной совместимости обычно лучше использовать значения, относящиеся к размеру шрифта пользователя по умолчанию.
Формальный синтаксис
font-size =
| (en-US)
| (en-US)
(en-US) | (en-US)
math
=
| (en-US)
Возможные подходы
Существуют разные способы задания размера шрифта. С помощью ключевых слов или с помощью числовых значений для размера пикселей или размера ems. Выберите подходящий метод в зависимости от потребностей конкретной веб-страницы.
Ключевые слова
Keywords are a good way to set the size of fonts on the web. By setting a keyword font size on the body element, you can set relative font-sizing everywhere else on the page, giving you the ability to easily scale the font up or down on the entire page accordingly.
Pixels
Setting the font size in pixel values ( px ) is a good choice when you need pixel accuracy. A px value is static. This is an OS-independent and cross-browser way of literally telling the browsers to render the letters at exactly the number of pixels in height that you specified. The results may vary slightly across browsers, as they may use different algorithms to achieve a similar effect.
Font sizing settings can also be used in combination. For example, if a parent element is set to 16px and its child element is set to larger , the child element displays larger than the parent element in the page.
Примечание: Defining font sizes in pixel is not accessible, because the user cannot change the font size from the browser. (For example, users with limited vision may wish to set the font size much larger than the size chosen by a web designer.) Therefore, avoid using pixels for font sizes if you wish to create an inclusive design.
Ems
Another way of setting the font size is with em values. The size of an em value is dynamic. When defining the font-size property, an em is equal to the size of the font that applies to the parent of the element in question. If you haven’t set the font size anywhere on the page, then it is the browser default, which is probably 16px. So, by default 1em = 16px, and 2em = 32px. If you set a font-size of 20px on the body element, then 1em = 20px and 2em = 40px. Note that the value 2 is essentially a multiplier of the current em size.
In order to calculate the em equivalent for any pixel value required, you can use this formula:
em = desired element pixel value / parent element font-size in pixels
For example, suppose the font-size of the body of the page is set to 1em, with the browser standard of 1em = 16px; if the font-size you want is 12px, then you should specify 0.75em (because 12/16 = 0.75). Similarly, if you want a font size of 10px, then specify 0.625em (10/16 = 0.625); for 22px, specify 1.375em (22/16).
A popular technique to use throughout the document is to set the the font-size of the body to 62.5% (that is 62.5% of the default of 16px), which equates to 10px, or 0.625em. Now you can set the font-size for any elements using em units, with an easy-to-remember conversion, by dividing the px value by 10. This way 6px = 0.6em, 8px = 0.8em, 12px = 1.2em, 14px = 1.4em, 16px = 1.6em. For example:
body font-size: 62.5%; /* font-size 1em = 10px on default browser settings */ > span font-size: 1.6em; /* 1.6em = 16px */ > The em is a very useful unit in CSS, since it automatically adapts its length relative to the font that the reader chooses to use.
One important fact to keep in mind: em values compound. Take the following HTML and apply it with the previous CSS above:
div> span>Outer span>innerspan> outerspan> div>
Assuming that the browser’s default font-size is 16px, the words «outer» would be rendered at 16px, but the word «inner» would be rendered at 25.6px. This is because the inner span’s font-size is 1.6 em which is relative to its parent’s font-size , which is in turn relative to its parent’s font-size . This is often called compounding.
Rems
rem values were invented in order to sidestep the compounding problem. rem values are relative to the root html element, not the parent element. In other words, it lets you specify a font size in a relative fashion without being affected by the size of the parent, thereby eliminating compounding.
The CSS below is nearly identical to the previous example. The only exception is that the unit has been changed to rem .
html font-size: 62.5%; /* font-size 1em = 10px on default browser settings */ > span font-size: 1.6rem; > Then we apply this CSS to the same HTML, which looks like this:
span>Outer span>innerspan> outerspan>
In this example, the words «outer inner outer» are all displayed at 16px (assuming that the browser’s font-size has been left at the default value of 16px).
Примеры
Пример 1
/* Set paragraph text to be very large. */ p font-size: xx-large > /* Set h1 (level 1 heading) text to be 2.5 times the size * of the text around it. */ h1 font-size: 250% > /* Sets text enclosed within span tag to be 16px */ span font-size: 16px; >
Пример 2
.small font-size: xx-small; > .larger font-size: larger; > .point font-size: 24pt; > .percent font-size: 200%; > h1 class="small">Small H1h1> h1 class="larger">Larger H1h1> h1 class="point">24 point H1h1> h1 class="percent">200% H1h1>
Live Sample
Примечание
em and ex units on the font-size property are relative to the parent element’s font size (unlike all other properties, where they’re relative to the font size on the element). This means em units and percentages do the same thing for font-size .
Спецификации
Совместимость браузеров
BCD tables only load in the browser
Found a content problem with this page?
This page was last modified on 22 февр. 2023 г. by MDN contributors.
Your blueprint for a better internet.
font-size
Определяет размер шрифта элемента. Размер может быть установлен несколькими способами. Набор констант ( xx-small , x-small , small , medium , large , x-large , xx-large ) задает размер, который называется абсолютным. По правде говоря, они не совсем абсолютны, поскольку зависят от настроек браузера и операционной системы.
Другой набор констант ( larger , smaller ) устанавливает относительные размеры шрифта. Поскольку размер унаследован от родительского элемента, эти относительные размеры применяются к родительскому элементу, чтобы определить размер шрифта текущего элемента.
В конечном итоге, размер шрифта сильно зависит от значения свойства font-size у родителя элемента.
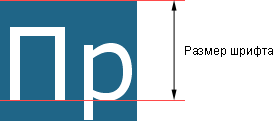
Сам размер шрифта определяется как высота от базовой линии до верхней границы кегельной площадки, как показано на рис. 1.
Синтаксис
font-size: абсолютный размер | относительный размер | значение | проценты | inherit
Значения
Для задания абсолютного размера используются следующие значения: xx-small , x-small , small , medium , large , x-large , xx-large . Их соответствие с размером шрифта в HTML приведено в табл. 1.
| CSS | xx-small | x-small | small | medium | large | x-large | xx-large |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HTML | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Относительный размер шрифта задается значениями larger и smaller .
Также разрешается использовать любые допустимые единицы CSS: em (высота шрифта элемента), ex (высота символа х), пункты ( pt ), пикселы ( px ), проценты ( % ) и др. За 100% берется размер шрифта родительского элемента. Отрицательные значения не допускаются.
inherit Наследует значение родителя.
HTML5 CSS2.1 IE Cr Op Sa Fx
Duis te feugifacilisi
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit, sed diem nonummy nibh euismod tincidunt ut lacreet dolore magna aliguam erat volutpat. Ut wisis enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exerci tution ullamcorper suscipit lobortis nisl ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Результат данного примера показан на рис. 1.
Рис. 2. Применение свойства font-size
Объектная модель
[window.]document.getElementById(» elementID «).style.fontSizeБраузеры
Internet Explorer до версии 7.0 включительно не поддерживает значение inherit .