- Генерация диапазона с плавающей запятой в Python
- Чего Не Хватает В Функции Диапазона Python?
- Почему Python range() не работает с float?
- Использование Yield для генерации диапазона с плавающей запятой
- Функция NumPy Arange() для диапазона значений с плавающей запятой
- Функция NumPy Linspace для генерации диапазона с плавающей запятой
- Генерация диапазона с плавающей запятой без использования сторонних модулей
- Использование значения с плавающей запятой в параметре step
- Создать диапазон с плавающей запятой, используя Itertools
- Резюме
- Generate float range in Python [9 ways]
- What is a floating-point number in Python?
- Why not use the simple and popular range() function?
- Python range float : How to generate floating-point numbers in Python?
- Using the numpy.linspace() method.
- Using the numpy.arange() method.
Генерация диапазона с плавающей запятой в Python
Вы хотите узнать, как генерировать диапазон чисел с плавающей запятой в Python? В этом руководстве вы найдете много способов получения значений с плавающей запятой в пределах заданного диапазона.
Мы рекомендуем вам по крайней мере использовать Python 3 для написания кода и запуска примеров. Python 2.x все еще получает обновления, но более новые версии более стабильны и продвинуты.
Чего Не Хватает В Функции Диапазона Python?
Диапазон Python может генерировать только набор целых чисел из данной полосы. Он также не допускает параметр типа с плавающей запятой и не может генерировать диапазон чисел с плавающей запятой.
Он принимает один, два или три параметра (старт / стоп / шаг). Однако все аргументы имеют целочисленный тип. Если вы передадите float, это приведет к ошибке TypeError.
start = 1 stop = 6.7 step = 0.1 for value in range(start, stop, step): print (value)
Когда вы запускаете приведенный выше код, он выдает следующую ошибку:
TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
Приведенный выше пример предполагает, что Python не предоставляет встроенного способа генерации диапазона с плавающей запятой. Поэтому нам нужно разработать собственную реализацию функции range.
Почему Python range() не работает с float?
Функция range генерирует конечный набор целых чисел. Вы можете определить размер, вычитая начальное значение из конечного значения (когда шаг = 1). Ниже приведена общая формула для расчета длины.
Проверьте примеры приведенные ниже, чтобы получить ясность.
>>> len(list(range(1,10,2))) 5 >>> 10-1/2 + 1 >>> (10-1)//2 + 1 5
Однако тот же диапазон фактически имеет бесконечное количество из чисел с плавающей запятой. Вы можете ограничить его, используя фиксированное значение точности. Следовательно, это может быть возможной причиной того, что range() не позволяет работать с float.
Использование Yield для генерации диапазона с плавающей запятой
Вы можете написать пользовательскую функцию Python, как показано ниже. Это может позволить вам указать значение с плавающей запятой для аргумента шага.
import decimal def float_range(start, stop, step): while start < stop: yield float(start) start += decimal.Decimal(step) print(list(float_range(0, 1, '0.1')))
[0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]
Мы использовали модуль decimal для сохранения точности.
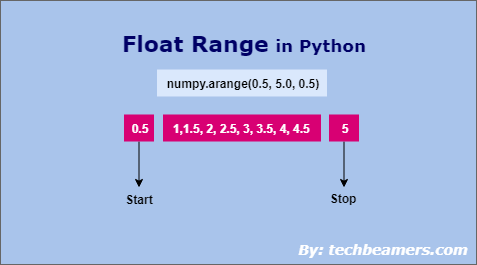
Функция NumPy Arange() для диапазона значений с плавающей запятой
Чтобы использовать функцию arange(), вам необходимо установить и импортировать пакет numpy. Эта библиотека имеет различные арифметические и числовые функции для генерации массивов / матриц разных размеров.
В любом случае, здесь мы будем использовать функцию arange() для генерации диапазона чисел с плавающей запятой.
Arange() имеет ту же сигнатуру, что и встроенный метод range. Но мы можем передать аргументы типа float (с плавающей запятой) в качестве параметров этой функции.
# Syntax import numpy arange(start, stop, step)
Теперь давайте рассмотрим пример, чтобы улучшить наше понимание.
from numpy import arange print("Float range using NumPy arange():") print("\nTest 1:") for i in arange(0.0, 1.0, 0.1): print(i, end=', ') print("\n\nTest 2:") for i in arange(0.5, 5.5, 0.5): print(i, end=', ') print("\n\nTest 3:") for i in arange(-1.0, 1.0, 0.5): print(i, end=', ') Float range using NumPy arange(): Test 1: 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.30000000000000004, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6000000000000001, 0.7000000000000001, 0.8, 0.9 Test 2: 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0 Test 3: -1.0, -0.5, 0.0, 0.5
Функция NumPy Linspace для генерации диапазона с плавающей запятой
У NumPy есть другой метод linspace(), позволяющий вам создать указанное количество чисел с плавающей запятой. Он имеет следующий синтаксис:
# Syntax linspace(start, stop, num, endpoint) start => starting point of the range stop => ending point num => Number of values to generate, non-negative, default value is 50. endpoint => Default value is True. If True, includes the stop value else ignores it.
Эта функция имеет больше аргументов, но мы описали те, которые соответствуют нашей цели.
Посмотрите на приведенные ниже примеры.
import numpy as np print("Print Float Range Using NumPy LinSpace()\n") print(np.linspace(1.0, 5.0, num = 5)) print(np.linspace(0, 10, num = 5, endpoint = False)) Print Float Range Using NumPy LinSpace() [1. 2. 3. 4. 5.] [0. 2. 4. 6. 8.]
Если вы не хотите устанавливать пакет NumPy, попробуйте подход в следующем примере.
Генерация диапазона с плавающей запятой без использования сторонних модулей
Здесь мы предоставили простую программу на Python для генерации диапазона чисел с плавающей запятой. Он принимает как положительное так и отрицательное значение для аргументов.
Этот пример имеет 2 логических деления. Первый определяет функцию float_range(). Другой вызывает его с разными входными значениями и печатает результат.
""" Desc : This function generates a float range of numbers w/o using any library. Params : A (int/float) : First number in the range L (int/float) : Last number in the range D (int/float) : Step or the common difference """ def float_range(A, L=None, D=None): #Use float number in range() function # if L and D argument is null set A=0.0 and D = 1.0 if L == None: L = A + 0.0 A = 0.0 if D == None: D = 1.0 while True: if D > 0 and A >= L: break elif D < 0 and APrinting float range Test 1: 0.1, 0.6, 1.1, 1.6, 2.1, 2.6, 3.1, 3.6, 4.1, 4.6, Test 2: -5, -3.5, -2, -0.5, 1, 2.5, 4, Test 3: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, Test 4: 10.1, 11.1, 12.1, 13.1, 14.1, 15.1, 16.1, 17.1, 18.1, 19.1,Использование значения с плавающей запятой в параметре step
В пользовательской функции диапазона мы можем предоставить значение типа с плавающей запятой в качестве аргумента шага. Это позволит нам генерировать числа в определенном интервале.
Давайте рассмотрим пример, в котором в качестве значения шага указано 3.7.
import numpy as pynum_float print( "Display range using a float value in the step\n", pynum_float.arange(3, 33, 3.7) )Display range using a float value in the step [ 3. 6.7 10.4 14.1 17.8 21.5 25.2 28.9 32.6]Создать диапазон с плавающей запятой, используя Itertools
Мы также можем использовать модуль itertools и его функции, такие как islice() и count. Посмотрите на приведенный ниже пример, где мы написали простой метод для создания диапазона.
from itertools import islice, count def iter_range(start, stop, step): if step == 0: raise ValueError("Step could not be NULL") length = int(abs(stop - start) / step) return islice(count(start, step), length) for it in iter_range(0, 10, 1.10): print ("".format(it), end = " ")0.0 1.1 2.2 3.3 4.4 5.5 6.6 7.7 8.8Резюме
Хотелось бы, чтобы вы узнали, как генерировать диапазон чисел с плавающей запятой. Вы можете выбрать любой из методов, описанных выше, и использовать его в своих задачах.
Generate float range in Python [9 ways]
There are sometimes when you need to generate a range of floating-point numbers, for making various codes easier to implement and execute. Here, the focus is on generating a range of floating-point numbers.
This tutorial demonstrates the several methods available to generate a range of float-point numbers.
- What is a floating-point number in Python?
- Why not use the simple and popular range() function?
- Python range float : How to generate floating-point numbers in Python?
- Using the numpy.linspace() method.
- Using the numpy.arange() method.
- Using list comprehension.
- Using generator comprehension.
- Using yield generator.
- Using a user-defined function.
- Using the itertools module and its functions.
- Using the map() function along with a lambda function.
- Using the round() function.
What is a floating-point number in Python?
A floating-point number, typically categorized and stored under the float data type, is capable of representing real numbers that contain both integer and fractional parts. A float can store numbers containing decimal points without any errors or loss of data.
Why not use the simple and popular range() function?
To simply carry out the operation of returning a sequence of numbers in Python, we typically use the range() function. However, the range() function is not applicable for use with the floating-point numbers and is incapable of accepting a floating-point number as its input.
If a floating-point number is entered as an input to the function, it automatically generates an error that displays the words TypeError .
Python range float : How to generate floating-point numbers in Python?
- Using numpy.linspace() method.
- Using numpy.arange() method.
- Using list comprehension.
- Using generator comprehension.
- Using yield generator.
- Using a user-defined function
- Using the itertools module and its functions.
- Using the map() function along with a lambda function.
- Using round() function.
Using the numpy.linspace() method.
The numpy.linspace() method takes in the start and stop values and moves on to return a sequence of numbers as specified by the user.
Further specifications on this function are done by specifying the num argument that the function takes in, which is utilized to specify the number of values that need to be generated within the given range.
This method comes under the NumPy library, which is utilized in dealing with arrays and matrices and needs to be imported to the Python code before using this method.
The following code uses the numpy.linspace() method to generate a range of float-point numbers in Python.
The above code provides the following output:
As seen in the above code, the endpoint argument can be optionally specified according to a particular user’s needs. This argument states whether the final value of the sequence needs to be included or not, and holds a default value of 0 .
Using the numpy.arange() method.
The numpy.arange() method, similar to the numpy.linspace() method, takes in the start and stop values and moves on to return a sequence of numbers as specified by the user. However, instead of the num argument, the numpy.arange() method takes in another step argument that is utilized to specify the step size between the sequence.
By default, start holds the value 0 while stop holds the value 1 .
This method comes under the NumPy library and is not a default Python function, which means it is necessary to import the NumPy library to the Python code before using this method.
The following code uses the numpy.arange() method to generate a range of float-point numbers in Python.